9
D5294 - 5 A SIL 3 NO contact Relay Out Module for NE or F&G/ND Load with full diagnostic and Modbus G.M. International ISM0123-14
Functional Safety Manual and Applications
Diagnostic Application for D5294S - SIL 2 for Modbus Output with RS485 connection
Description:
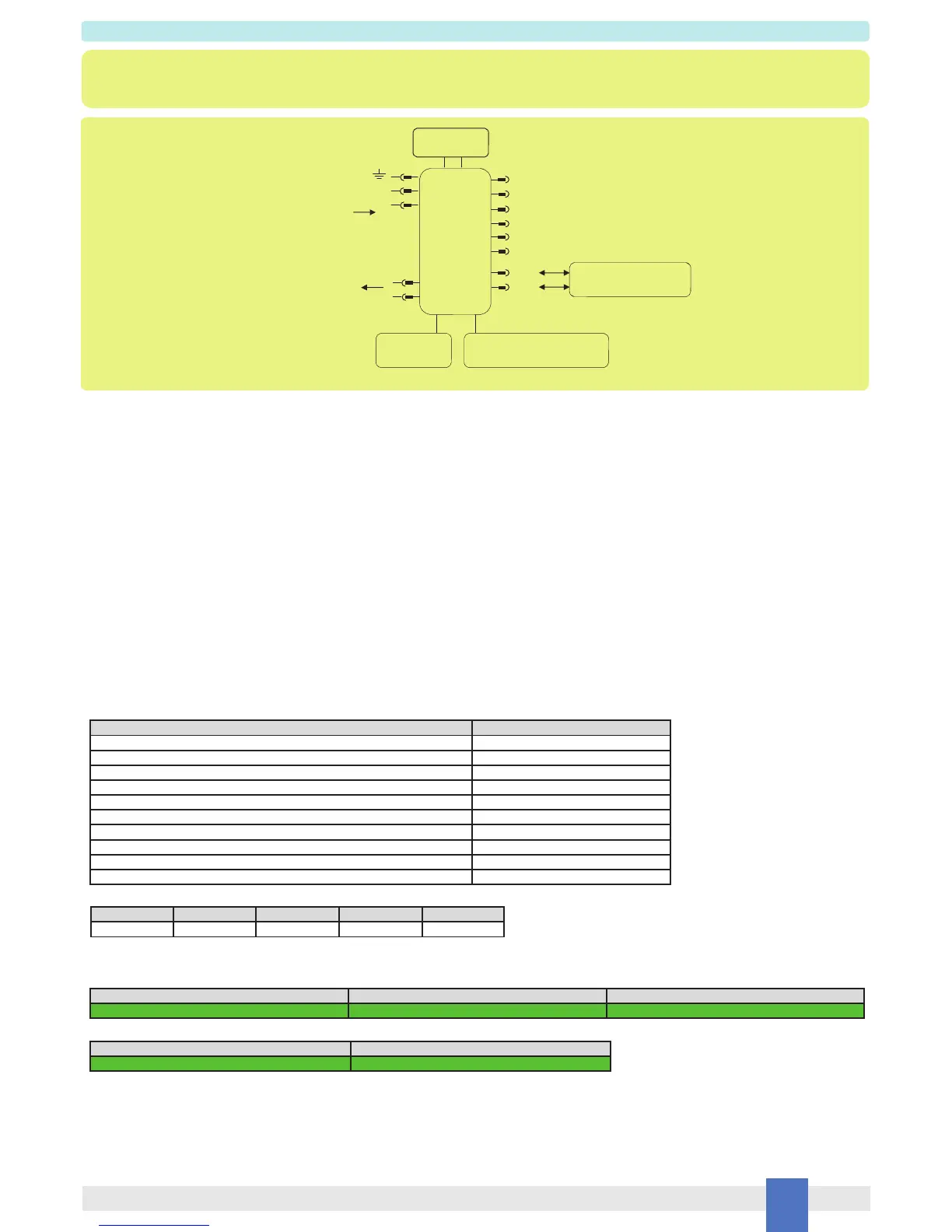
In this application D5294S module monitors Load Power DC/AC line (Pins 15-16) and Out NE or F&G/ND Load (Pins 13-14) by internal diagnostic circuits and uses Modbus protocol
with RS485 connection to signal presence of faults on them. At pages 11-12 it’s shown how to configure and to monitor the diagnostic operation parameters (as fault conditions),
by means of Modbus IN/OUT protocol with RS485 connection (Pins 5-6) or by PPC5092 adapter and SWC5090 related software. When diagnostic supply is connected
to Pins 9(+) - 10(-), the power green led is ON. NE or F&G/ND load connected on Pins 13-14 is controlled by input signal Pins 1-2 from PLC/DCS.
As shown in the diagram, Modbus RS485 is available on Pins 5-6 or on Power Bus connector or on Termination Boards connector. At pages 11-12 it’s described how modbus pa-
rameters change theirs status when internal diagnostic circuits detect presence of faults on Load Power DC/AC line or Out NE or F&G/ND Load.
Safety Function and Failure behavior:
D5294S is considered to be operating in Low Demand mode, as a Type B module, having Hardware Fault Tolerance (HFT) = 0.
The failure behaviour is described by the following definitions:
Fail-Safe State: it is defined as the ModBus communication being shut down OR any analog measure value (expressed in ModBus parameters) going to Fail High or Fail Low;
Fail Safe: this failure causes the system to go to the defined Fail-Safe state without a process demand;
Fail Dangerous: failure mode that does not respond to a demand from the process (i.e. being unable to go to the defined Fail-Safe state), so that any analog measure expressed
in ModBus parameters) is deviated by more than ± 20% of the correct value;
Fail High: it is defined as a failure that causes any analog measure (expressed in ModBus parameters) to go above its maximum allowed value (which can be set by the user);
Fail Low: it is defined as a failure that causes any analog measure (expressed in ModBus parameters) to go below its minimum allowed value (which can be set by the user).
Fail “No Effect”: failure mode of a component that plays a part in implementing the safety function but that is neither a safe failure nor a dangerous failure; in particular,
analog measure (expressed in ModBus parameters) is deviated by less than ± 20% of the correct value. When calculating the SFF, this failure mode is not taken into account;
Fail “Not part”: failure mode of a component which is not part of the Safety function but part of the circuit diagram and is listed for completeness. When calculating the SFF,
this failure mode is not taken into account. The input and relay blocks failures are classified as “Not Part” failures.
As the module is supposed to be proven-in-use device, therefore according to the requirements of IEC 61511-1 section 11.4.4, a HFT = 0 is sufficient for SIL 2 (sub-) systems includ-
ing Type B components and having a SFF equal or more than 60%.
Failure rate date: taken from Siemens Standard SN29500.
Failure rate table:
Failure rates table according to IEC 61508:2010 Ed.2 :
This type “B” system has SFF = 73.82% 60% and HFT = 0, which is sufficient to get SIL 2 in accordance with the requirements of IEC 61511-1 section 11.4.4 during
a proven-in-use assessment.
PFDavg vs T[Proof] table (assuming Proof Test coverage of 99%), with determination of SIL supposing module contributes 10% of total SIF dangerous failures:
PFDavg vs T[Proof] table (assuming Proof Test coverage of 99%), with determination of SIL supposing module contributes >10% of total SIF dangerous failures:
Failure category Failure rates (FIT)
dd
= Total Dangerous Detected failures 127.75
du
= Total Dangerous Undetected failures 87.46
sd
= Total Safe Detected failures 0.00
su
= Total Safe Undetected failures 118.83
λ
tot safe
= Total Failure Rate (Safety Function) = λ
dd
+ λ
du
+ λ
sd
+ λ
su
334.04
MTBF (safety function, single channel) = (1 / λ
tot safe
) + MTTR (8 hours) 341 years
no effect
= “No effect” failures 212.65
not part
= “Not Part” failures 681.50
λ
tot device
= Total Failure Rate (Device) = λ
tot safe
+ λ
no effect
+ λ
not part
1228.20
MTBF (device, single channel) = (1 / λ
tot device
) + MTTR (8 hours) 92 years
T[Proof] = 1 year T[Proof] = 2 years T[Proof] = 20 years
PFDavg = 3.85 E-04 - Valid for SIL 2 PFDavg = 7.70 E-04 - Valid for SIL 2 PFDavg = 7.70 E-03 - Valid for SIL 1
T[Proof] = 10 years
PFDavg = 3.85 E-03 - Valid for SIL 2
T[Proof] = 20 years
PFDavg = 7.70 E-03 - Valid for SIL 1
Termination Board Connector
Modbus RS485
Power Bus
Modbus RS485
MODBUS
IN/OUT RS485
5
A-
B+
D5294S
9 +
10 -
Diagnostic Supply
24 Vdc
1
2
6
14
13
11
12
3
4
Fault Out 2
Fault Out 1
Input signal from PLC/DCS
16
15
Load Power
DC/AC
21
Out NE or
F&G/ND Load
λ
sd
λ
su
λ
dd
λ
du
SFF
0.00 FIT 118.83 FIT 125.75 FIT 87.46 FIT 73.82%

 Loading...
Loading...