The 8051 Instruction Set
1-5 Atmel 8051 Microcontrollers Hardware Manual
4316B–8051–02/04
1.3 Arithmetic
Instructions
The menu of arithmetic instructions is listed in Table 1-2. The table indicates the
addressing modes that can be used with each instruction to access the <byte> operand.
For example, the ADD A, <byte> instruction can be written as:
ADD A,7FH (direct addressing)
ADD A,@ R0(indirect addressing)
ADD A,R7 (register addressing)
ADD A,# 127(immediate constant)
The execution times listed in Table 1-2 assume a 12 MHz clock frequency and X1
mode. All of the arithmetic instructions execute in 1 µs except the INC DPTR instruction,
which takes 2 µs, and the Multiply and Divide instructions, which take 4 µs.
Note that any byte in the internal Data Memory space can be incremented or decre-
mented without going through the Accumulator.
One of the INC instructions operates on the 16-bit Data Pointer. The Data Pointer is
used to generate 16-bit addresses for external memory, so being able to increment it in
one 16-bit operation is a useful feature.
The MUL AB instruction multiplies the Accumulator by the data in the B register and puts
the 16-bit product into the concatenated B and Accumulator registers.
The DIV AB instruction divides the Accumulator by the data in the B register and leaves
the 8-bit quotient in the Accumulator, and the 8-bit remainder in the B register.
Oddly enough, DIV AB finds less use in arithmetic “divide” routines than in radix conver-
sions and programmable shift operations. An example of the use of DIV AB in a radix
conversion will be given later. In shift operations, dividing a number by 2
n
shifts its n bits
to the right. Using DIV AB to perform the division completes the shift in 4 µs leaves the B
register holding the bits that were shifted out.
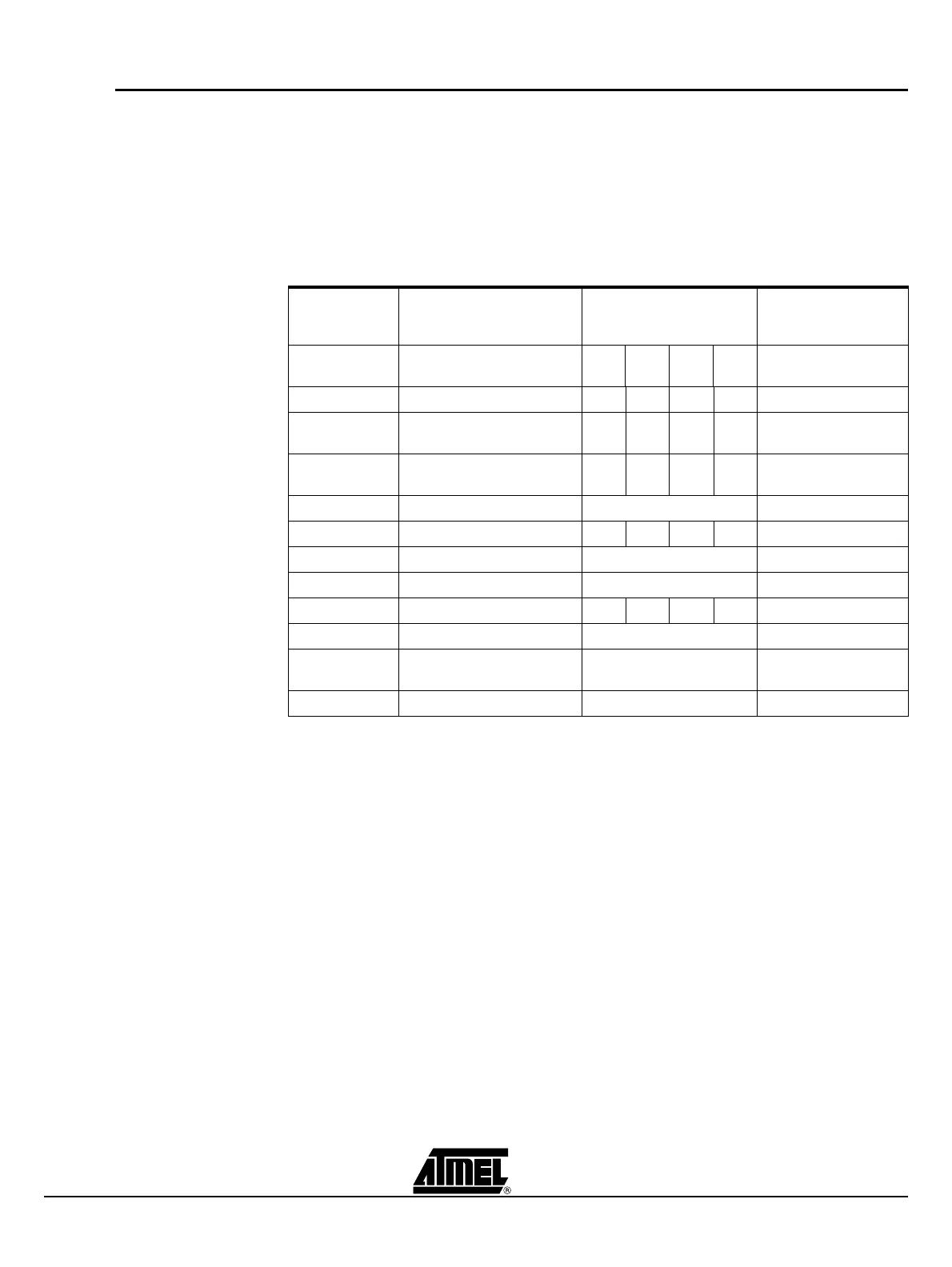
Table 1-2. A list of the Atmel 8051 Arithmetic Instructions.
Mnemonic Operation Addressing Modes
Execution Time in X1
Mode
@12 MHz (µs)
Dir Ind Reg
Im
m
ADD A, <byt>e A = A + <byte> X X X X
ADDC A,
<byte>
A = A + <byte> + C X X X X 1
SUBB A,
<byte>
A = A – <byte> – C X X X X 1
INC A A = A + 1 Accumulator only 1
INC <byte> <byte> = <byte> + 1 X X X 1
INC DPTR DPTR = DPTR + 1 Data Pointer only 2
DEC A A = A – 1 Accumulator only 1
DEC <byte> <byte> = <byte> – 1 X X X 1
MUL AB B:A = B × A ACC and B only 4
DIV AB
A = Int [A/B]
B = Mod [A/B]
ACC and B only 4
DA A Decimal Adjust Accumulator only 1
 Loading...
Loading...