6
All information herein is proprietary and condential and may not be copied or reproduced without the expressed written consent of BRAY INTERNATIONAL, Inc.
The technical data herein is for general information only. Product suitability should be based solely upon customer’s detailed knowledge and experience with their application.
Series 92-93 Pneumatic Actuator
Operations and Maintenance Instructions
Assembly
To identify component names and shapes and
for the numbers in parentheses ( ) below, refer
to the Exploded View of the actuator shown on
Figure 3, pg. 11. Easiest assembly will result from lubricat-
ing all bearings and seals as they are installed. The lubricant
should be a high pressure or extreme pressure petroleum
grease with a lithium based thickener which meets the NLGI
grade 2. Grease which meets this specication should be
available from any automotive supply store.
Pinion (3) - Install bearing rings (6 & 7) and o-rings (21
& 22) in their appropriate grooves. Insert the pinion
through the large hole in the center bottom of the body
(1). With the pinion part of the way into the body, slide
the cam (16) over the pinion being careful to align the
punch mark on the cam with the punch mark(s) on the
pinion. For normal installation and rotation (Fail Close),
align the single marks. For Fail Open operation described
in Method 2 on page 3, align the single mark on the cam
with the two marks on the pinion. For Fail Open opera-
tion described in Method 3 on page 3, align the single
marks. Next, install the spacer (15) above the cam. Then
insert the pinion through the hole at the top of the body
and secure it with the washer (9) and retaining ring (8).
Travel Stop Screws (13) - Slip the o-ring (14) over the
at end of the screw until it is 5-7 threads from the end.
Thread the screw into the hole in the body, at end
rst. Repeat these steps for the second screw. Thread
the lock nuts (12) onto the screws and tighten the nuts
against the body. This will seal the threads for testing.
It is not necessary to set the travel stops at this time, as
they may have to be reset when the actuator is installed
on the valve.
Pistons (2) - Install the bearing pad (10) on the back
of the rack and the o-ring (19) and guide ring (11) in
their appropriate piston grooves. The o-ring goes in the
groove nearest the rack. With the ports on the actuator
body toward you, turn the pinion so that the slot is ap-
proximately 45° to the right of perpendicular with the
long side of the body. Grasp the pistons in the spring
pockets so that the piston in the right hand has the
bearing pad toward you and the piston in the left hand
has the bearing pad away from you. Slide the pistons
into the body so that they both engage the teeth on the
pinion at the same time. Apply enough steady force to
compress the o-ring into the body bore. At this point,
you may continue pushing or use a wrench on the top
of the pinion to pull the pistons into the body.
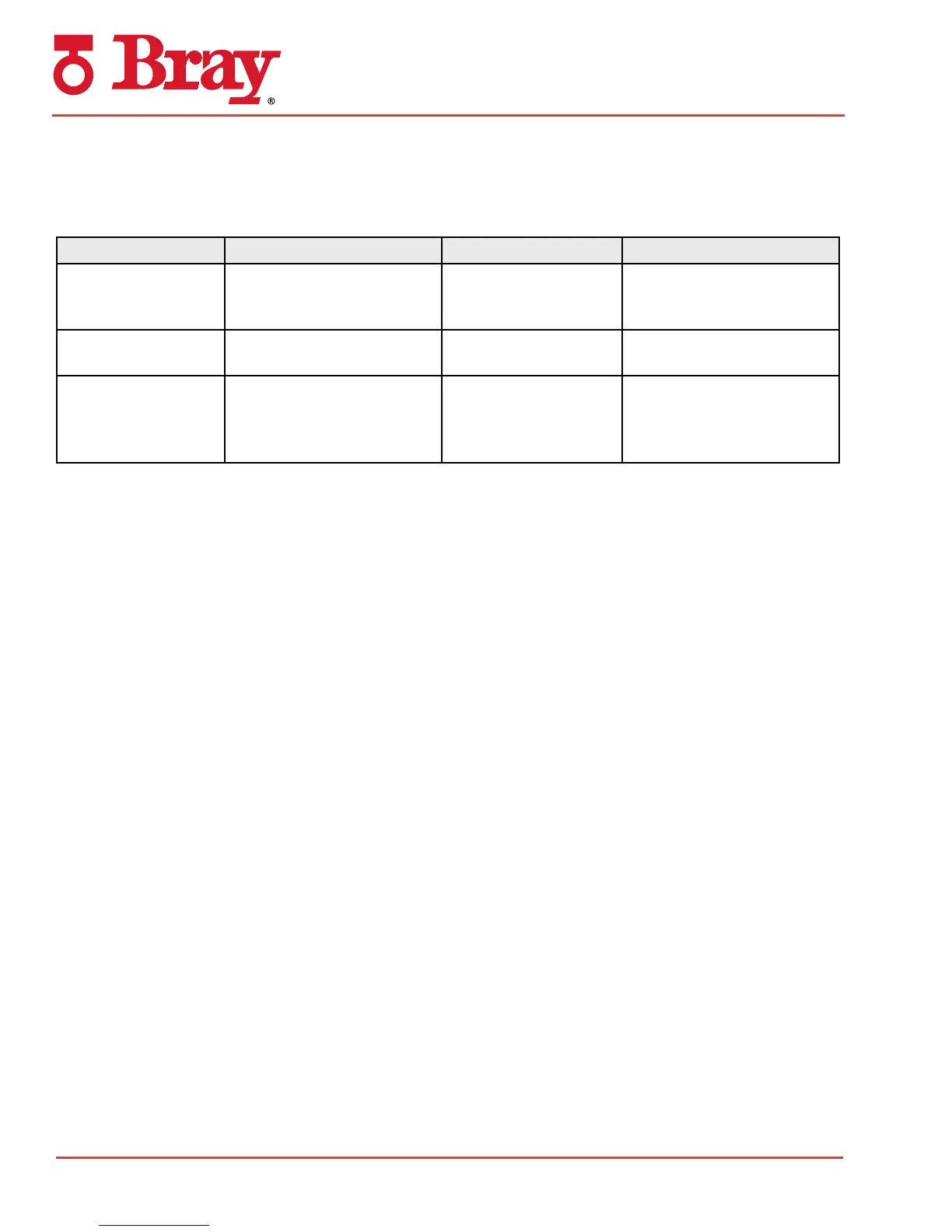
Symptom Probable Cause Check Remedy
Loss of Power Low air supply pressure, or
damaged O-rings
Air supply pressure at
actuator, leakage across
O-rings
Boost air supply pressure,
repair air supply line leaks,
replace O-rings
Binding between
valve and actuator
Misalignment of coupling Alignment Realign coupling
Valve “pops” out of
seat and slams open
Valve torque too high, actua-
tor sized too small, or insuf-
cient air supply ow
Valve torque, actuator
sizing calculations, size
of air supply lines and/
or solenoid valve
Repair valve, use proper size
actuator, use larger air supply
lines and/or solenoid valve
with higher ow
Troubleshooting
Table 1 shows several common symptoms and their remedies.

 Loading...
Loading...