Brief descript ion of mainboard
PCI bus interrupts - Selecting correct PCI slot
Extensive information on this section is contained in the manual "Basic informa tion on mainboard".
To achieve optimum stability, performance an d compatibility, avoid the multiple use
of ISA IRQs or PCI IRQ Lines (IRQ sharing). Should IRQ sharing be unavoidable,
then all involved devices and their drivers must support IRQ sharing.
Which ISA IRQs are assigned to the PCI IRQ Lines is normally automatically
specified by the BIOS ( see "BIOS Setup" description).
Monofu nct ional expansion cards
PCI/PCI Express expansion cards require a max imum of one interrupt, which is called the PCI
interrupt INT A. Expansion cards that do not require an interrupt ca n be installed in any desired slot.
Multifunctio nal expansi on cards or expansion cards with integrated P CI-PCI bridge
These expansion cards require up to fo ur PCI interrupts: INT A, INT B, INT C, INT D. How many
and which of these interrupts are used is specified in the documentation provided with the card.
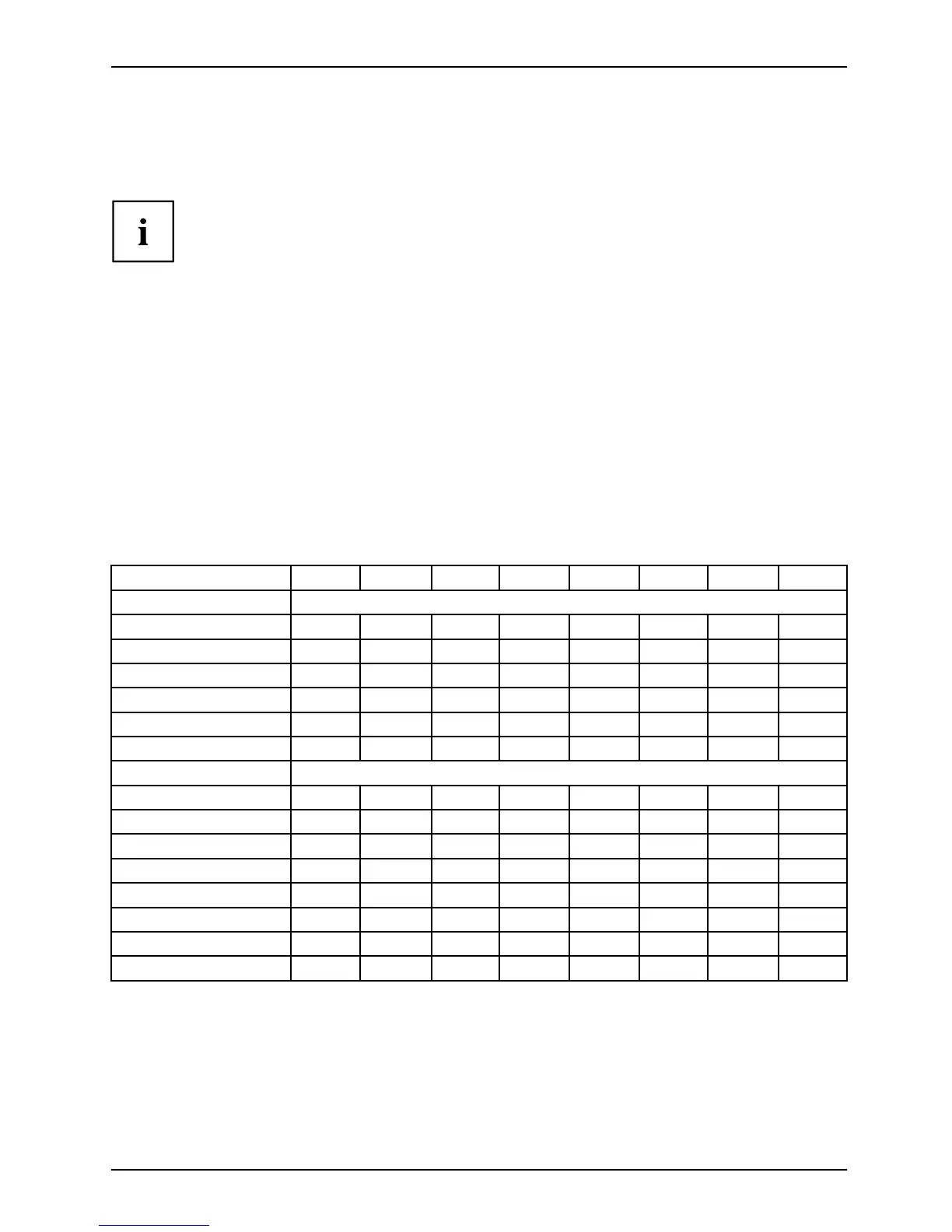
The assignment of the PCI interrupts to the IRQ Lines is shown in the following table:
On board con troller
PCI INT LINE 1 (A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 5 (E) 6 (F) 7 (G) 8 (H)
UHCI U S B 1.1
Dev 1A Fn 0
1th
----
x
---
Dev 1A Fn 1
2nd
--
x
-----
Dev 1D Fn 0
3rd
----
x
---
Dev 1D Fn 1
4th
------
x
-
Dev 1A Fn 2
5th
---
x
----
Dev 1D Fn 2
6th
-----
x
--
EHCI USB 2.0
Dev 1A Fn 7
--
x
-----
Dev 1D Fn 7
----
x
---
SATA #1
---
x
----
SATA #2
------
x
-
SMBus
------
x
-
Intel LAN
-------
x
HD Audio
----
x
---
Onboard Graphik
x
-------
A26361-D2811-Z210-1-8N19, edition 1 English - 5

 Loading...
Loading...