NEO-8Q / NEO-M8 - Hardware Integration Manual
UBX-15029985 - R04 Production Information Product handling
Page 24 of 31
Most defects caused by ESD can be prevented by following strict ESD protection rules for production and
handling. When implementing passive antenna patches or external antenna connection points, then additional
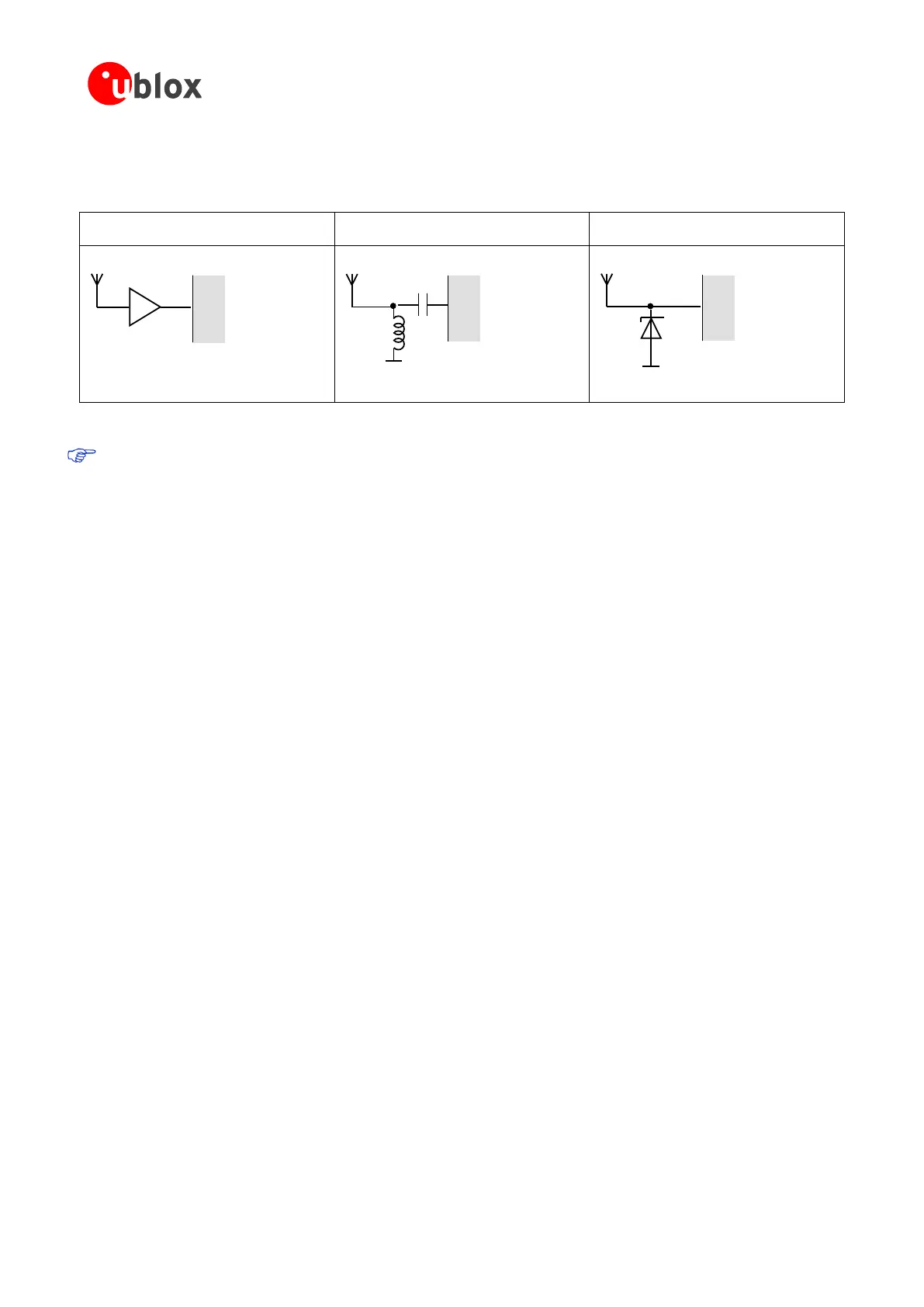
ESD measures can also avoid failures in the field as shown in Figure 12.
Small passive antennas (<2 dBic and
performance critical)
Passive antennas (>2 dBic or performance
sufficient)
LNA with appropriate ESD rating
Figure 12: ESD Precautions
Protection measure A is preferred because it offers the best GNSS performance and best level of ESD
protection.
Electrical Overstress (EOS)
Electrical Overstress (EOS) usually describes situations when the maximum input power exceeds the maximum
specified ratings. EOS failure can happen if RF emitters are close to a GNSS receiver or its antenna. EOS causes
damage to the chip structures. If the RF_IN is damaged by EOS, it is hard to determine whether the chip
structures have been damaged by ESD or EOS.

 Loading...
Loading...