www.weg.net
48 l Installation, operation and maintenance manual – Squirrel cage motor – M line – Vertical 11371757
8 MOTOR DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
All the repair, disassembly and assembly services must be performed
only by properly qualified and trained
professionals; otherwise, equipment damage and personal injury may occur. If any further explanations are
necessary, consult WEG.
The disassembly and assembly sequence
s depend on the motor model.
Always use proper tools and devices.
Any damaged part (cracks, dents on machined parts, faulty threads)
must be replaced, avoiding restorations.
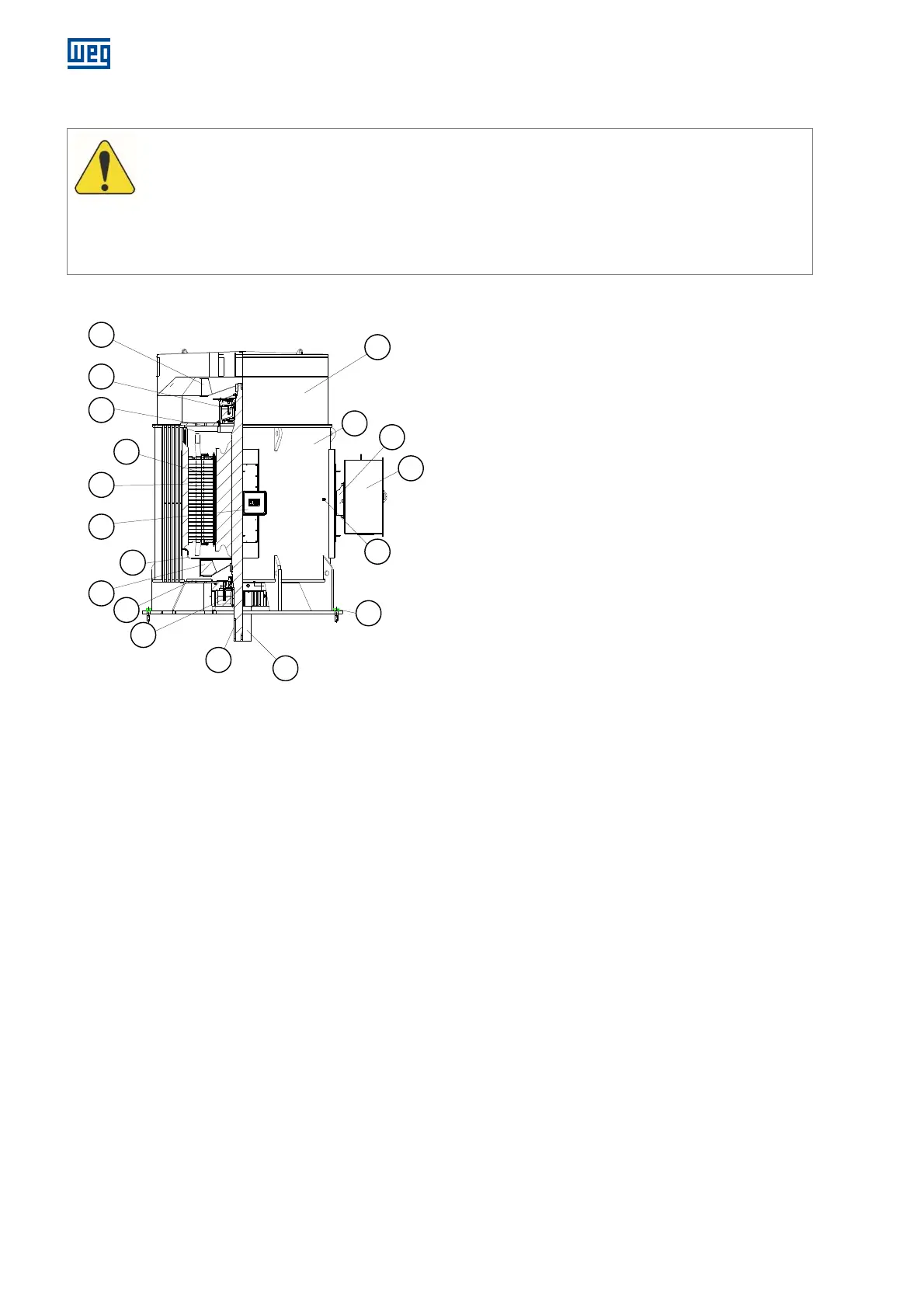
8.1 PARTS LIST
Figure 8.1: Overview of a typical motor with solid shaft and oil-
lubricated rolling bearings
Figure 8.1 legend:
1. Frame
2. Stator
3. Rotor
4. Internal fan
5. External fan
6. Fan cover
7. Grounding terminal
8. Shaft
9. D-end shield
10. ND-end shield
11. DE bearing
12. NDE bearing
13. Key
14. Terminal box support
15. Accessory terminal box
16. Stator terminal box
17. Ventilation box
18. Fastening bolts
8.2 DISASSEMBLY
The following precautions must be taken when
disassembling the motor:
1. Before disassembling the motor, disconnect the water
cooling and lubrication pipes (if any);
2. Disconnect the motor electrical connections and those
of the accessories;
3. Remove the heat exchanger and the noise suppressor
(if any);
4. Remove the bearing temperature sensors and the
grounding brush;
5. In order to prevent damages to the rotor, provide a
support for the shaft on both drive and non-drive ends;
6. In order to disassemble the bearings, follow the
procedures described in this manual, according to the
bearing type;
7. Use a proper device to remove the rotor from the
motor, taking extreme care not to drag the rotor
against the stator laminated core or coil heads, thus
preventing damages.
8.3 ASSEMBLY
In order to assemble the motor, follow the disassembly
procedures in the reverse order.
8.4 AIR-GAP MEASUREMENT
After disassembling and assembling the motor, it is
necessary to measure the air gap in order to check the
concentricity between rotor and stator.
The difference between the air-gap measured in two
points diametrically opposed must be less than 10% of
the average air gap.
16
8
13
7
18
17
1
14
10
2
15
12
5
3
6
11
9
4

 Loading...
Loading...