Thorium is a low-level radioactive hazard and many users have switched
to other alternatives. Thorium is an alpha emitter but when enclosed in a
tungsten matrix, the risks are negligible.
Thus holding a stick of Thoriated tungsten in your hand should not pose a great
threat unless a welder has open cuts on their skin. Thoriated tungsten should
not get in contact with open cuts or wounds. The more significant danger to
welders can occur when thorium oxide gets into the lungs. This can happen
from the exposure to vapours during welding or from ingestion of material/
dust in the grinding of the tungsten. Follow the manufacturer’s warnings,
instructions, and the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for its use.
Zirconiated (Color Code: White)
Zirconiated tungsten electrodes (AWS classification EWZr-1) contain a
minimum of 99.10 percent tungsten and 0.15 to 0.40 percent zirconium. Most
commonly used for AC welding Zirconiated tungsten produces a very stable
arc and is resistant to tungsten spitting. It is ideal for AC welding because it
retains a balled tip and has a high resistance to contamination. Its current-
carrying capacity is equal to or greater than that of thoriated tungsten.
Zirconiated tungsten is not recommended for DC welding.
Tungsten Electrode Current Ranges
Tungsten
Diameter
DC Current Amps
T
orch Negative
2% Thoriated
AC Current Amps
Balanced Wave
0.8% Zirconiated
1.0mm 15 - 80 20 - 60
1.6mm 70 - 150 60 - 120
2.4mm 150 - 250 100 - 180
3.2mm 250 - 400 160 - 250
4.0mm 400 - 500 200 - 320
TUNGSTEN PREPARATION
Always use DIAMOND wheels when grinding and cutting. While tungsten is a
very hard material, the surface of a diamond wheel is harder, and this makes
for smooth grinding. Grinding without diamond wheels, such as aluminium
oxide wheels, can lead to jagged edges, imperfections, or poor surface
finishes not visible to the eye that will contribute to weld inconsistency and
weld defects.
Always grind the tungsten in a longitudinal direction. Tungsten electrodes are
manufactured with the molecular structure of the grain running lengthwise
and thus grinding crosswise is “grinding against the grain.” If electrodes are
ground crosswise, the electrons have to jump across the grinding marks and
the arc can start before the tip and wander. Grinding longitudinally with the
grain, the electrons flow steadily and easily to the end of the tungsten tip. The
arc starts straight and remains narrow, concentrated, and stable.
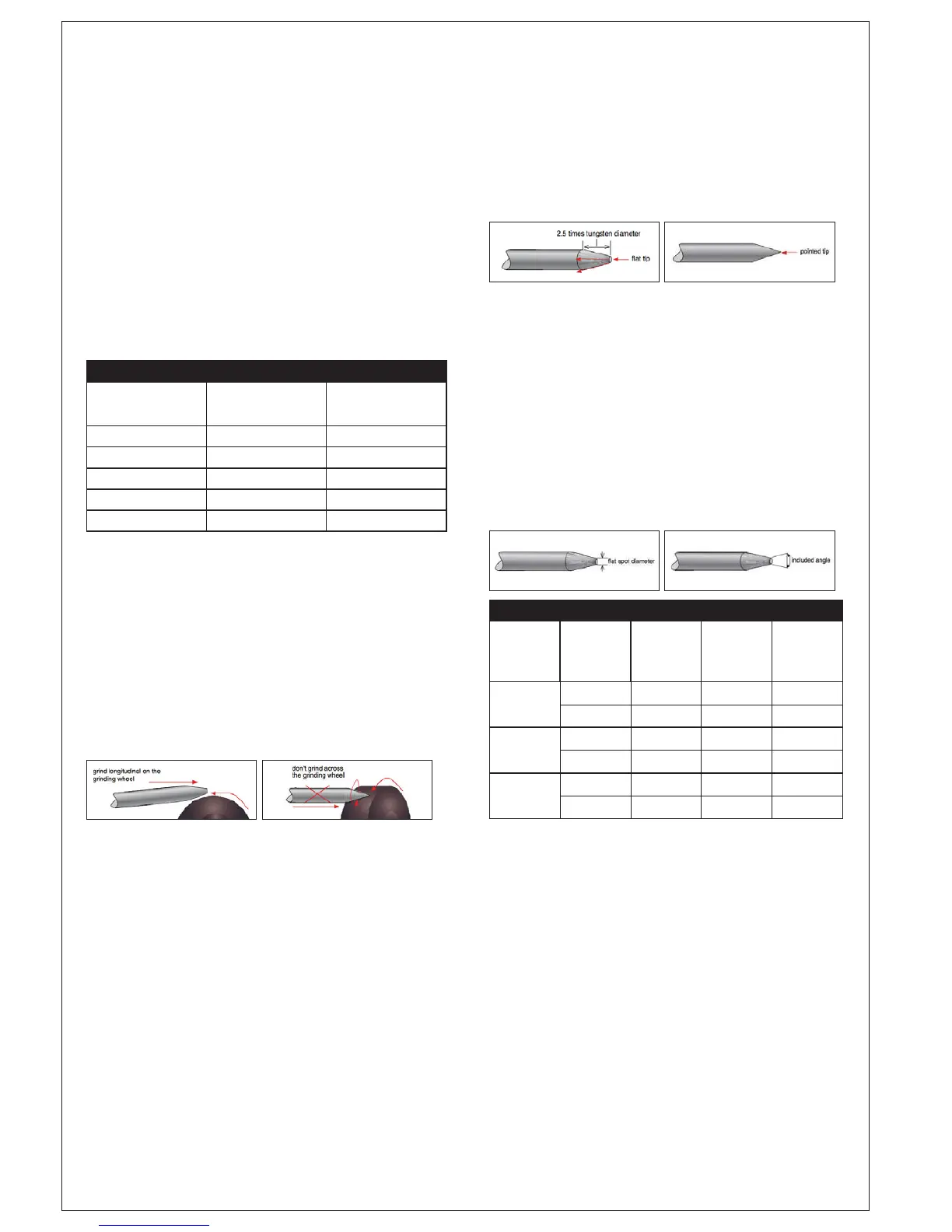
Electrode Tip/Flat
The shape of the tungsten electrode tip is an important process variable in
precision arc welding. A good selection of tip/flat size will balance the need for
several advantages. The bigger the flat, the more likely arc wander will occur
and the more difficult it will be to arc start. Increasing the flat to the maximum
level that still allows arc start and eliminates arc wonder will improve the weld
penetration and increase the electrode life. Some welders grind electrodes to
a sharp point, which makes arc starting easier but can contribute to decreased
welding performance due to the tip melting and falling into the weld pool.
Electrode Included Angle/Taper - DC Welding
Tungsten electrodes for DC welding should be ground longitudinally and
concentrically with diamond wheels to a specific included angle in conjunction
with the tip/flat preparation. Different angles produce different arc shapes
and offer different weld penetration capabilities. In general, electrodes that
have an appropriate included angle and a suitable flat on the tip, exhibit the
following benefits:
• Last Longer
• Have better weld penetration
• Have a narrower arc shape
• Can handle more amperage without eroding.
Sharper electrodes with smaller included angle provide:
• Offer less arc weld
• Have a wider arc
• Have a more consistent arc
The included angle determines weld bead shape and size. Generally, as the
included angle increases, penetration increases and bead width decreases.
Tungsten Electrode Preperation
Tungsten
Electrode
Diameter
(mm)
Flat Spot
Diameter
at the Tip
(mm)
T
ip Included
Angle
(Degrees)
Current
Range
(Amps)
Current
Pulsed
(Amps)
1.6
.500 25 08 - 50 05 - 100
.800 30 10 - 70 10 - 140
2.4
.800 35 12 - 90 12 - 180
1.100 45 15 - 150 15 - 250
3.2
1.100 60 20 - 200 20 - 300
1.500 90 25 - 250 25 - 350
 Loading...
Loading...