Data sheet PAH 2/4/6.3, PAH 10/12.5, PAH 20/25/32 and PAH 50/63/70/80/100 pumps
24 | 180R380 | AQ213286502970en-000701 | IOM PAH 20-100 pumps
© Danfoss | DCS (im) | 2021.11
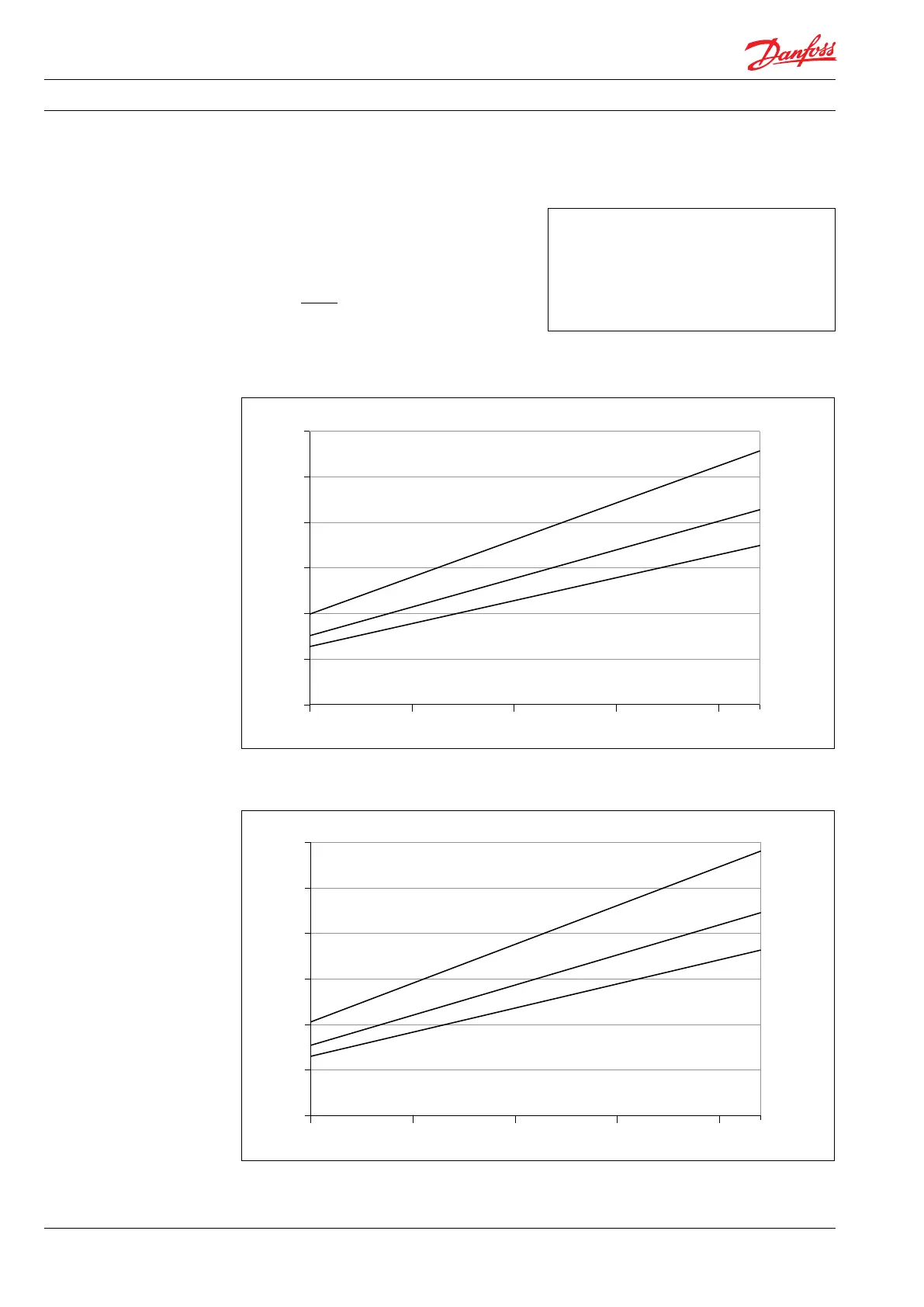
5. Flow The ow (Q
e
) at various pressure (p
max
) can be
calculated with the following equation:
Q
e
= Q
(th)
– [(Q
(th)
– Q (p
max
)) x (p / p
max
)]
The theoretical ow can be calculated with the
following equation:
V x n
Q
(th)
=
1000
At zero pressure the true ow equals the
theoretical ow Q
(th)
.
Q
(th)
: Theoretical ow (l/min / gpm)
Q (p
max
): Flows at max. pressure (l/min and
gpm), see 4.1-4.4
p
max
: Max pressure (barg / psig)
p: Pressure (barg / psig)
V: Displacement (cm
3
/ rev.)
n: Motor speed (rpm)
60
50
40
30
20
10
0 rpm
PAH 20
PAH 25
PAH 32
l/min
700
950
1200
1450
1700
1800
15
12.5
10
7.5
5
2.5
0 rpm
PAH 20
PAH 25
PAH 32
gpm
700
950
1200
1450
1700
1800
60
50
40
30
20
10
0 rpm
PAH 20
PAH 25
PAH 32
l/min
700
950
1200
1450
1700
1800
15
12.5
10
7.5
5
2.5
0 rpm
PAH 20
700
950
5.3 PAH 20-32 typical ow curves at max pressure
 Loading...
Loading...