148
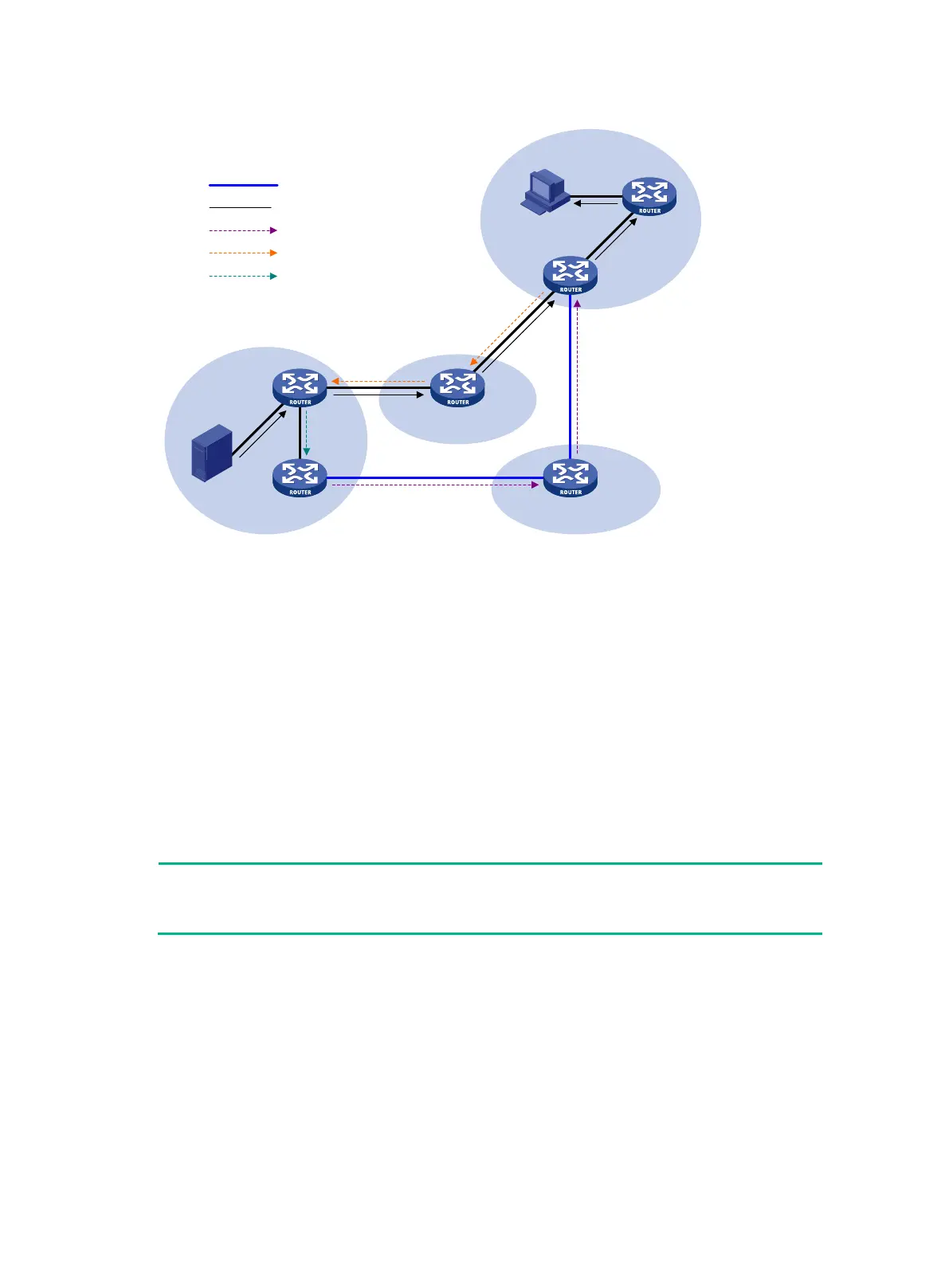
Figure 50 Inter-domain multicast delivery through MSDP
The process of implementing PIM-SM inter-domain multicast delivery by leveraging MSDP peers is
as follows:
1. When the multicast source in PIM-SM 1 sends the first multicast packet to multicast group G,
DR 1 encapsulates the data within a register message. It sends the register message to RP 1,
and RP 1 obtains information about the multicast source.
2. As the source-side RP, RP 1 creates SA messages and periodically sends them to its MSDP
peer.
An SA message contains the address of the multicast source (S), the multicast group address
(G), and the address of the RP that has created this SA message (RP 1, in this example).
3. On MSDP peers, each SA message undergoes an RPF check and multicast policy-based
filtering. Only SA messages that have arrived along the correct path and passed the filtering are
received and forwarded. This avoids delivery loops of SA messages. In addition, you can
configure MSDP peers into an MSDP mesh group to avoid SA message flooding between
MSDP peers.
NOTE:
An MSDP mesh group refers to a group of MSDP peers that establish MSDP peering
relationships with each other and share the same group name.
4. SA messages are forwarded from one MSDP peer to another. Finally, information about the
multicast source traverses all PIM-SM domains with MSDP peers (PIM-SM 2 and PIM-SM 3, in
this example).
5. After receiving the SA message that RP 1 created, RP 2 in PIM-SM 2 examines whether any
receivers for the multicast group exist in the domain.
If a receiver exists in the domain, the RPT for the multicast group G is maintained between
RP 2 and the receivers. RP 2 creates an (S, G) entry and sends an (S, G) join message. The
join message travels hop by hop toward the multicast source, and the SPT is established
across the PIM-SM domains.
The subsequent multicast data flows to RP 2 along the SPT, and from RP 2 to the
receiver-side DR along the RPT. After receiving the multicast data, the receiver-side DR
RP 1
DR 1
Source
PIM-SM 1
PIM-SM 3
PIM-SM 2
PIM-SM 4
RP 3
RP 2
DR 2
MSDP peers
SA message
Join message
Multicast packets
Register message
Receiver

 Loading...
Loading...