Cisco Systems, Inc.
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2004 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Important Notices and Privacy Statement.
Page 16 of 29
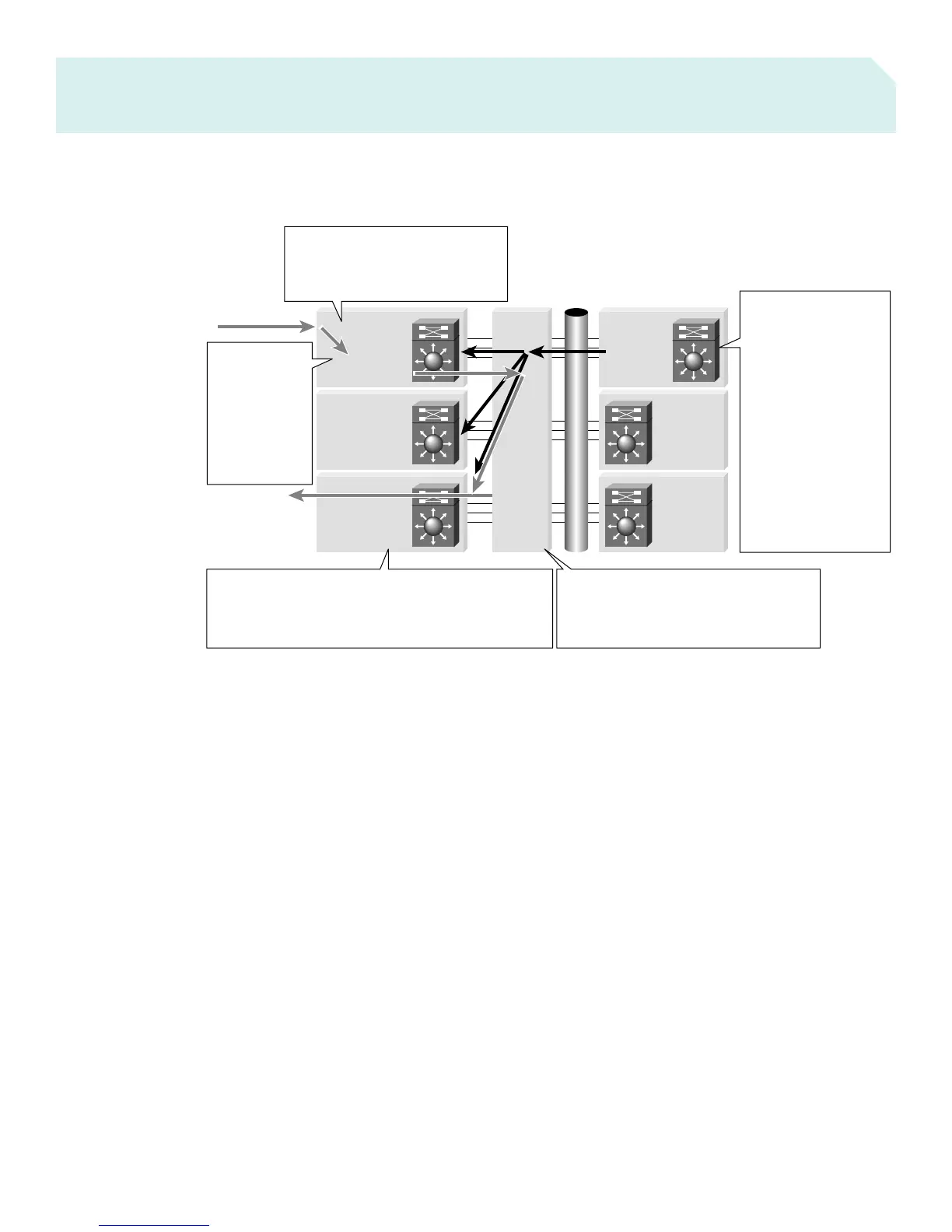
Figure 6
Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding Packet Flow
dCEF-based forwarding requirements: Requires a Cisco Catalyst Supervisor Engine 720 for the dCEF720 interface
module; requires either a Catalyst Supervisor Engine 720 or a Catalyst Supervisor Engine 2-MSFC2 and a SFM
for the dCEF256 interface module.
CISCO IOS SOFTWARE AND CATALYST OPERATING SYSTEM SOFTWARE
Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series switches offer two operating modes of software, the Cisco Catalyst Operating System
Software with optional Cisco IOS Software on the MSFC, and Cisco IOS Software for the supervisor engines. Each
operating mode can be deployed at different hierarchies of the network, depending on the network’s requirements.
These software solutions for the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series switches provide full Layer 2 through 4 switching
and routing functions at high performances.
Today, either of these operating modes can be deployed in an entire network environment, or the operating modes
canvarywithin an environmenttomeetdifferent requirements. Oneoperatingmodeis not areplacementforanother,
but is recommended for varying feature requirements.
• Cisco IOS Software for the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series
• Cisco Catalyst Operating System Software with optional Cisco IOS Software on the MSFC
Fabric
Enabled
Line Card
DFC
Fabric
Enabled
Line Card
DFC
Fabric
Enabled
Line Card
DFC
MSFC2
PFC2
Supervisor
Line
Card
Line
Card
Fabric
Switch
Module
DBus
MSFC Has CEF-Based
Control Plane
1. MSFC Delivers
Forwarding Table to
All DFC-Enabled
Modules
• Eliminates Supervisor
Engine from
Forwarding Path (incl.
card to card traffic)
• Enables Local
Intelligent Switching,
Supporting Network
Services (security,
QoS, etc.)
4. SFM Receives Packet, Examines Tag,
Makes Switching Decision
• Determines Outgoing Port on Line Card and
Switches Packet to Specified Line Card
5. Line Card Takes Frame from SFM and Places on Its Own
Local Bus
• The DFC Provides Destination Port and Exit Port
• Packet is Queued, QoS Applied and Packet Exits Line Card
3. If Destination
is on Another
Line Card, DFC
Tells SFM to
Prepend Tag
on Packet with
Exit SFM Port
Info
2. Packet Enters Switch/Line Card
• All Local Ports and DFC See Frame
• DFC Uses Lookup Table for Local
or Other Line Card Destination
 Loading...
Loading...











