31
0
Heat
Output
(%)
Cool
Output
(%)
1000
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
Max. Cool
Output = 75%*
Max. Heat
Output = 88%*
0
100
Q Heater = 1.5kW
Q Cooler = 0.75kW
Output Off
Hysteresis Band
=15%*
*User definable limits
Tr ansition
Bandwidth
20%
Proportional Band
(Cool) 25.0%
Integral Action Value
(Cool)
Derivative Action Value
Proportional Band
(Heat) 20.0%
Integral Action Value
(Heat)
Derivative Action Value
100%
0%
PID Output (%)
Crossover Value (33%)
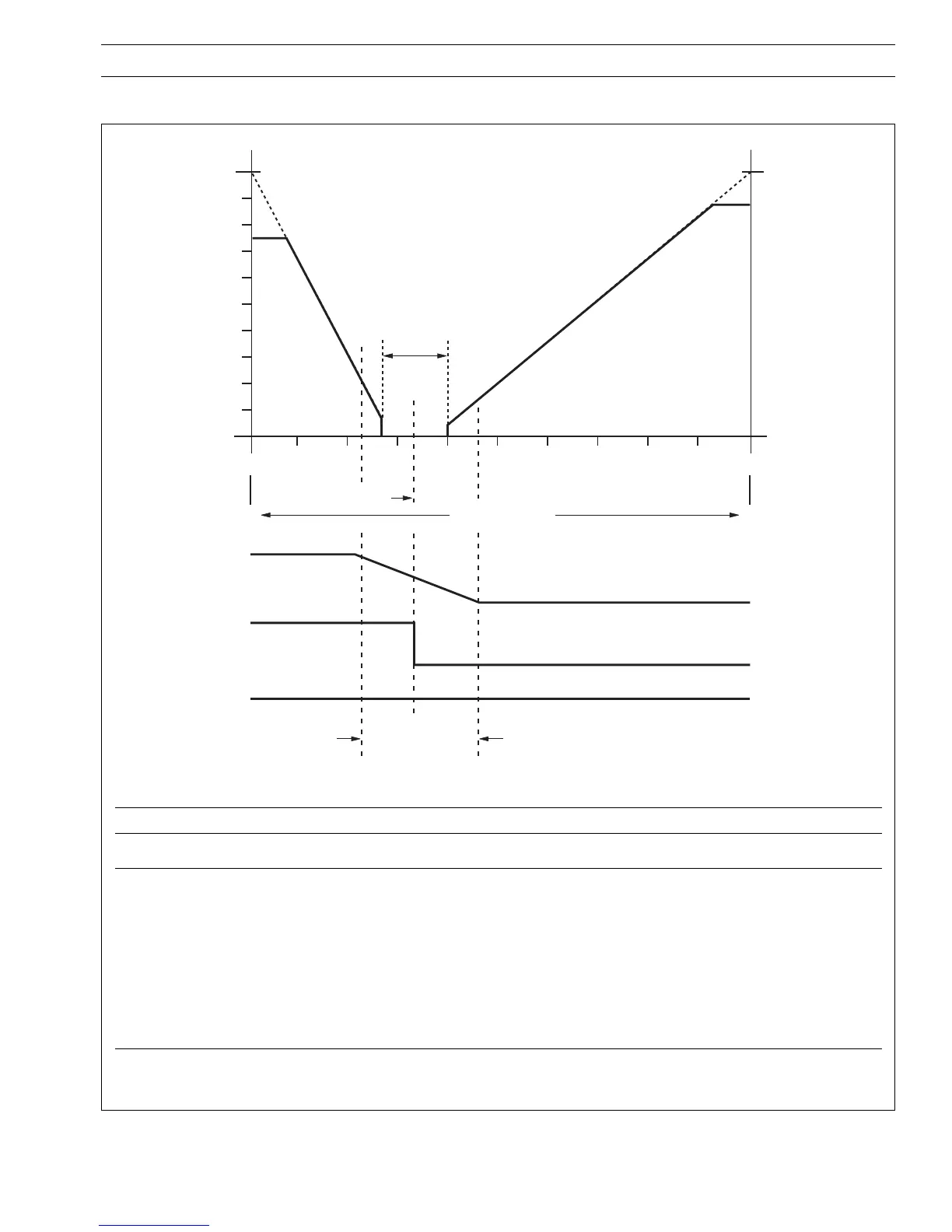
5 CONTROL OPERATION…
5.10 Introduction to Heat/Cool Control
Note. Refer to Sections 5.10.2 and 5.10.3 for Crossover Value and Transition Bandwidth Value examples.
Information.
•PID Output – is the output value calculated by the controller. The output is divided into two different control elements one
for raising the product temperature (heat output) and one for lowering the product temperature (cool output).
• Transition Bandwidth – used to transfer smoothly from one set of control terms to the other.
• Crossover Value – defines the changeover point between heat output active and cool output active. The crossover value
is also the centre of the transition and off hysteresis bands.
• Output Off Hysteresis Band – for the majority of applications Outputs 1 and 2 have opposing control actions i.e. one is
direct acting and the other is reverse. In this configuration both outputs are at 0% within the off hysteresis band. The band
setting is used to prevent oscillation of control changes.
• Heat/Cool Outputs – refer to PID Output, above.
Fig. 5.18 Heat/Cool Control – Principle of Operation
 Loading...
Loading...