Page 14
7.2.3 Temperature Compensation
The slope of a pH sensor (section 7.2.2) is affected by temperature. This effect is
compensated for either by using an Automatic Temperature Compensation
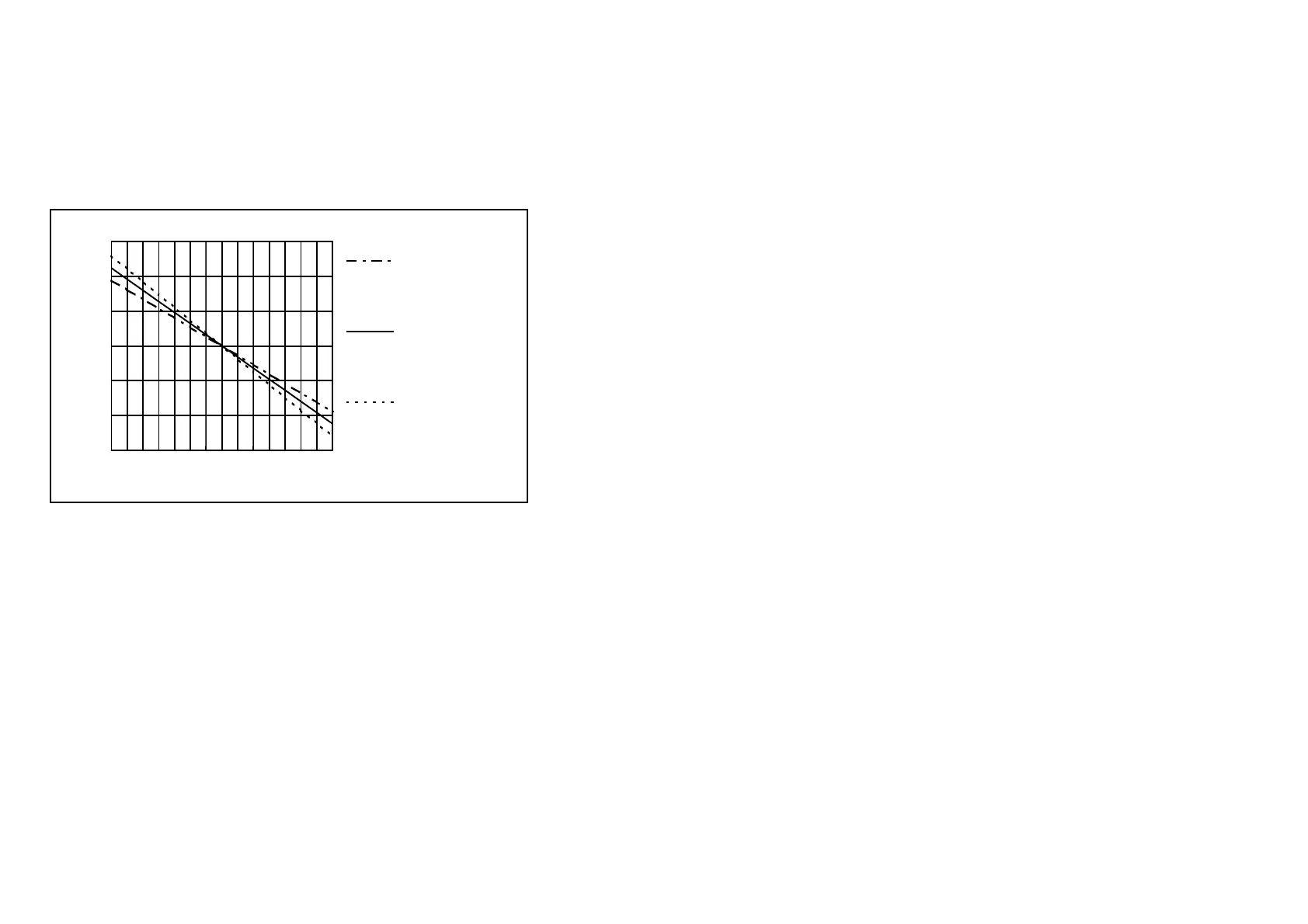
(ATC) sensor or by entering the sample temperature manually. Figure 7-3 shows
the slope of a pH sensor at various temperatures.
-600
-400
-200
0
200
400
600
0714
Electrode
Potential (mV) at
0 oC (54mV/pH)
Electrode
Potential (mV) at
50 oC (64mV/pH)
Electrode
Potential (mV) at
100 oC (74mV/pH)
pH Electrode Response, as a Function of Temperature
Electrode Response (mV)
pH
Figure 7-3
7.3 Checking the reference junction of a pH sensor.
If pH readings are inaccurate or unstable, the reference junction of the sensor
may be blocked. The following test can be performed to determine if the
reference junction of a pH sensor is making adequate contact with the sample
solution.
1. Calibrate the pH Cube, as per section 3.
2. Dilute 1 part of pH6.88 buffer with 9 parts of distilled water.
3. Measure the pH of the diluted buffer. The result should be 7.06 +/-0.05 pH.
4. If the value obtained is outside of these limits, then clean the reference
junction as per the instructions supplied with the pH sensor.
5. Re-calibrate the pH Cube and repeat the test.
6. If the value obtained is still outside 7.06 +/-0.05 pH, then the sensor should be
replaced.
 Loading...
Loading...