Page 23
Section 7. PROTOCOL CONVERSION
7.1 Message format
The KITZ interface unit main function is to convert K-Bus message data to
IEC-870 - 5 FT1.2 format for communication with a PC.
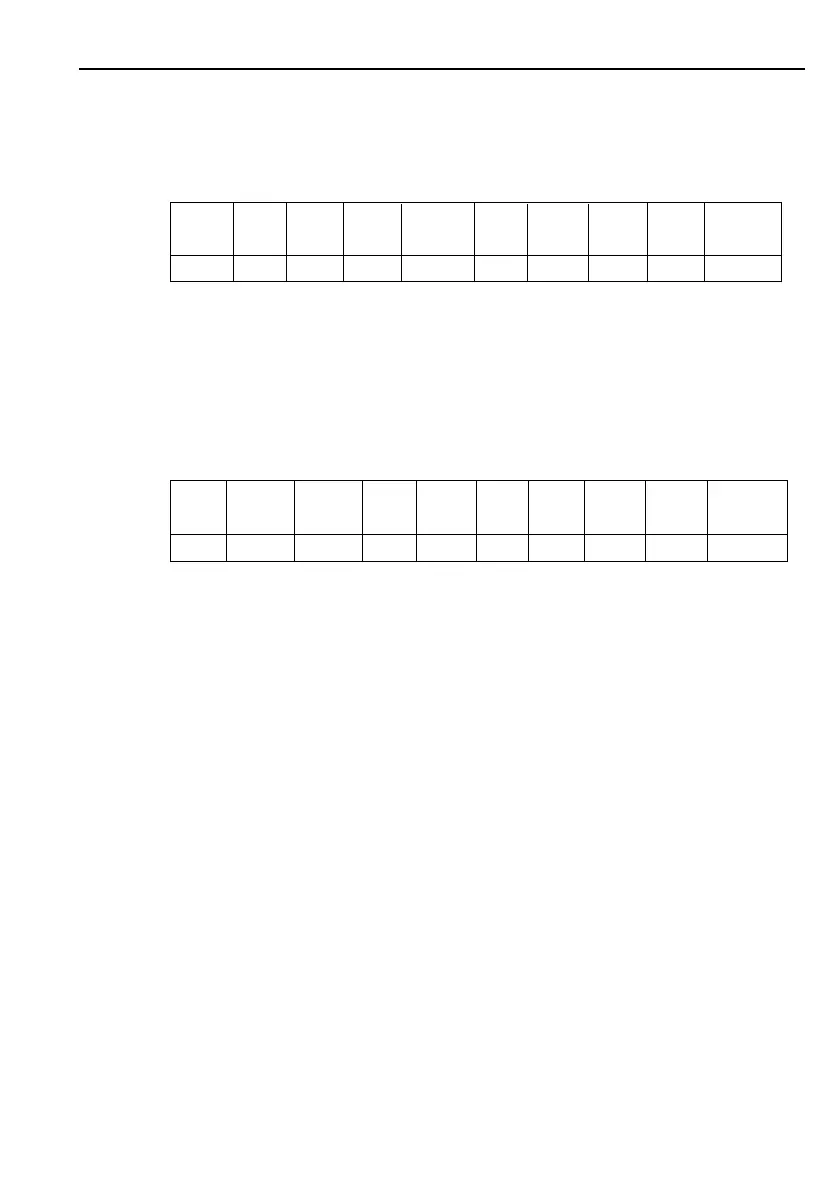
The K-Bus message format is shown below:
PRE- START A0-5 0 Message DTL Control DTLs CRC CLOSING
AMBLE FLAG Length + Data FLAG
FFFFh 7Eh 0 61h 7Eh
The K-Bus frame is based upon the ISO High level Data Link Control (HDLC)
protocol. This is a bit-oriented protocol and eliminates much of the control
overhead associated with byte-oriented protocols. The information field of the
HDLC frame is totally transparent and the information can take on any form and
contain any binary bit combination.
The IEC-870 Message format as used by a PC-based K Range master station is
shown below:
START Message Message START Control A0-5 0 DTLs Check- CLOSING
FLAG Length Length FLAG + Data sum FLAG
68h 68h 0 16h
For further details of the IEC-870 - 5 FT1.2 message format see the appropriate
IEC specification.
7.2 Message validation
Message validation takes place during and after message reception.
7.2.1 K-Bus message validation
The framing of the K-Bus message must be correct (HDLC Start and Stop flags
present).
At the end of a frame:
a) CRC (HDLC)
b) Data overrun
c) Residue (HDLC information field is an exact number of bytes)
d) Correct message length (matches received message data)
During a frame:
a) Character time-out
b) Receive Buffer overflow
c) Message is too long
7.2.2 IEC message validation
The framing of the message must be correct for IEC-870 - 5 FT1.2.
At the start of a frame:
a) A correct header frame must be present (2 Starts + matching lengths).
 Loading...
Loading...