17 of 24 © 2005 D 420 - 06/05
In some cases, multiple boilers may be required. In these
cases, the 420 allows for a connection to a tekmar Boiler
Control 264, 265, or 268. The 420 uses the modulating
output to provide a 0 - 10 V (dc) signal to the external input
terminals on the Boiler Control. The 420 controls the Boiler
Control target temperature by changing the voltage signal.
The Boiler Control responds to the boiler target by staging
the multiple boilers.
tekmar Stager Operation Section D
To use the tekmar Staging operation, the following DIP
switch settings are required:
1. Set the 420 Off / tekmar Stager DIP switch to tekmar
Stager.
2. Set the 420 Boil On-Off / Mod DIP switch to Mod.
The 420 boiler sensor must be located on the supply pipe
leading from the boilers. On the Boiler Control 264, 265, or
268, the External Input / Stand Alone DIP switch must be set
to External Input. Any domestic hot water (DHW) demands
or setpoint demands in the system must connect to the 420
in order to allow for DHW or setpoint priority.
Zone Load Shedding Section E
The control has a feature called zone load shedding. In
certain cases, the boiler may not have enough capacity
to satisfy all heating loads. In this case the control
prioritizes the heating loads and also prioritizes zones
in the following order:
First Priority: DHW and Setpoint loads while priority
is selected.
Second Priority: Boiler zones starting with network
address 1 up to 24.
Domestic Hot Water Temperature Operation Section F
DHW Demand
A powered DHW Demand is required in order for the control
to provide heat to the DHW system. A DHW aquastat or
setpoint control is used as a switch in the DHW demand
circuit. The control registers a DHW Demand when a
voltage between 24 and 230 V (ac) is applied across the
DHW Demand terminals (53 and 54).
Once the control detects a DHW demand, the DHW Demand
segment turns on in the LCD.
Boiler Target Temperature
The boiler target temperature is at least as hot as the DHW
Exchange setting. The DHW demand overrides the boiler
reset target temperature, except when the boiler reset target
is higher than the DHW exchange setting.
• Locate the DHW Exchange setting in the Adjust menu.
DHW During UnOccupied
The control has a DHW Exchange UnOccupied setting that
allows the installer to select On or Off. When set to On, and
the control receives a DHW Demand during an UnOccupied
or Sleep period, the control continues operation of the DHW
system as it would during the Occupied and Wake periods.
When set to Off, the control can ignore a DHW Demand for
the duration of the UnOccupied and Sleep periods.
DHW Mode and Priority Operation
The control has four different settings available for DHW
Mode that affect pump operation. The required DHW Mode
setting will depend on the piping arrangement of the DHW
tank and whether or not priority for DHW is necessary. DHW
Priority stops or limits the delivery of heat to the building
heating system while the DHW tank calls for heat. This
allows for quick recovery of the DHW tank.
• Locate the DHW Mode setting in the Adjust menu.
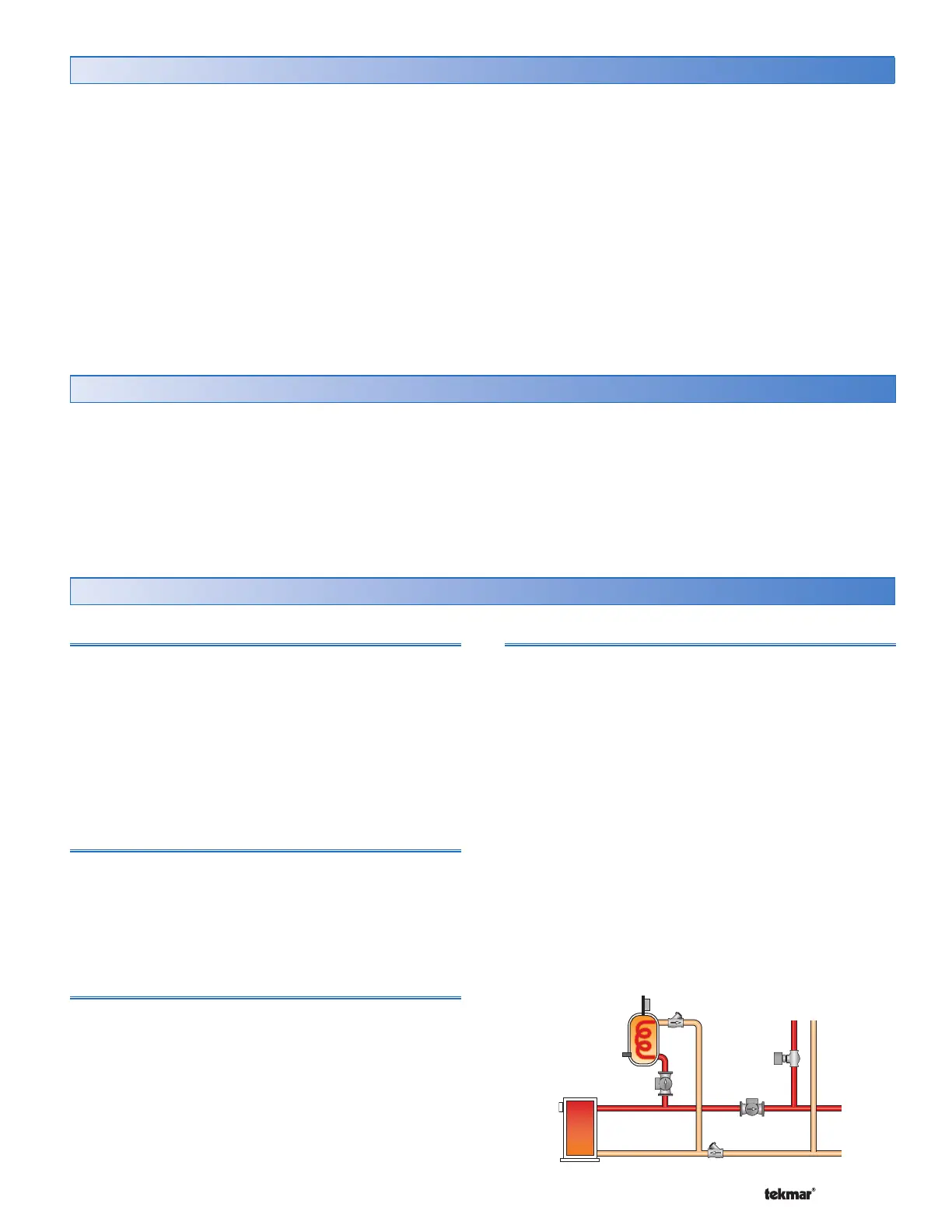
DHW MODE 1 - DHW in Parallel no Priority
When a DHW Demand is present, the DHW Pump contact
closes. The primary pump (P1) does not turn on, but may
operate based on either Boiler or Mixing requirements or
a Setpoint Demand.
It is assumed that the DHW pump will provide adequate
flow through the heat exchanger and the boiler.
Mode = 1
DHW
Pump
Primary
Pump

 Loading...
Loading...