4. Installation
42 PNEG-2381 2000 Series U-Trough Bin Sweep Auger Unload System (72' - 78')
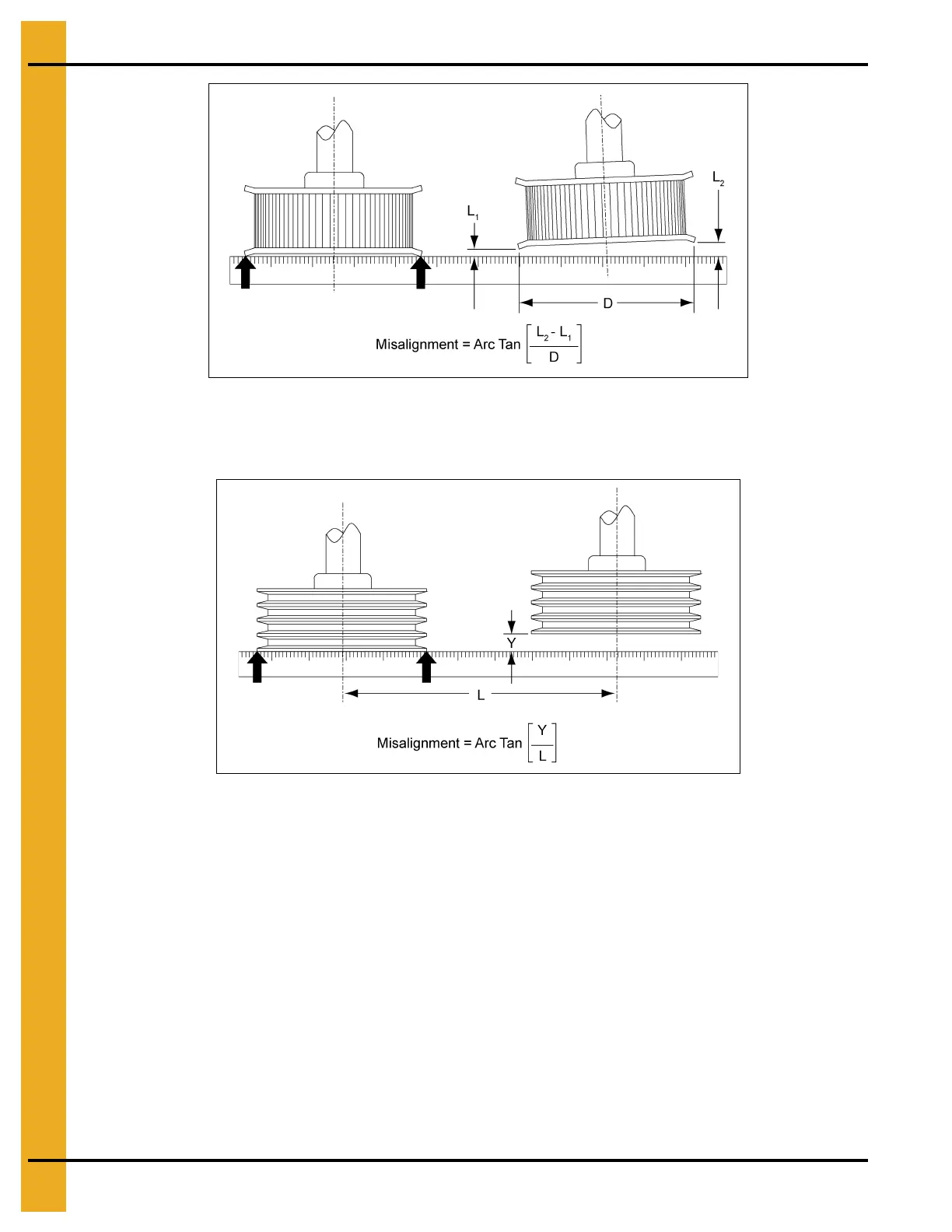
Figure 4BJ
The angle of parallel misalignment can be quantified as the difference in clearance between the
straightedge and the outer surfaces of the two sheaves or sprockets across the separation distance.
Figure 4BK
The total allowable misalignment recommended for V-belts, in general, is 1/2°. While individual V-belts are
known to be capable of handling greater amounts of misalignment before becoming unstable, maintaining
the misalignment to within 1/2° will maximize belt life.
The total amount of misalignment recommended for synchronous, urethane 60° belts (Polyflex), and
poly-V belts (Micro-V) is 1/4°. These drives are less tolerant of misalignment than conventional
V-belt drives, and must be aligned more accurately.
When determining if a V-type drive system is aligned within these recommendations, the angular and
parallel misalignment must both be measured and quantified individually, and then added together.
The total sum of angular and parallel misalignment can then be compared to the belt manufacturer’s
recommendations for the particular type of drive.
The sprockets for synchronous belts are made with face widths greater than the belt width to prevent belt
fit problems from tolerance accumulations. This additional sprocket face width allows the belt to free float
across the sprocket faces.

 Loading...
Loading...



