SI-Ethernet User Guide 141
Issue: 1
Safety
information
Introduction
Mechanical
installation
Electrical
installation
Getting started Parameters
Key features
and Protocols
PC Applications Security Diagnostics
Glossary of
terms
Index
7.4.2 Setting the destination slot and menu (Base address + 3)
The destination slot and menu address is sent in the format SMM, where S is the slot
number and MM is the two digit menu number.
Examples
• For the drive application menu 3, the value sent would be “20”.
• For the SI-Applications Plus register 70 in slot 3, the value sent would be “370”.
7.4.3 Setting the destination parameter address (Base address + 4)
The destination parameter address is sent in the format PPP, where PPP is the three
digit parameter number.
Examples
• For parameter “021”, the value sent would be “21”.
• For parameter “104”, the value sent would be “104”.
7.4.4 Setting the parameter value to write
The destination parameter value is sent in two signed 16-bit values, therefore it must
be converted into two signed 16-bit words.
Base address + 5 (LSW)
The least significant word of the parameter value is converted to a signed 16-bit value
stored in a 32-bit variable by bitwise ANDing it with the hexadecimal value 0x00007FFF
and subtracting the decimal value 32768 if the result was greater than the decimal
value 32767.
Base address + 6 (MSW)
The most significant word of the parameter value is converted to a signed 16-bit value
stored in a 32-bit variable by bitwise shifting it 16 places right and bitwise ANDing the
result with the hexadecimal value 0x00007FFF, then subtracting the decimal value
32768 if the most significant bit is set to 1.
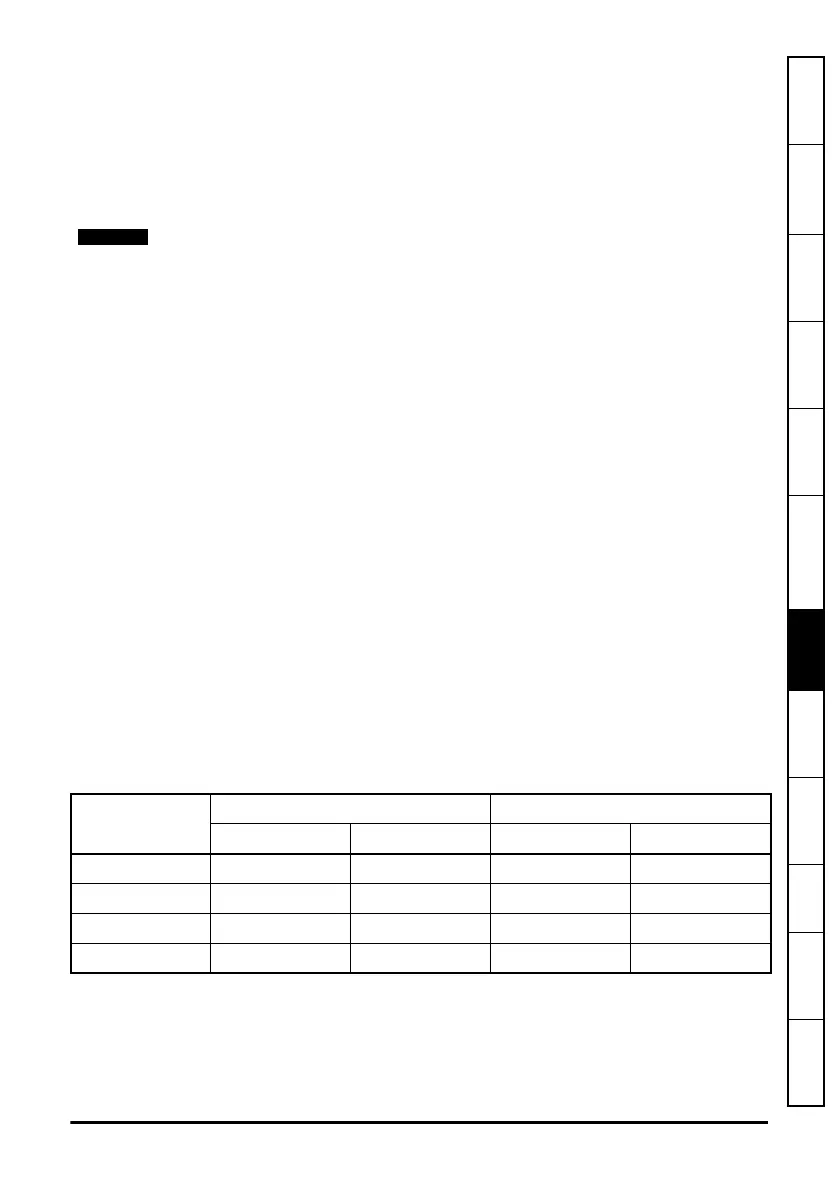
Examples
Only menus numbers 0 to 99 are possible using this method.
Value to write
MSW LSW
Decimal Hex Decimal Hex
3515 0 00000000 3515 00000DBB
123456 1 00000001 -7616 FFFFE240
-123456 -2 FFFFFFFE 7616 00001DC0
-678900 -11 FFFFFFF5 -23540 FFFFA40C

 Loading...
Loading...











