28
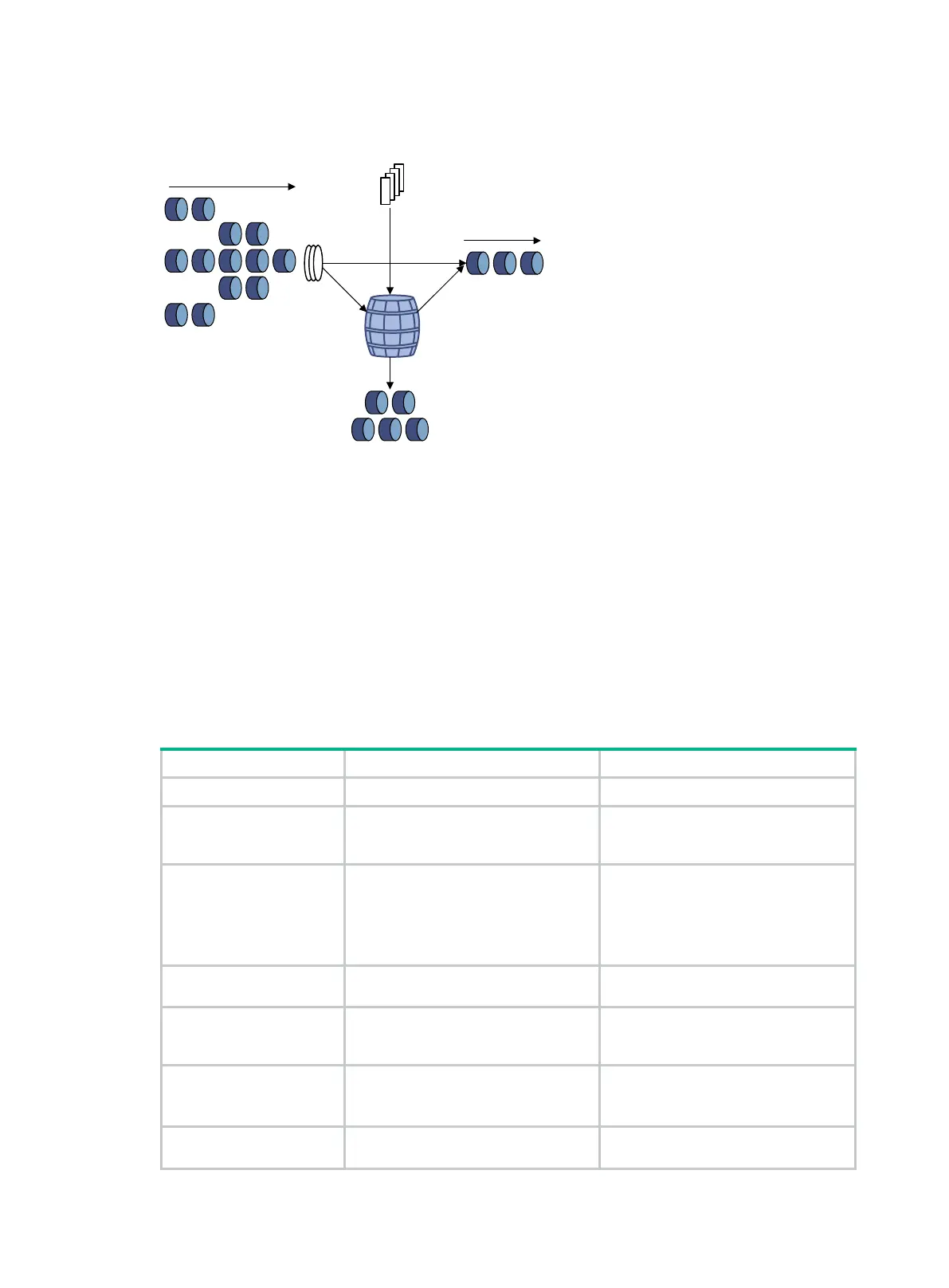
Figure 6 Traffic policing
Traffic policing is widely used in policing traffic entering the ISP networks. It can classify the policed
traffic and take predefined policing actions on each packet depending on the evaluation result:
• Forwarding the packet if the evaluation result is "conforming."
• Dropping the packet if the evaluation result is "excess."
Configuration procedure
You can configure traffic policing for an interface only by using the MQC approach. You can configure
traffic policing for a user profile by using the MQC approach or non-MQC approach.
Configuring traffic policing by using the MQC approach
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Create a traffic class
and enter traffic class
view.
traffic classifier
classifier-name
[
operator
{
and
|
or
} ]
By default, no traffic class exists.
3. Configure match
criteria.
if-match
[
not
]
match-criteria
By default, no match criterion is
configured.
For more information about the
if-match
command, see ACL and
QoS Command Reference.
4. Return to system
view.
quit
N/A
5. Create a traffic
behavior and enter
traffic behavior view.
traffic behavior
behavior-name
By default, no traffic behavior exists.
6. Configure a traffic
policing action.
car cir
committed-information-rate
[
cbs
committed-burst-size ] [
green
action |
red
action |
yellow
action ] *
By default, no traffic policing action is
configured.
7. Return to system
view.
quit
N/A
Token
bucket
Drop
Classify
Packets to be sent
out this interface
Packets sent
Put tokens into the bucket at
the set rate

 Loading...
Loading...