21 of 29
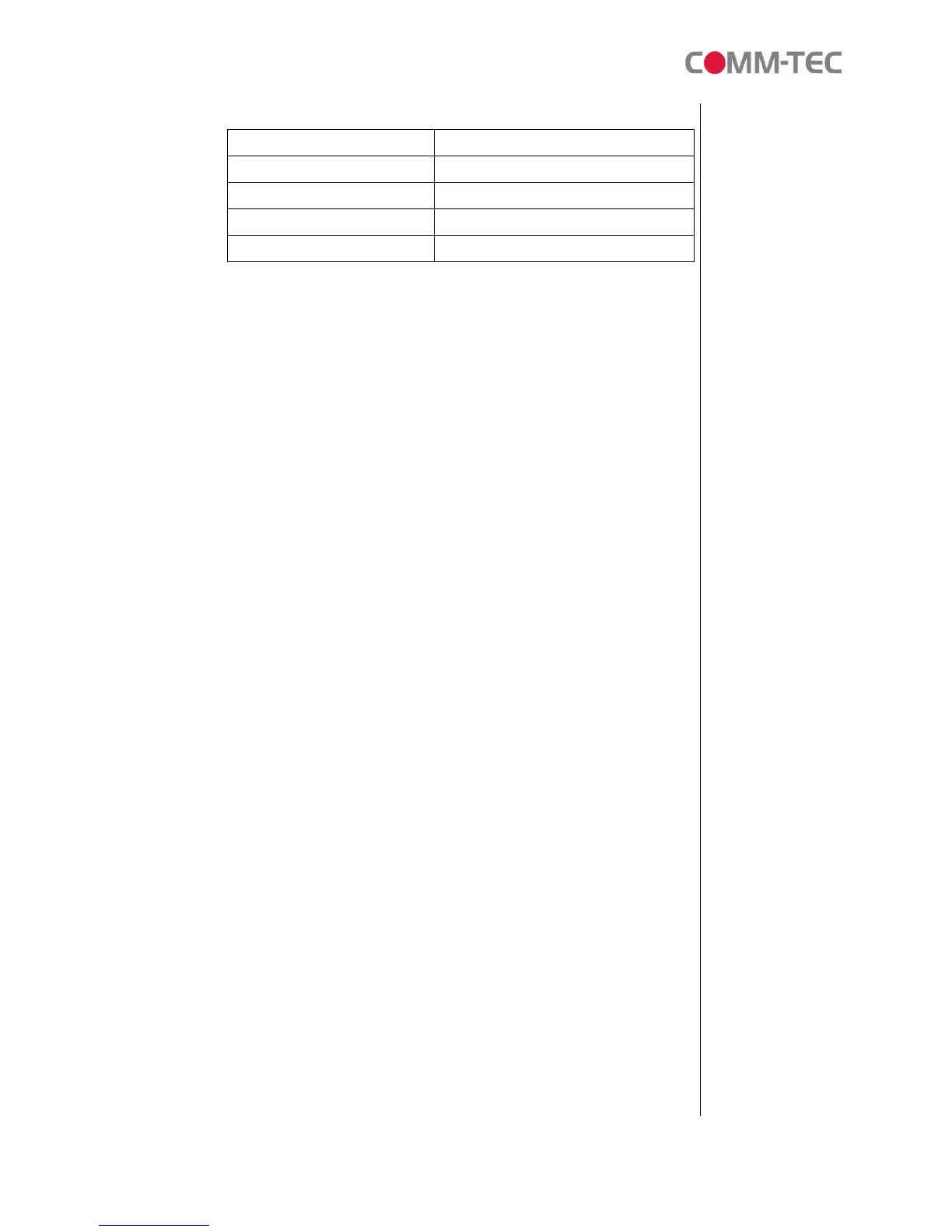
MPEG-2 / NTSC (30 Hz)
Source Resolution Output Resolution
720 x 480 (recommended) 720 x 480
704 x 480 720 x 480
352 x 480 720 x 480
352 x 240 720 x 480
• The playback machine uses a Compact Flash
memory card.
Important: Your content should be no larger than the memory on the
Flashcard minus 0.5 MB. Preferably, leave more memory available – at
least 5 MB is a good rule of thumb.
• Keep in mind that videos can be transferred via the Internet, often using
slow connections. It is recommended that you keep the size of your
variable content (i.e. content that changes often) down to a minimum.
• To avoid confusion, keep all filenames and all links in lower case only.
• Long filenames are supported by renaming: ProPLAY Studio software
renames the files. Nevertheless, it is best to keep filenames short (“8.3”
format, e.g. “12345678.123”) to start with.
• Once you have content, you should create project file(s) and playlist(s)
using “ProPLAY Studio” software.
• Copy it to the flash card, using a CF card reader/writer.
6.3 General Display Design Guidelines
Graphics - a monitor or television screen has a lower resolution (less than 72 dpi)
than a computer screen. Make your graphics as "clean" as possible, therefore. Use
the anti-aliasing capabilities of graphics software to eliminate the "stairstep" effect.
Interlacing - TV monitors paint the screen in two passes, the even lines first and
then the odd ones. The entire image is actually never on the screen all at once;
persistence of human vision makes up the difference. Small (1 or 2 pixel-high) areas
of detail in the image flicker in reaction to interlacing. Computer monitors paint the
screen all at once (known as de-interlaced or progressive scan), so you won't notice
this problem on your computer screen. Feathering and/or anti-aliasing areas of
detail can avoid this defect. Use the blur tool. Areas of significant detail should be
made larger.
 Loading...
Loading...