Proservo NMS80/81/83
Endress+Hauser 19
Proof-testing
Check the operativeness and safety of safety functions at appropriate intervals! The operator must
determine the time intervals.
The values and graphics in the "Additional safety-related characteristics" section can be used for this
purpose (→ 5). The test must be carried out in such a way that it verifies the correct operation of
the protective system in interaction with all of the components.
In a single-channel architecture, the PFD
avg
value to be used depends on the diagnostic rate of
coverage for the proof-test (PTC = proof test coverage) and the intended lifetime (LT =
lifetime), as specified in the following formula:
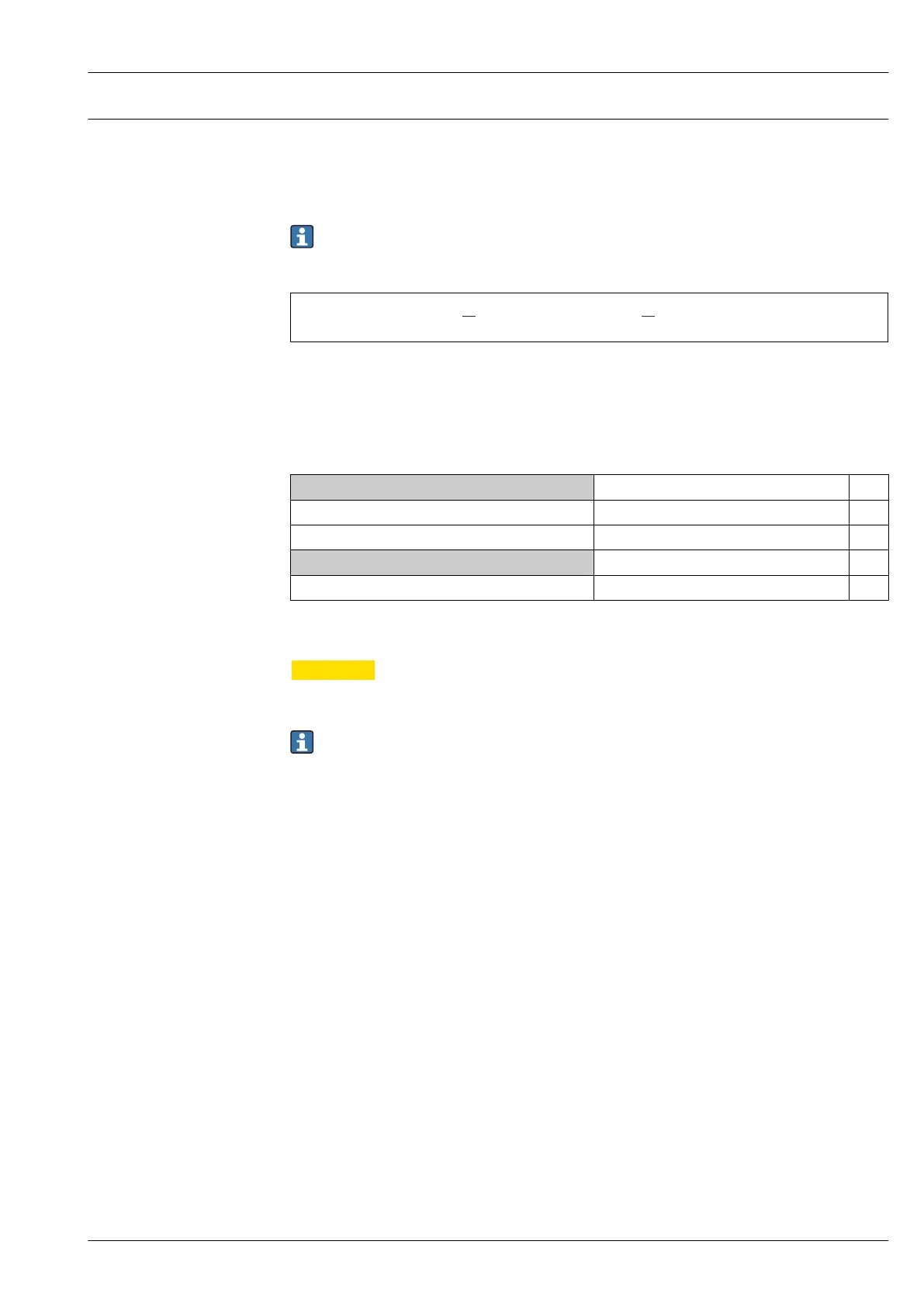
• • • •• • •
PFD = T +PTC MTTR + (1 – PTC) LTl l l
avg DU 1 DD DU
1 1
2 2
A0024244
For the proof-tests described as follows, the respective proof test coverages are specified, which may
be used for calculation. The proof test coverage rates depend on the specific test sequence.
A test sequence for the proof test must be selected from the following table for every safety function
used. If both safety functions are used, two test sequences must be performed for the proof test.
Safety function 1 (level measurement) PTC
Test sequence A – Approach the level 99%
Test sequence B – Simulate the level 91%
Safety function 2 (current input measurement)
Test sequence C – Feed-in real currents 99%
You must also check that all cover seals and cable entries are sealing correctly.
L
CAUTION
To ensure process safety.
‣
During the proof-test, alternative monitoring measures must be taken to ensure process safety.
If one of the test criteria from the following test sequences is not fulfilled, the device may no
longer be used as part of a protective system. The purpose of proof-testing is to detect random
device failures (λ
du
). The impact of systematic faults on the safety function is not covered by this
test and must be assessed separately. Systematic faults can be caused, for example, by process
material properties, operating conditions, build-up or corrosion.

 Loading...
Loading...











