71
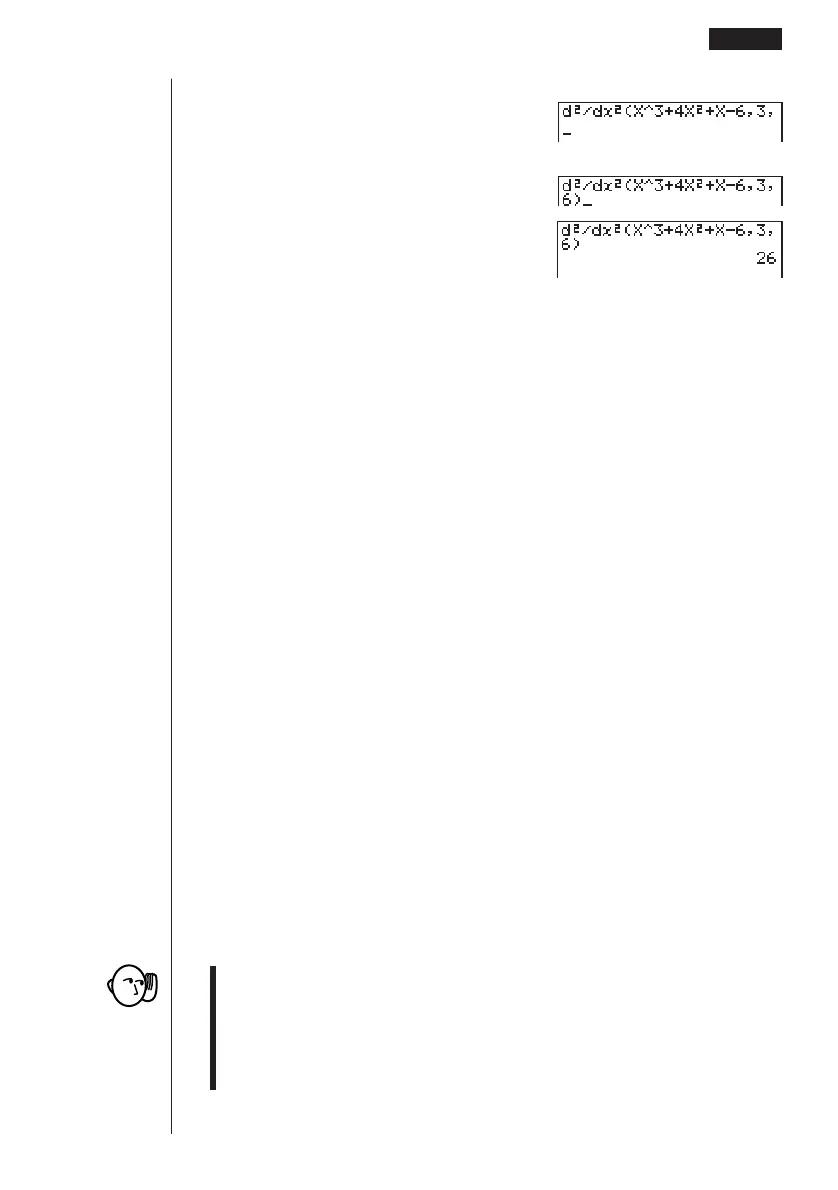
Input 3 as point
a, which is differential coefficient point.
d,
Input 6 as n, which is final boundary.
g)
w
• In the function
f(x), only X can be used as a variable in expressions. Other vari-
ables (A through Z, r,
θ
) are treated as constants, and the value currently as-
signed to that variable is applied during the calculation.
• Input of the final boundary value n and the closing parenthesis can be omitted.
• Discontinuous points or sections with drastic fluctuation can adversely affect pre-
cision or even cause an error.
kk
kk
k Quadratic Differential Applications
• Arithmetic operations can be performed using two quadratic differentials.
Therefore:
f ''(a) + g''(a), f ''(a) × g''(a)
• The result of a quadratic differential calculation can be used in a subsequent
arithmetic or function calculation.
2 × f ''(a), log ( f ''(a) )
• Functions can be used within the terms (
f(x), a, n ) of a quadratic differential
expression.
• Note that you cannot use a Solve, differential, quadratic differential, integration,
maximum/minimum value or Σ calculation expression inside of a quadratic differ-
ential calculation term.
• Use only integers within the range of 1 to 15 for the value of final boundary n.
Use of a value outside this range produces an Ma ERROR.
• You can interrupt an ongoing quadratic differential calculation by pressing the
A key.
• You should always specify radians (Rad) as the unit of angle unit before per-
forming a quadratic differential calculation using trigonometric functions.
d
2
d
2
––– f (a) = f ''(a), ––– g (a) = g''(a)
dx
2
dx
2
d
2
––– (sin x + cos x, sin 0.5)
dx
2
Quadratic Differential Calculations 3 - 4
 Loading...
Loading...