10
Selecting the installation site
5. Selecting the installation site
5.1 General
Installation must be in accordance with local regulations.
If they do not exist, follow EN378 .
⊲ Maximum altitude for installation: 1000m.
During positioning consider these elements:
• customer approval
• unit weight and bearing point capacity
• safe accessible position
• functional spaces
• spaces for the air intake/exhaust
• Electrical connections
• max. distance allowed by the electrical connections
• Water connections
5.2 Functional spaces
Functional spaces are designed to:
• guarantee good unit operation
• carry out maintenance operations
• protect authorized operators and exposed people
ATTENTION
⊲ Respect all functional spaces indicated in the
DIMENSIONS section.
⊲ Do not smoke or use open flames within this area
5.3 Positioning
ATTENTION
⊲ Do not go up to the surface
⊲ Do not place heavy loads.
Units are designed to be installed:
• in fixed positions
• level
Put the unit in a position where any leaking gas cannot
enter buildings or stagnate in closed areas. In the latter
case, observe the rules for machinery rooms (ventilation,
leak detection, etc.).
Choose the installation place according to the following
criteria:
• avoid installations in places subject to flooding
• install the unit raised from the ground
• bearing points aligned and leveled
• discharged condensation water must not cause harm/
danger to people and property
• the accumulation of snow must not cause clogging of
the coils
Limit vibration transmission:
• use anti-vibration devices or neoprene strips on the
unit support points
• install flexible joints on the hydraulic and aeraulic
connections
Protect the unit with suitable fence in order to avoid
access to unauthorised personnel (children, vandals, etc.)
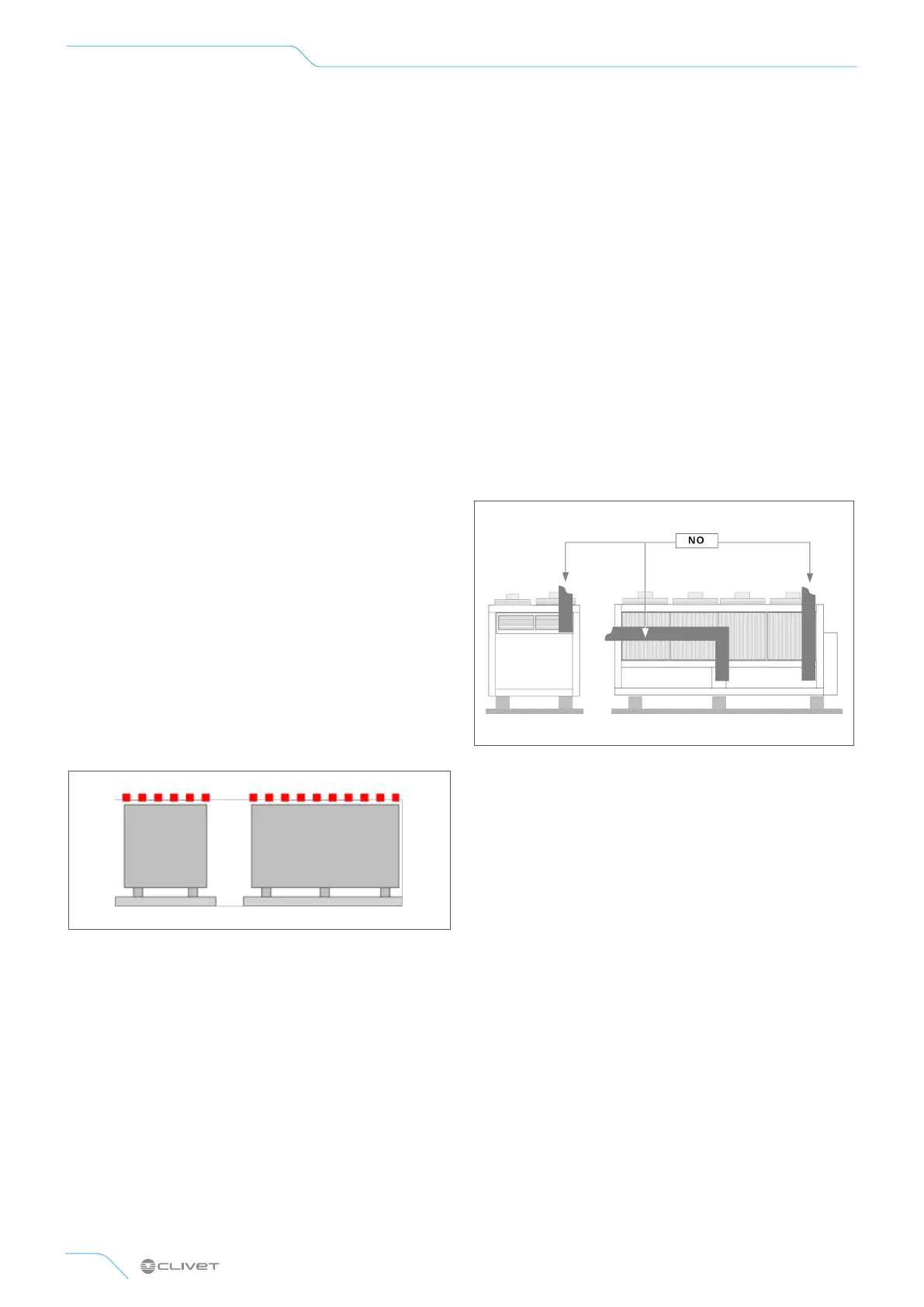
5.4 Air flow-rate on the coils
ATTENTION
⊲ The air flow must not be obstructed
A correct circulation of the air is mandatory to guarantee
the good unit operating.
Avoid therefore:
• obstacles to the airflow
• diculty of exchange
• leaves or other foreign bodies that can obstruct the air
coil
• winds that hinder or favour the airflow
• heat or pollution sources close to the unit (chimneys,
extractors etc..)
• stratification (cold air that stagnates at the bottom)
• recirculation (expelled air that is sucked in again)
• incorrect positioning, close to very high walls, attics
or in angles that could give rise to stratification or
recirculation phenomenons
Ignoring the previous indications could:
• reduce energy eciency
• alarm lockout due to HIGH PRESSURE (in summer) or
LOW PRESSURE (in winter)
5.5 Saftey valve gas side

 Loading...
Loading...











