OPERATION
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
higher gear. This will reduce braking and may
cause a loss of control.
Apply the service brakes and/or retarder to pre-
vent exceeding engine governed speed in the lower
gear selected.
• To use the engine as a braking force, the operator
must take his foot off the accelerator. The trans-
mission will start to down shift and the exhaust
brake will be applied.
• If the machine is exceeding the maximum speed
for this gear, use the service brakes and/or re-
tarder to slow the machine.
• When a lower speed is reached, the TCU will au-
tomatically down shift the transmission.
• Engine braking provides good speed control for
travelling downhill. When the machine is fully
loaded, or the gradient is steep, it may be desir-
able to pre-select a lower gear before reaching
the gradient.
• Use the hydraulic retarder on severe gradients.
• If engine-governed speed is exceeded, the trans-
mission will up shift automatically to the next
gear.
• The maximum speed down slopes calculations
are given on the decal in the cab (and in the decal
chapter of this manual).
• A knowledge of the site is important, especially
the altitude of the site and the maximum percent-
age slope liable to be encountered and also the
continuous slope at the site. Remember that the
calculations on the decal were calculated at sea
level. Also take into account the ground condi-
tions at the site when deciding upon gear
selection.
• The maximum slope values on the following
charts are calculated with the exhaust brake and
exhaust valve brake fully functional, the transmis-
sion retarder set to maximum and the transmis-
sion locked in a specified gear.
• The continuous slope values are with the exhaust
brake and exhaust valve brake fully functional.
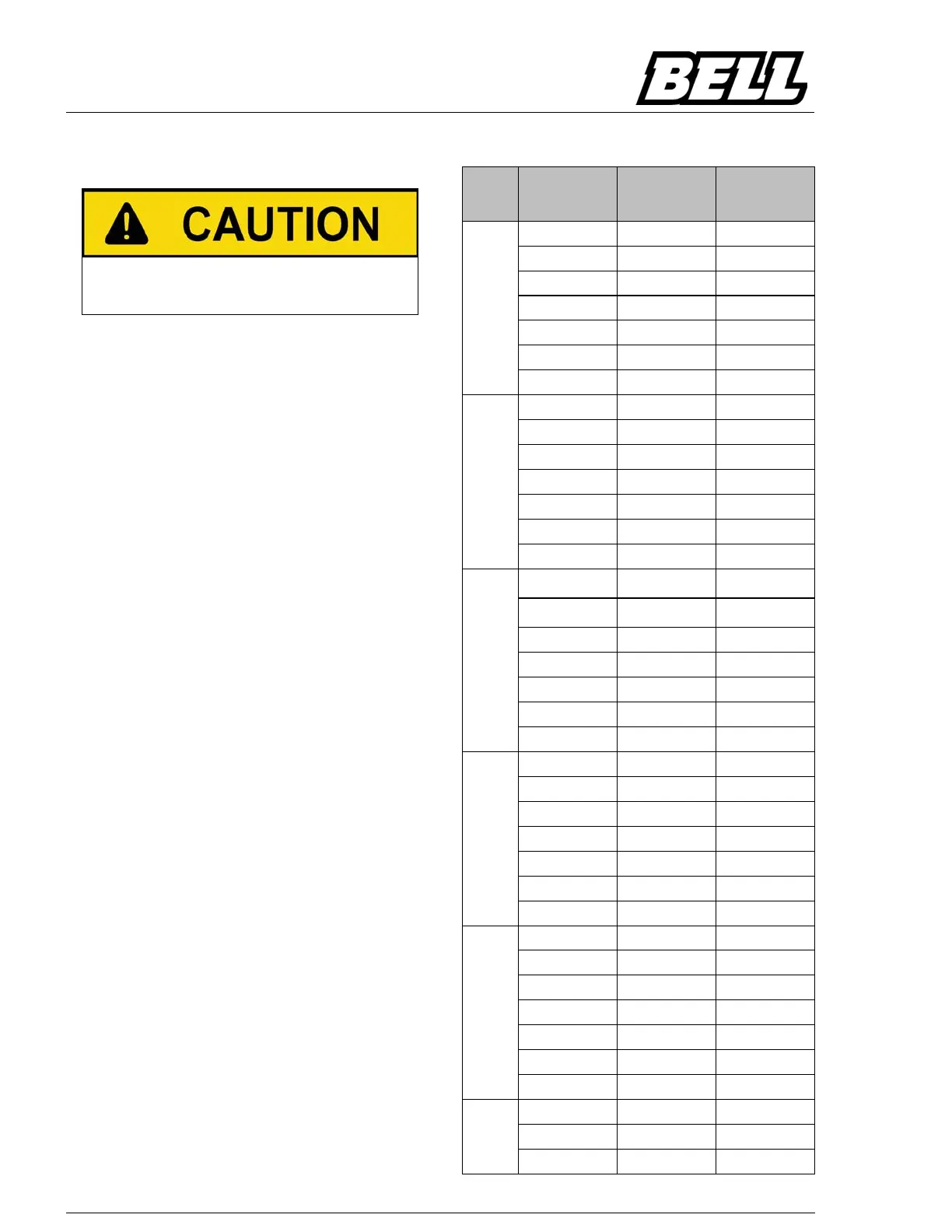
B35E Gradient Values At Altitude
Gear
Altitude (m)
Max slope at
altitude
Continuous
slope at
altitude
1
0 25% 25%
500 25% 25%
1000 25% 25%
1500 25% 25%
2000 25% 25%
2500 25% 25%
3000 25% 24%
2
0 24% 15%
500 23% 14%
1000 22% 14%
1500 22% 13%
2000 21% 13%
2500 20% 12%
3000 19% 12%
3
0 20% 11%
500 19% 11%
1000 19% 10%
1500 18% 10%
2000 17% 9%
2500 17% 9%
3000 16% 9%
4
0 13% 8%
500 13% 8%
1000 12% 7%
1500 12% 7%
2000 11% 7%
2500 11% 7%
3000 10% 6%
5
0 11% 6%
500 11% 6%
1000 10% 6%
1500 10% 5%
2000 9% 5%
2500 9% 5%
3000 9% 5%
6
0 10% 6%
500 10% 6%
1000 9% 6%

 Loading...
Loading...