DHR Series Getting Started Guide Page 37
Discovery Series Rheometer Geometries
Standard geometries for the rheometers are constructed from stainless steel, hard anodized aluminium, or
titanium.
NOTE: This applies only to the face of the geometry in direct contact with the sample, the shaft may be
constructed from other materials.
Other materials may be available on request, at additional charge. The geometry should be as low in den-
sity possible, to minimize its moment of inertia, it should be chemically resistant to the sample, and it
should have a surface texture that provides adhesion to the sample, to eliminate slippage.
The available geometries are listed below. Refer to TRIOS Online Help for additional details.
• Cone and plate
• Parallel plate
• Concentric cylinders
• Double gap concentric cylinders
• Solid sample (rectangular)
• SER2 Universal Testing Platform
• Interfacial
•Starch
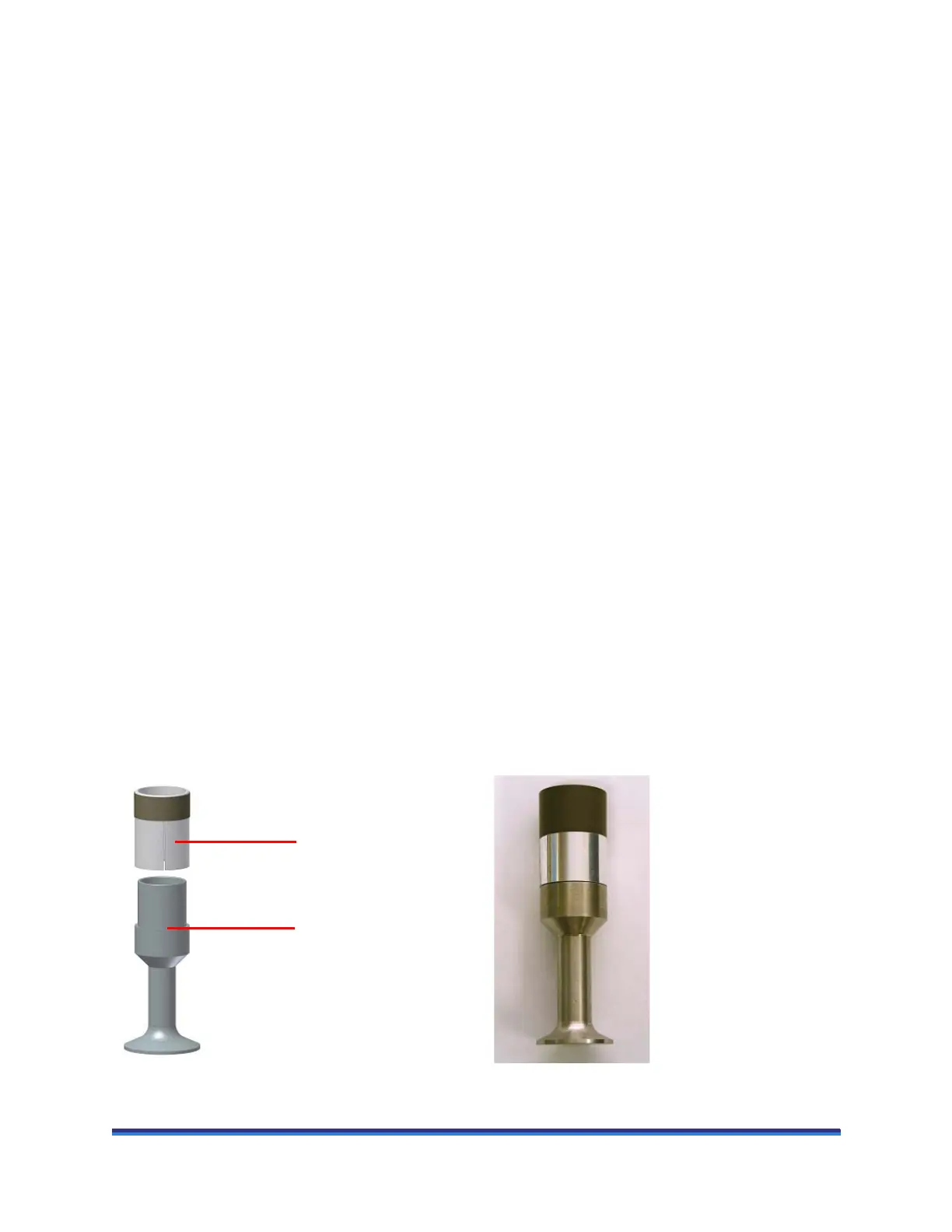
Smart Swap™ Geometries
Each geometry has a unique six-digit serial number for identification purposes. When the geometry is set
up for the first time this number is encoded into the magnetic strip and a link is established to a geometry
file in the instrument control software. The geometry then becomes “Smart”. When a Smart Swap Geome-
try is attached to the rheometer, a sensor registers the attachment and slowly spins the shaft to read the
serial number from the magnetic strip. The geometry file associated with this serial number is then loaded
by the software.
Figure 17 Smart Swap geometry.
Sleeve with
magnetic strip
Geometry base
 Loading...
Loading...