67
3-3 Differential Calculations
• To perform differential calculations, first display the function analysis menu, and
then input the values shown in the formula below.
2(d/dx) f(x),a,∆x)
The differentiation for this type of calculation is defined as:
In this definition,
infinitesimal
is replaced by a
sufficiently small
∆x, with the value in
the neighborhood of f ' ( a) calculated as:
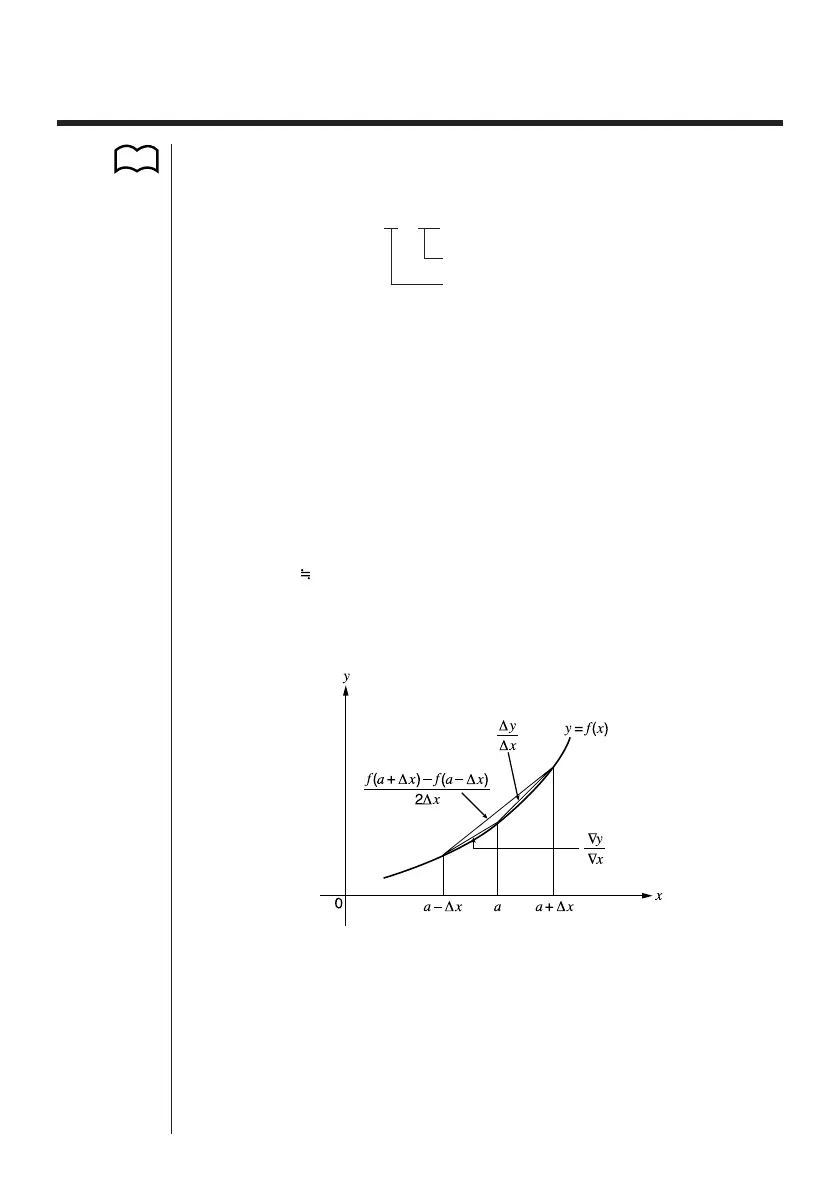
In order to provide the best precision possible, this unit employs central difference to
perform differential calculations. The following illustrates central difference.
The slopes of point a and point a + ∆x, and of point a and point a – ∆x in function
y = f(x) are as follows:
In the above, ∆
y/∆x is called the forward difference, while ∇y/∇x is the backward
difference.To calculate derivatives, the unit takes the average between the value of
∆y/∆x and ∇y/∇x, thereby providing higher precision for derivatives.
P.64
Increase/decrease of
x
Point for which you want to determine the derivative
d
d/dx ( f (x), a, ∆x) ⇒ ––– f (a)
dx
f (a + ∆x) – f (a)
f '(a) = lim –––––––––––––
∆x∆x→0
f (a + ∆x) – f (a) ∆y f (a) – f (a – ∆x) ∇y
––––––––––––– = ––– , ––––––––––––– = –––
∆x ∆x ∆x ∇x
f (a + ∆x) – f (a)
f '(a)
–––––––––––––
∆x
 Loading...
Loading...