
 Loading...
Loading...





Do you have a question about the Alesis Fusion and is the answer not in the manual?
| Type | Workstation |
|---|---|
| Polyphony | 64 voices |
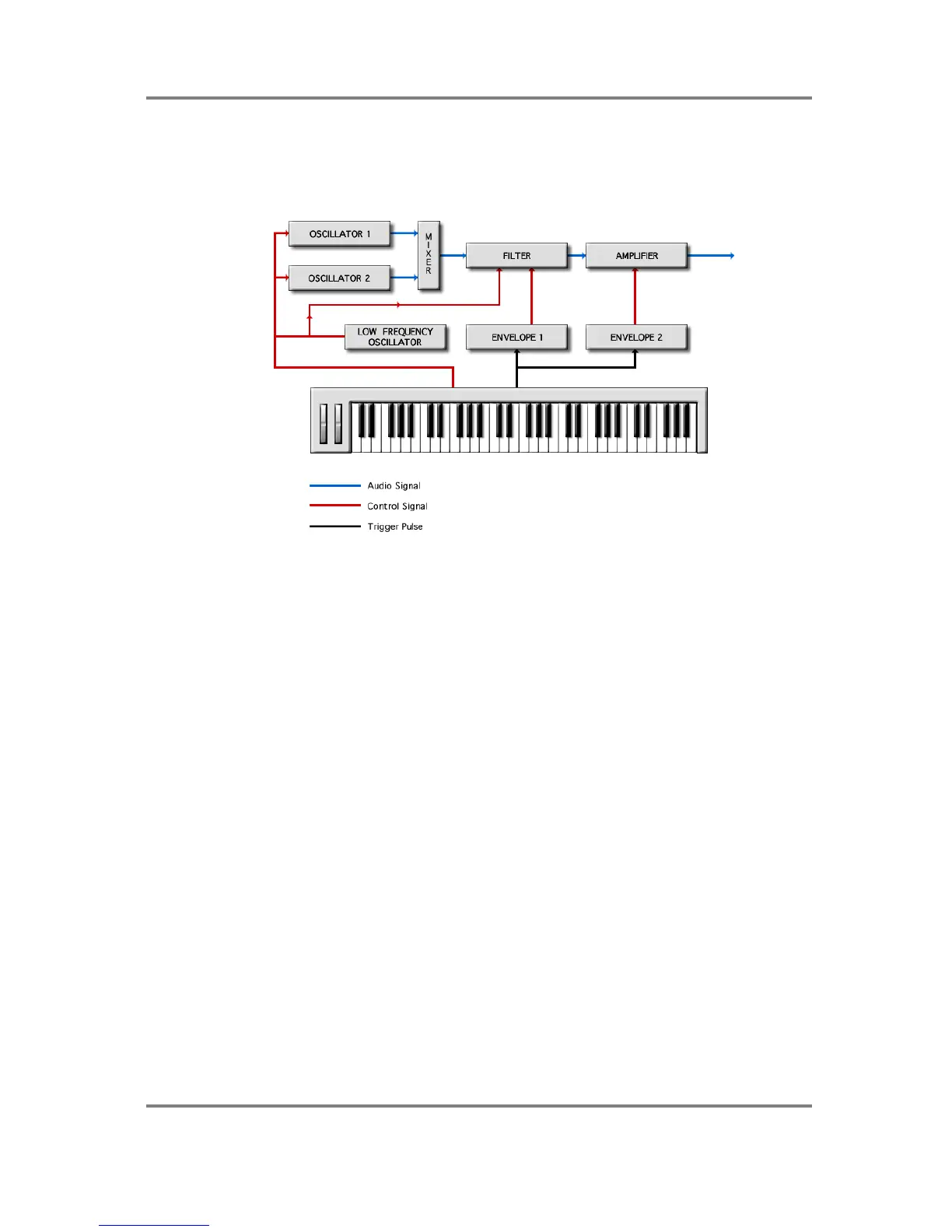
| Synthesis Types | Sample Playback, Virtual Analog, FM, Physical Modeling |
| Display | 240 x 128 pixel LCD |
| MIDI | In, Out, Thru |
| RAM | 64MB (expandable to 192MB) |
| Weight (61-key) | 28 lbs |
| Keyboard | 61 or 88 keys |
| Keyboard Type | Semi-weighted (61-key), Hammer action (88-key) |
| Effects | Reverb, Chorus, Delay, Flanger, Phaser, Distortion, EQ |
| Storage | 40GB internal hard drive |
| Sampling | Yes |
| Inputs | 2 x 1/4" inputs, 1 x XLR |
| Outputs | 4 x 1/4" outputs, 1 x Headphone |