150
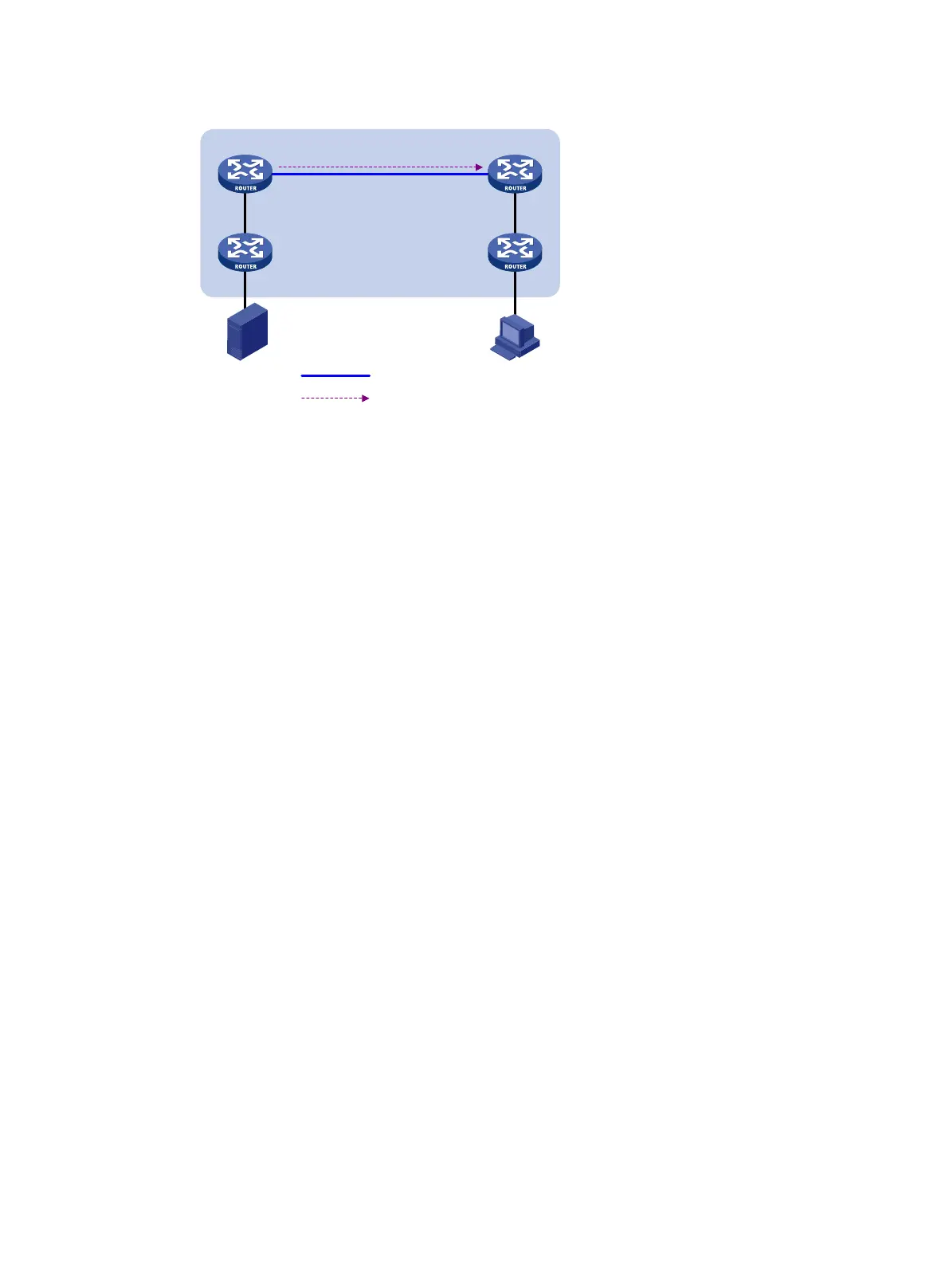
Figure 51 Anycast RP through MSDP
The following describes how Anycast RP through MSDP is implemented:
a. After receiving the multicast data from Source, the source-side DR registers with the closest
RP (RP 1 in this example).
b. After receiving the IGMP report message from the receiver, the receiver-side DR sends a
join message toward the closest RP (RP 2 in this example). An RPT rooted at this RP is
established.
c. The RPs share the registered multicast source information through SA messages. After
obtaining the multicast source information, RP 2 sends an (S, G) source-specific join
message toward the source to create an SPT.
d. When the multicast data reaches RP 2 along the SPT, the RP forwards the data along the
RPT to the receiver. After receiving the multicast data, the receiver-side DR determines
whether to initiate an RPT-to-SPT switchover process based on its configuration.
MSDP peer-RPF forwarding
The MSDP peer-RPF check is used for forwarding SA messages on a network that runs MSDP. If the
peer-RPF check succeeds, the SA message is accepted and forwarded. Otherwise, the SA message
is discarded.
As shown in Figure 52:
There are five ASs on the network. IGP runs within each AS, and BGP or MBGP runs between
these ASs.
Each AS contains a minimum of one PIM-SM domain, and each PIM-SM domain contains a
minimum of one RP.
MSDP peering relationship has been established among these RPs.
RP 3, RP 4, and RP 5 are in the same MSDP mesh group.
RP 6 is configured as the static RPF peer of RP 7.
SA message
Source Receiver
Router A
Router B
RP 1 RP 2
PIM-SM
MSDP peers
DR DR

 Loading...
Loading...