Chapter 9 -- Measurement of Small Current Signals--Measurement System Model and Physical Limitations
9 - 2
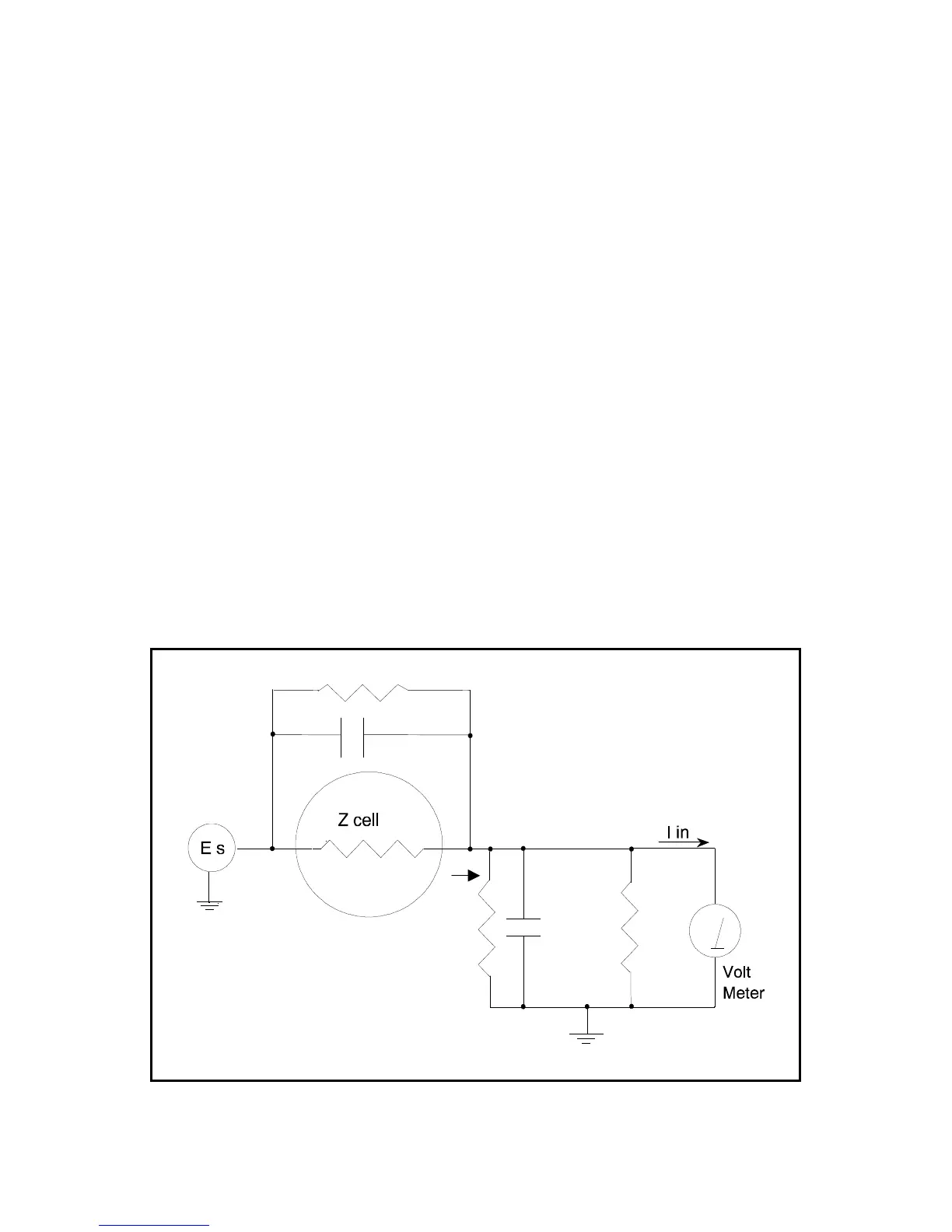
In Figure 9-1:
E
s
Is an ideal signal source
Z
cell
Is the unknown cell impedance
I
cell
Is the “real” cell current
R
m
Is the current measurement circuit's current measurement resistance
R
shunt
Is an unwanted resistance across the cell
C
shunt
Is an unwanted capacitance across the cell
C
in
Is the current measurement circuit's stray input capacitance
R
in
Is the current measurement circuit's stray input resistance
I
in
Is the measurement circuit's input current
In the ideal current measurement circuit R
in
is infinite while C
in
and I
in
are zero. All of the cell current, I
cell
,
flows through R
m
.
With an ideal cell and voltage source, R
shunt
is infinite and C
shunt
is zero. All the current flowing into the
current measurement circuit is due to Z
cell
.
The voltage developed across R
m
is measured by the meter as V
m
. Given the idealities discussed above, one
can use Kirchoff's and Ohms law to calculate Z
cell
:
Z
cell
= E
s
* R
m
/ V
m
Figure 9-1
Equivalent Measurement Circuit
Icell
C shunt
R shunt
R in
Rm
 Loading...
Loading...