Common Features Description
2-81 Atmel 8051 Microcontrollers Hardware Manual
4316B–8051–02/04
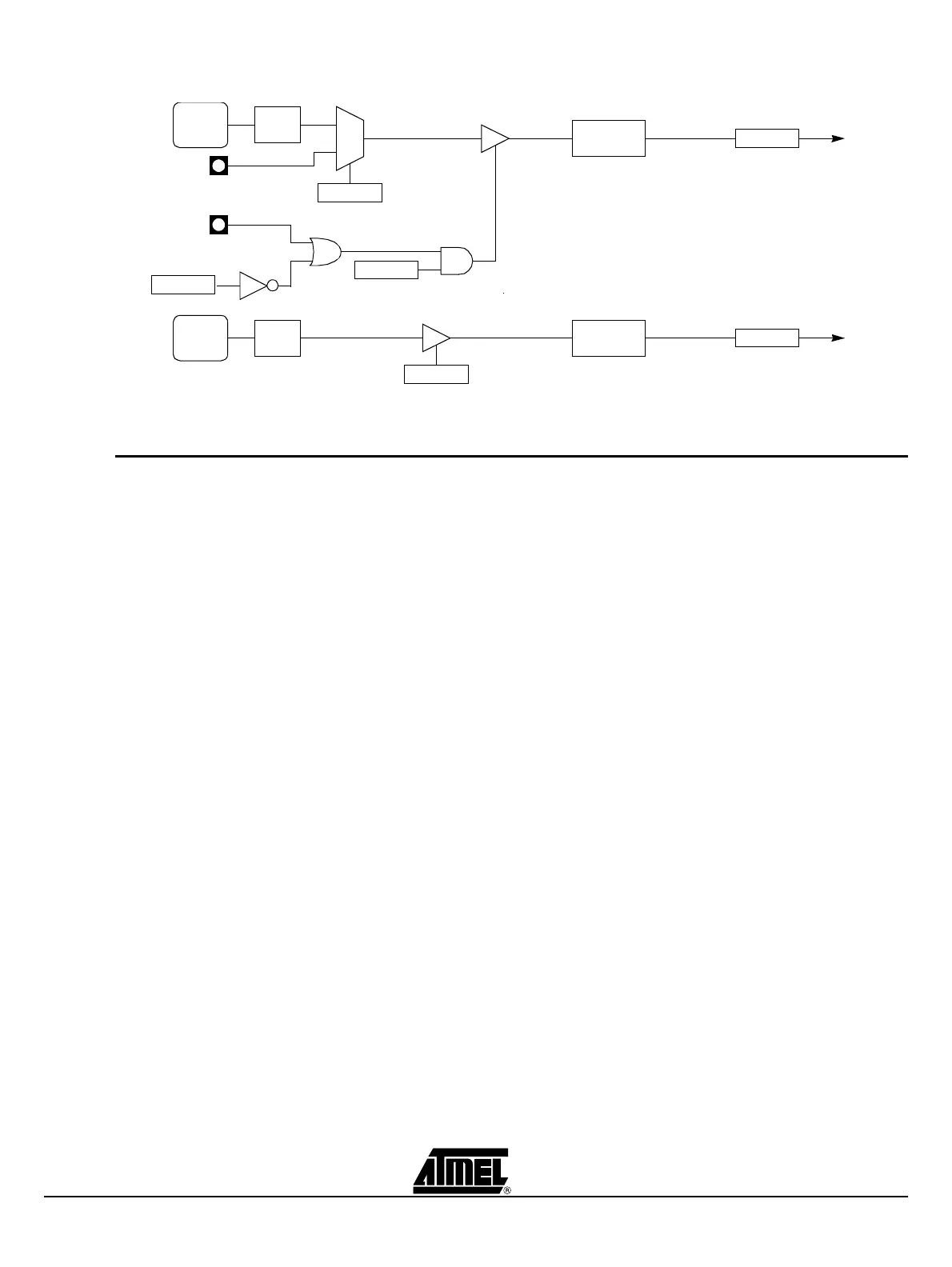
Figure 2-12. Timer/Counter 0 in Mode 3: Two 8-bit Counters
2.11 Timer 1 Timer 1 is identical to timer 0, except for mode 3, which is a hold-count mode. The fol-
lowing comments help to understand the differences:
• Timer 1 functions as either a timer or event counter in three modes of operation.
Figure 2-9 to Figure 2-11 show the logical configuration for modes 0, 1, and 2. Timer
1’s mode 3 is a hold-count mode.
• Timer 1 is controlled by the four high-order bits of the TMOD register (see Table 2-5
on page 82) and bits 2, 3, 6 and 7 of the TCON register (see Table 2-3 on page 83).
The TMOD register selects the method of timer gating (GATE1), timer or counter
operation (C/T1#) and mode of operation (M11 and M01). The TCON register
provides timer 1 control functions: overflow flag (TF1), run control bit (TR1), interrupt
flag (IE1) and interrupt type control bit (IT1).
• Timer 1 can serve as the baud rate generator for the serial port. Mode 2 is best
suited for this purpose.
• For normal timer operation (GATE1 = 0), setting TR1 allows TL1 to be incremented
by the selected input. Setting GATE1 and TR1 allows external pin INT1# to control
timer operation.
• Timer 1 overflow (count rolls over from all 1s to all 0s) sets the TF1 flag generating
an interrupt request.
• When timer 0 is in mode 3, it uses timer 1’s overflow flag (TF1) and run control bit
(TR1). For this situation, use timer 1 only for applications that do not require an
interrupt (such as a baud rate generator for the serial port) and switch timer 1 in and
out of mode 3 to turn it off and on.
• It is important to stop timer/counter before changing modes.
2.11.1 Mode 0 (13-bit
Timer)
Mode 0 configures Timer 1 as a 13-bit timer, which is set up as an 8-bit timer (TH1 reg-
ister) with a modulo-32 prescaler implemented with the lower 5 bits of the TL1 register
(see Figure 2-9). The upper 3 bits of the TL1 register are ignored. Prescaler overflow
increments the TH1 register.
TR0
TCON.4
TF0
TCON.5
INT0#
0
1
Overflow
Timer 0
Interrupt
Request
C/T0#
TMOD.2
TL0
(8 bits)
TR1
TCON.6
TH0
(8 bits)
TF1
TCON.7
Overflow
Timer 1
Interrupt
Request
T0
PERIPH
CLOCK
÷ 6
PERIPH
CLOCK
÷ 6
GATE
 Loading...
Loading...