19 of 24 © 2005 D 420 - 06/05
DHW with Low Temperature Boilers Section G
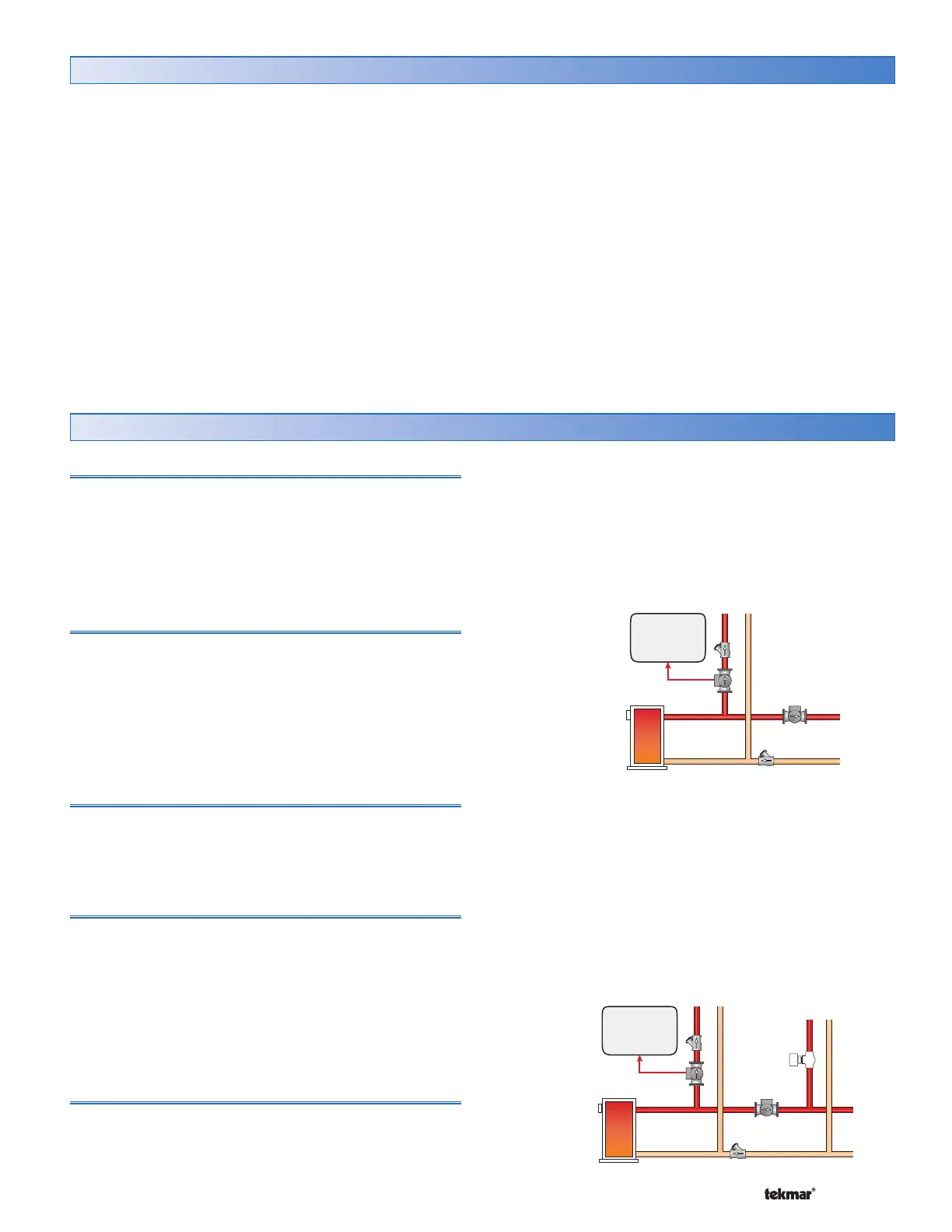
If DHW heating is to be incorporated into a low temperature
system such as a radiant floor heating system, a mixing
device is often installed to isolate the high DHW supply
temperature from the lower system temperature. If a mixing
device is not installed, high temperature water could be
supplied to the low temperature system while trying to
satisfy the DHW demand. This may result in damage to
the low temperature heating system.
The control is capable of providing DHW heating in such a
system while minimizing the chance that the temperature
in the heating system exceeds the design supply water
temperature. In order to do this, the control must be set
to DHW MODE 2 or DHW MODE 4 and Boil MIN must be
set to OFF.
On a call for DHW, the control provides DHW priority by
sending a message on the boiler temperature bus to the tN4
thermostats to shut off the heating zones for a period of time.
The length of time is based on the outdoor air temperature
as described in the DHW Priority Override section. However,
if the DHW Demand is not satisfied within the allotted time,
the boiler shuts off and the heat of the boiler is purged into
the DHW tank. A DHW mixing purge occurs in order to
reduce the boiler water temperature and once the boiler
supply temperature is sufficiently reduced, the DHW Pump
contact shuts off. The heating system zones are allowed
to turn on for a period of time to prevent the building from
cooling off. After a period of heating, and if the DHW Demand
is still present, the control shuts off the heating system and
provides heat to the DHW tank once again.
Setpoint Temperature Operation Section H
Setpoint
The control can operate to satisfy the requirements of a
setpoint load in addition to a space heating load and a
DHW load. A setpoint load overrides the current outdoor
reset temperature and WWSD setting in order to provide
heat to the setpoint load.
Setpoint Demand
A Setpoint Demand is required in order for the control to
provide heat to a setpoint load.
The control registers a setpoint demand when a voltage
between 24 and 230 V (ac) is applied across the Setpoint
Demand terminals (55 and 56). Once voltage is applied,
the Setpoint Demand segment turns on in the LCD.
Boiler Target During Setpoint
The boiler target temperature during a Setpoint Demand is
increased to at least the Setpoint setting. This temperature is
maintained as long as the control has a setpoint demand.
Setpoint During UnOccupied
The control has a Setpoint UnOccupied setting that allows
the installer to select On or Off. When set to On, and the
control receives a Setpoint Demand during an UnOccupied or
Sleep period, the control continues operation of the Setpoint
system as it would during Occupied and Wake periods. When
set to Off, the control can ignore a Setpoint Demand for the
duration of the UnOccupied and Sleep periods.
Setpoint Modes
The Setpoint Mode determines the operation of the primary
pump. The Setpoint Mode setting is found in the Adjust
menu.
Setpoint Mode 1 - Setpoint in Parallel
Whenever a setpoint demand is present, the boiler is
operated to maintain the setpoint target. The primary pump
(P1) does not turn on, but may operate based on either a
Boiler, Mixing or a DHW Demand.
It is assumed that the Setpoint pump will provide adequate
flow through the heat exchanger and the boiler.
Primary
Pump
Setpoint
Mode = 1
Setpoint Mode 2 - Setpoint in Parallel with Priority
When a Setpoint Demand is present, the boiler is operated
to maintain the setpoint target. The primary pump (P1) can
operate when a boiler demand is present. If the boiler is
unable to maintain the boiler target temperature, space heating
zones are shut off sequentially using tN4 communication in
order to provide priority for the setpoint load. This is known
as zone load shedding.
It is assumed that the setpoint pump will provide adequate
flow through the heat exchanger and the boiler.
Setpoint
Primary
Pump
OFF
Mode = 2

 Loading...
Loading...