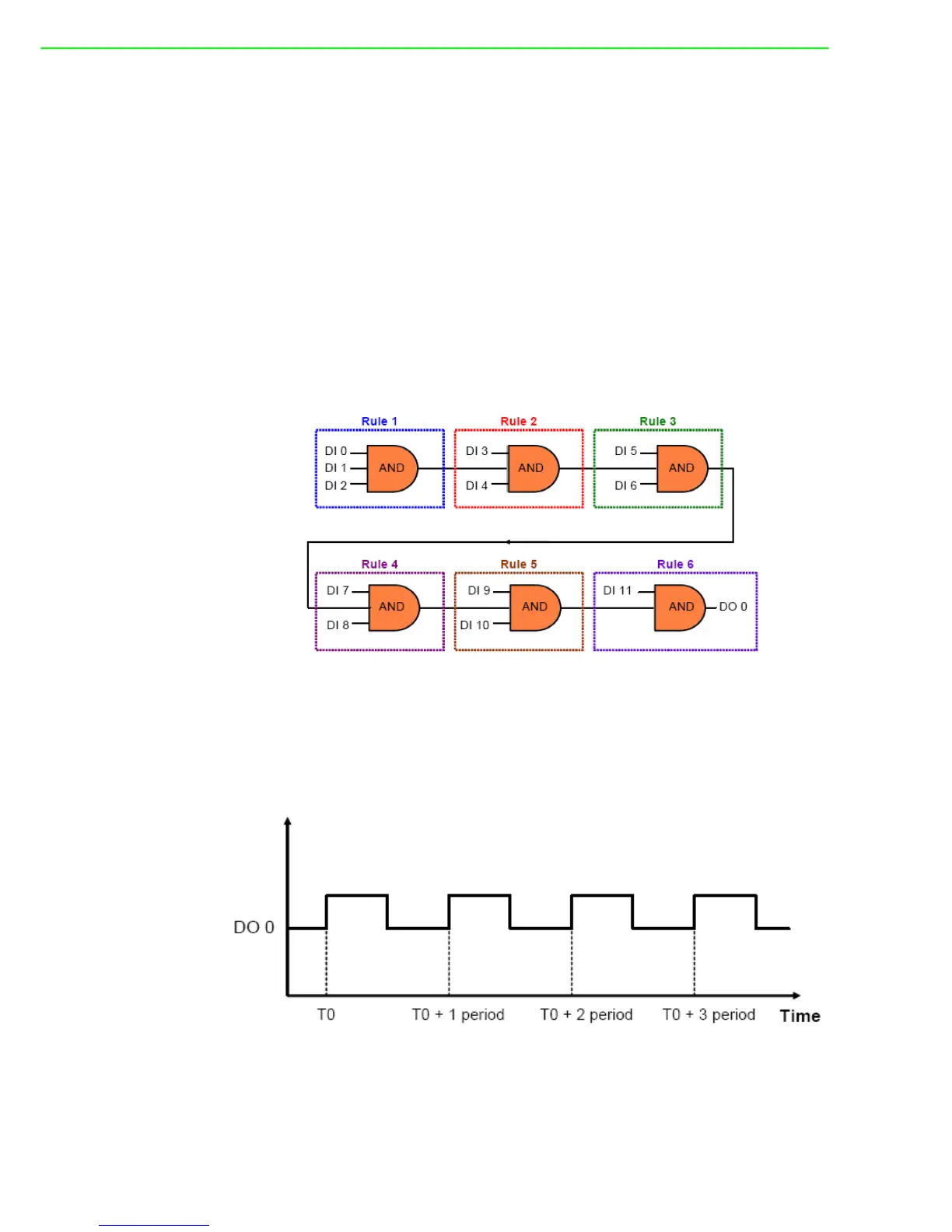
ADAM-6200 User Manual 112
You can simply implement one AND logic operator to achieve this control system.
However, since one logic rule only has three inputs, we need to use Logic Cascade
function to have 12 inputs. There are two ways to achieve Logic Cascade:
a. Select SendtoNextRule in Execution Stage of one logic rule. It will combine this
logic rule to the next logic rule.
b. Assign output of one logic rule and input of another logic rule to the same inter-
nal flag, combining the two logic rules together.
With the first method, the two logic rules must be next to each other. For example,
rule 1 and rule 2 can be combined together. But you cannot combine rule 1 and rule
3. There is no such limitation if you use the second method to combine two different
logic rules. Using the second method, you can even combine two rules on different
modules together. Here, this example project adapts the first method for Logic Cas-
cade. So the GCL logic architecture can be shown as below:
5. Flicker
Flicker is commonly used in automation control application. Typical example is we
want to make the alarm flashing, controlled by digital output. This application requires
a continuous pulse train by a digital output channel and we can decide the period of
the pulse train. The time chart for flicker application can be shown as below:
We need to use 1 Internal Flag (Flag 0) and 2 logic rules for the Flicker application
described above. In logic rule 1, the value of Flag 0 is inverted (By choosing NAND in
the Logic stage) periodically. (Here, it is 0.5 second) The period is defined by the
Execution_Period in the Execution Stage. The status of DO 0 is controlled by Flag 0

 Loading...
Loading...