FRITZ!Card PCI on the ISDN Line
36 FRITZ!Card PCI – 5 How FRITZ!Card PCI Works
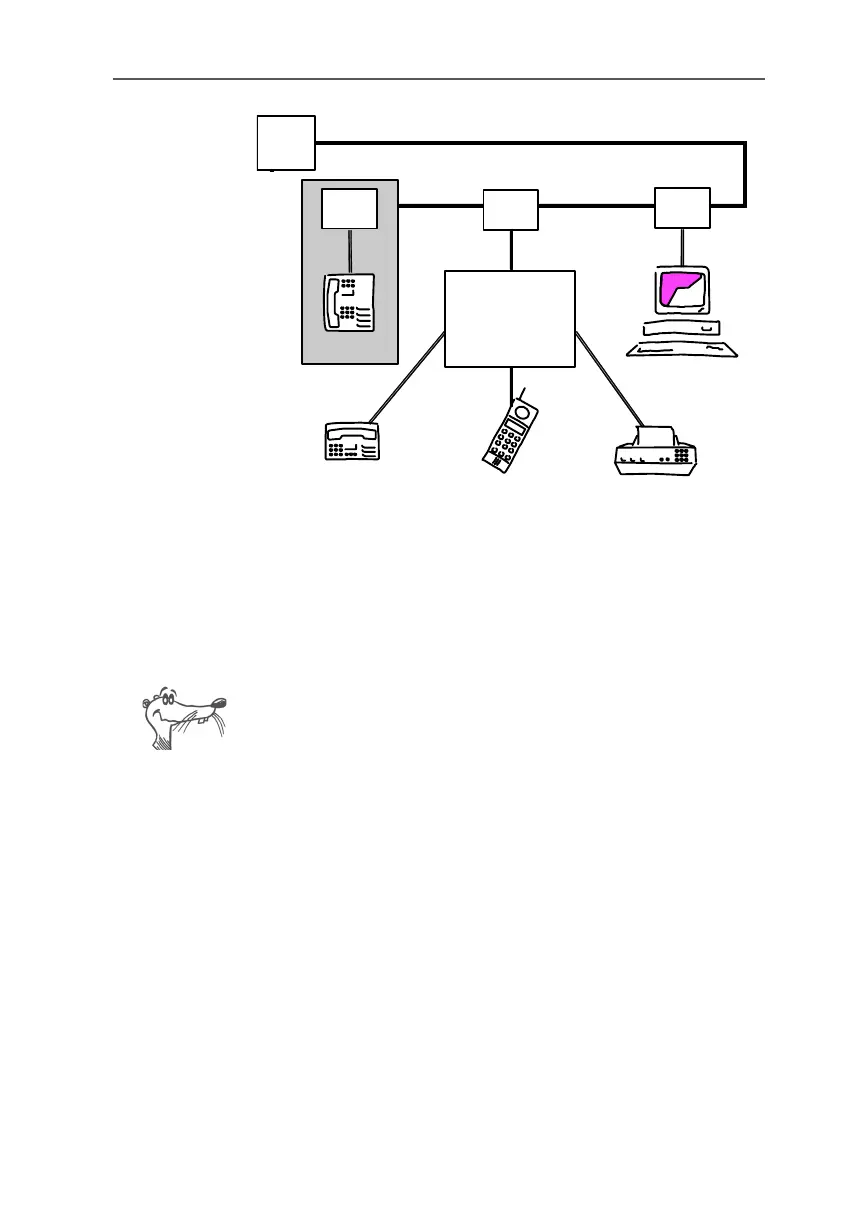
Typical configuration of a point-to-multipoint ISDN line
Some PBX systems provide both analog and digital exten-
sions. ISDN terminal devices may be connected directly to
these digital extensions. Digital extensions are also known
as “internal S
0
interfaces”. These connections are an alter-
native to external S
0
interfaces.
No matter which interface your FRITZ!Card PCI is connected
to, an internal or an external S
0
interface, the terminal de-
vice is not the ISDN-Controller FRITZ!Card PCI, but rather the
ISDN software on your PC: for instance, the FRITZ! modules
FRITZ!data and FRITZ!fax.
Whenever a call arrives on your ISDN line, it is necessary to
decide who will answer it: a FRITZ! module, the ISDN tele-
phone, or the PBX. For incoming calls, a service indicator is
transmitted first. This service indicator distinguishes be-
tween data calls and fax calls, for instance. For incoming an-
alog calls no such differentiation is possible: telephone calls
and G3 (analog) faxes are both designated by the “voice”
service indicator. In order to route such calls correctly, differ-
ent MSNs must be assigned to the different terminal devices
or FRITZ! modules. See the section “MSNs for FRITZ! Mod-
ules” on page 32 for more information.
Analog phone with
answering machine
ISDN phone
Fax
Cordless
phone
PBX
with analog
extensions
NT
NT
Computer with
FRITZ!Card
S
S
O
O
S
S
O
O
S
S
O
O

 Loading...
Loading...