Description 6 (18)
2.2 Data Exchange
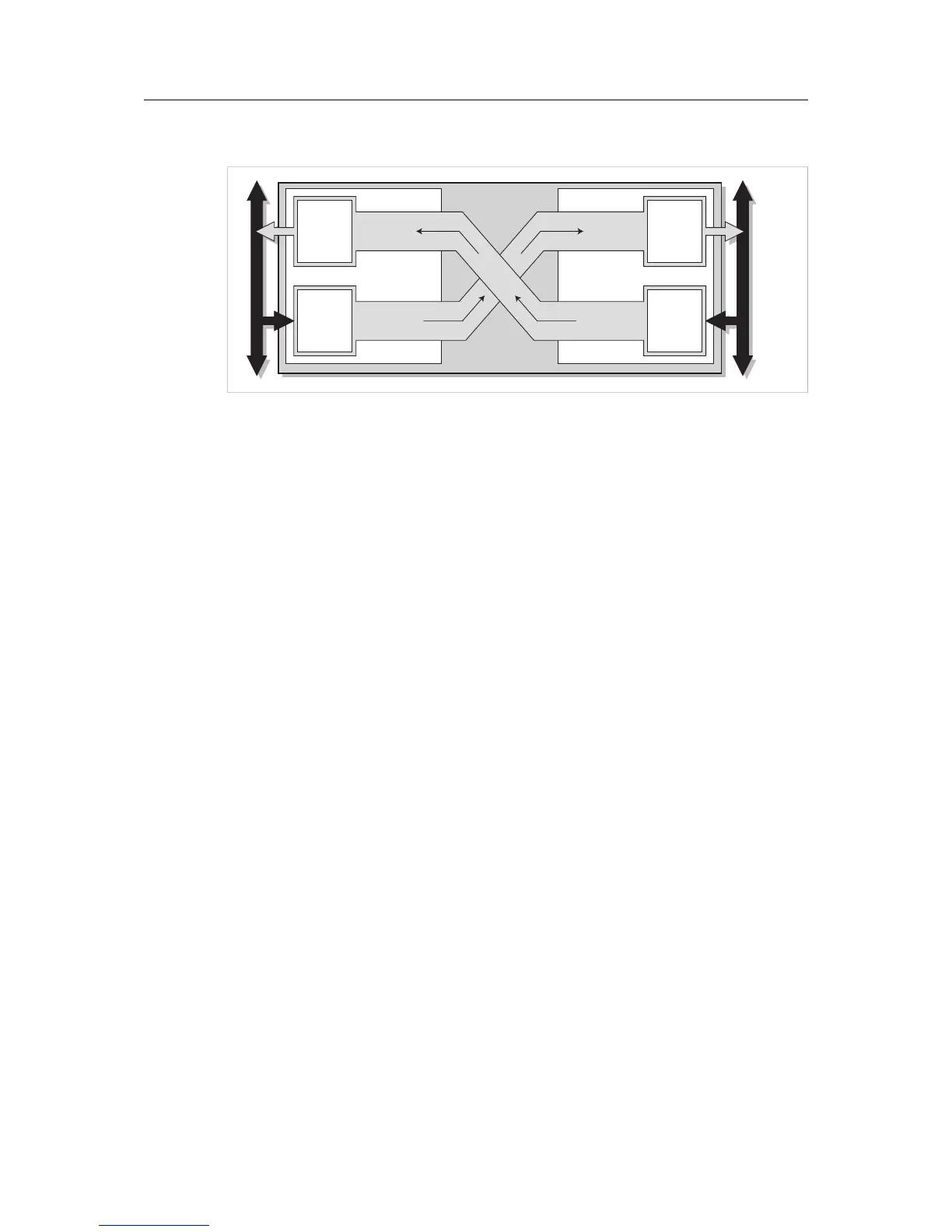
Fig. 2 Anybus X-gateway data exchange
The terminology and definitions used for different types of data vary between different network
types. Most networks distinguish between fast, cyclical I/O data, and less time-critical acyclic
data. In the Anybus X-gateway these types of data are generally referred to respectively as I/O
Data and Parameter Data.
Each of the two network interfaces exchanges data on its network through its own buffer, which
can hold up to 512 bytes of data. The actual amount of data that can be exchanged depends on
the settings in the network interface and may therefore be significantly less than 512 bytes,
which is only the maximum size of the buffer. The default setting is 20 bytes in each direction.
See the Network Guide for the respective network interface for more information.
In addition to the I/O data the buffers may contain network status information and instructions
for controlling the network interface. Depending on the type of network interface this may be
general diagnostic information (Status Word), a list of the active slaves (Live List), or other net-
work-specific information. In a network master, part of the buffer may be used to start/stop data
exchange and to reset the gateway (Control Word).
The exchange of data between the buffers is separate from the network data exchange. While
the X-gateway ensures data consistency (where applicable), it does not feature any mecha-
nisms for synchronisation between the two networks.

 Loading...
Loading...