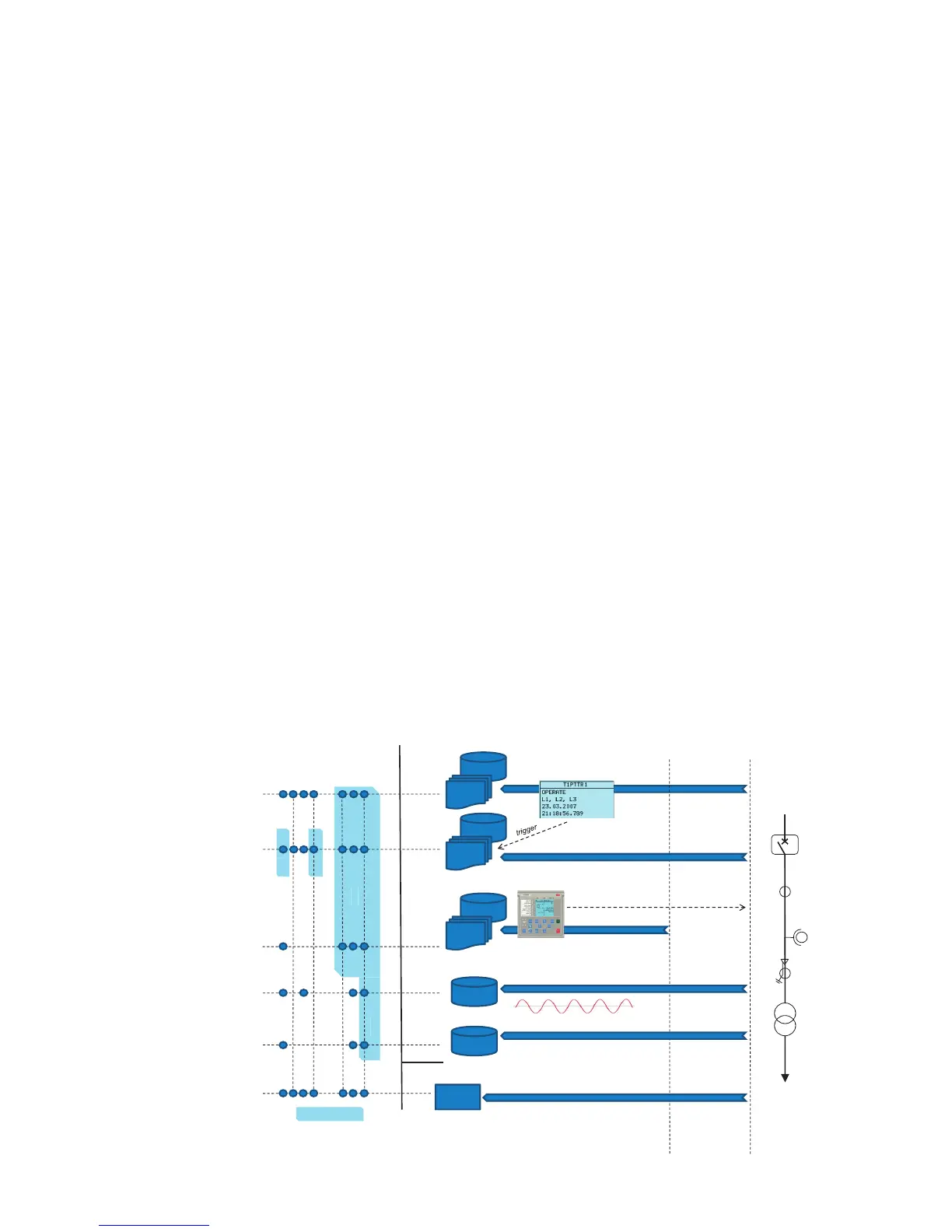
11. Event log
To collect sequence-of-events information, the re-
lay has a nonvolatile memory capable of storing
1024 events with the associated time stamps. The
non-volatile memory retains its data even if the re-
lay temporarily loses its auxiliary supply. The event
log facilitates detailed pre- and post-fault analyses
of feeder faults and disturbances. The considerable
capacity to process and store data and events in
the relay facilitates meeting the growing informa-
tion demand of future network configurations. The
sequence-of-events information can be accessed
either via local HMI or remotely via the communica-
tion interface of the relay. The information can also
be accessed locally or remotely using the Web HMI.
12. Recorded data
The relay has the capacity to store the records of
the 128 latest fault events. The records can be used
to analyze the power system events. Each record in-
cludes, for example, current, voltage and angle val-
ues and a time stamp. The fault recording can be
triggered by the start or the trip signal of a protec-
tion block, or by both. The available measurement
modes include DFT, RMS and peak-to-peak. Fault
records store relay measurement values at the mo-
ment when any protection function starts. In addi-
tion, the maximum demand current with time
stamp is separately recorded. The records are
stored in the non-volatile memory.
13. Condition monitoring
The condition monitoring functions of the relay
constantly monitor the performance and the condi-
tion of the circuit breaker. The monitoring com-
prises the spring charging time, SF6 gas pressure,
the travel time and the inactivity time of the circuit
breaker.
The monitoring functions provide operational cir-
cuit breaker history data, which can be used for
scheduling preventive circuit breaker maintenance.
In addition, the relay includes a runtime counter for
monitoring of how many hours a protected device
has been in operation thus enabling scheduling of
time-based preventive maintenance of the device.
14. Trip-circuit supervision
The trip-circuit supervision continuously monitors
the availability and operability of the trip circuit. It
provides open-circuit monitoring both when the
circuit breaker is in its closed and in its open posi-
tion. It also detects loss of circuit-breaker control
voltage.
Figure 14. Recording
and event capabil-
ities overview
1024
PROCESS LEVEL
USER LEVEL
Fault summary;
Trip timestamp, Function, Currents, Voltages, etc.
BASIC FUNCTIONS
IEC 61850-8-1
Modbus
IEC 103
DNP3
LHMI
WHMI
PCM600
Process
events
(FIFO)
128
Fault
records
(FIFO)
System and security-related events;
Configuration changes, Control, Login, etc.
2048
Audit
trail
events
(FIFO)
n…100
Disturbance
records
...7 yrs
Load profile
record
Historical load data captured at a periodical
time interval (Demand interval 1 ...180min)
Function specific data
Min/max demand currents, Operation counters, etc.
History view
27

 Loading...
Loading...