TD 92579EN
15 February 2012 / Ver. H
Installation and Operation Manual
IP-DECT Base Station & IP-DECT Gateway (software version 5.0.x)
159
dynamically connected towards the IP-PBX network. In addition to the load balancing of
the traffic, redundancy is also achivied.
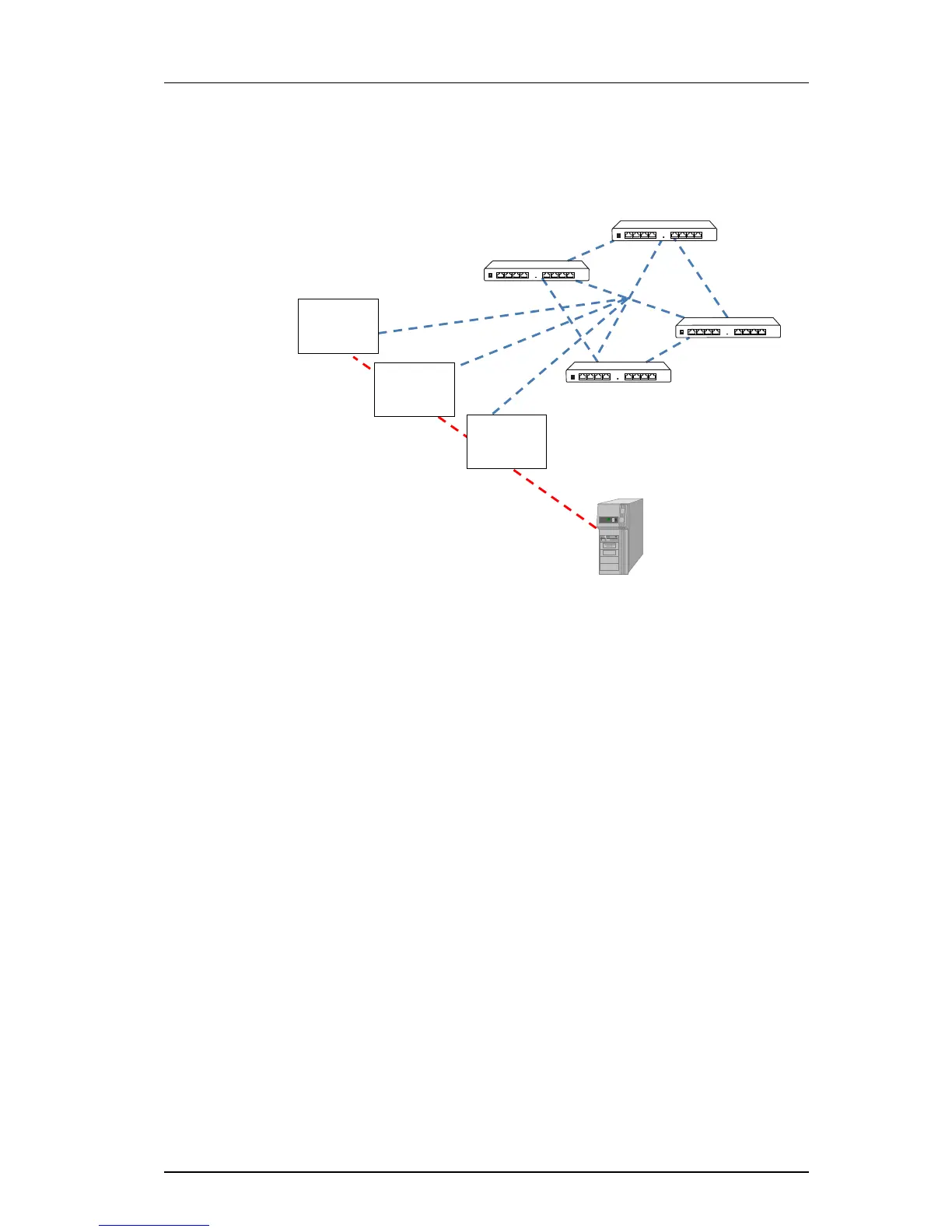
Figure 2. Load balancing using dynamic connection towards IP-PBX network.
E.2.1 How the Load Balancing Works
When you register a handset, a SRV-type query is sent to the DNS server asking for existing
SIP proxys (IP-PBXs) in the domain defined in the Master. The DNS server will reply with a
list of SRV (Service) records, one for each IP-PBX. Each SRV record contains a priority and a
weight value. Lower priority value means more preferred. When there are two or more
records with the same priority, then the weight value determines which IP-PBX the user
should be dynamically connected to.
A DNS server assign each user a primary and a secondary proxy address using DNS-SRV
service mechanism.
E.2.2 Local Site Redundancy
If redundancy is wanted in a remote site, that is you want to be able to make emergency
phone call if the WAN connection to the central site goes down, a local site proxy server,
e.g. SRST (Cisco), can be used in the remote site, see figure 3 on page 160.
Master 0
Pari Master
Master 1
Master 2
IP-PBX
IP-PBX
IP-PBX
IP-PBX
DNS Server
 Loading...
Loading...