CHASSIS
4-1
EAS2GBB136
CHASSIS
EAS2GBB137
SELECTION OF THE SECONDARY REDUC-
TION RATIO (SPROCKET)
<Requirement for selection of secondary gear
reduction ratio>
• It is generally said that the secondary gear ra-
tio should be reduced for a longer straight por-
tion of a speed course and should be
increased for a course with many corners. Ac-
tually, however, as the speed depends on the
ground condition of the day of the race, be
sure to run through the circuit to set the ma-
chine suitable for the entire course.
• In actuality, it is very difficult to achieve set-
tings suitable for the entire course and some
settings may be sacrificed. Thus, the settings
should be matched to the portion of the
course that has the greatest effect on the race
result. In such a case, run through the entire
course while making notes of lap times to find
the best balance; then, determine the second-
ary reduction ratio.
• If a course has a long straight portion where a
machine can run at maximum speed, the ma-
chine is generally set such that it can develop
its maximum revolutions toward the end of the
straight line, with care taken to avoid the en-
gine over-revving.
Riding technique varies from rider to rider and
the performance of a machine also vary from
machine to machine. Therefore, do not imitate
other rider’s settings from the beginning but
choose your own setting according to the level
of your riding technique.
EAS2GBB138
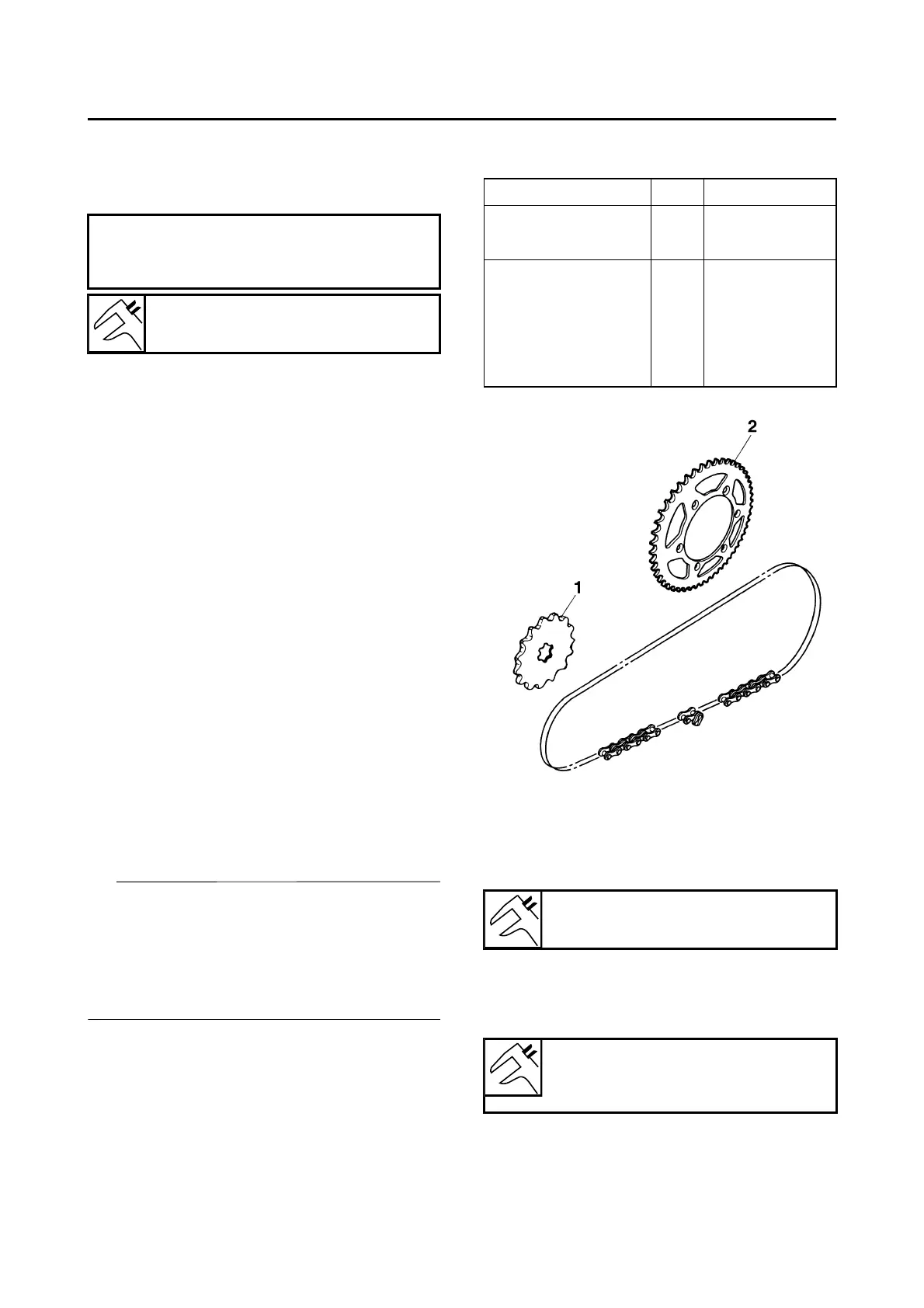
DRIVE AND REAR WHEEL SPROCKETS
SETTING PARTS
EAS2GBB139
TIRE PRESSURE
Tire pressure should be adjusted to suit the
road surface condition of the circuit.
• Under a rainy, a muddy, a sandy, or a slippery
condition, the tire pressure should be lower
for a larger area of contact with the road sur-
face.
Secondary reduction ratio = Number of
rear wheel sprocket teeth/Number of
drive sprocket teeth
Secondary reduction ratio
3.846 (50/13)
Part name Type Part number
Drive sprocket “1”
(STD) 13T 9383B-13218
Rear wheel sprock-
et “2”
48T 5GS-25448-50
(STD) 50T 5TJ-25450-80
52T 5TJ-25452-80
Standard tire pressure
100 kPa (1.00 kgf/cm
2
,15 psi)
Extent of adjustment
60–80 kPa (0.60–0.80 kgf/cm
2
, 9–
12 psi)

 Loading...
Loading...











