Sensor Integration and Material Calibration Chapter 3
Configuration and Calibration Guide HD0679 Rev 1.2.0 35
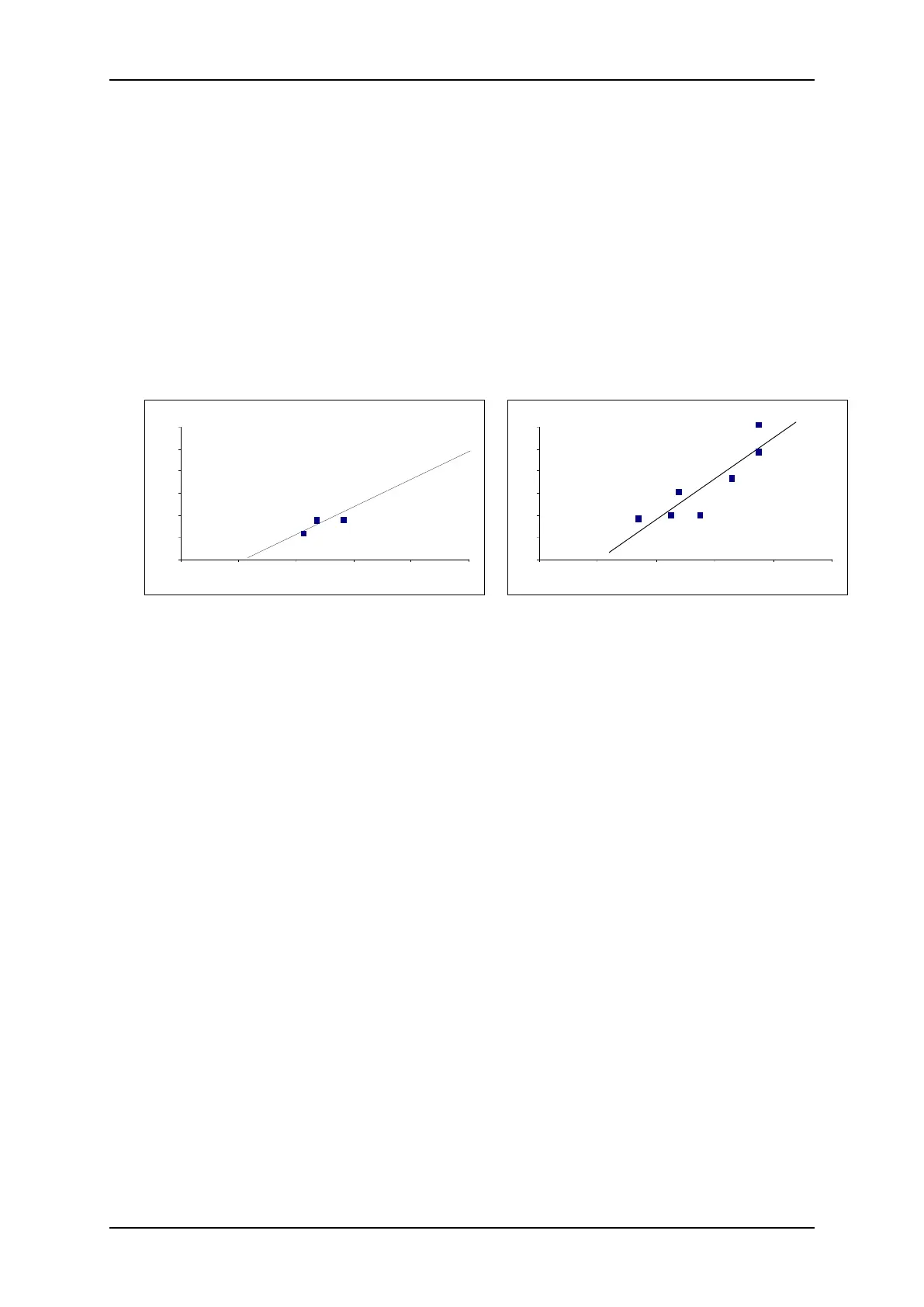
Poor Moisture Calibration Data
Poor Moisture Calibration Data
6.1 Calibration Inaccuracy is Likely to Result If:
• Too small a sample of material is used for measuring the moisture content.
• A very small number of calibration points are used (in particular 1 or 2 points).
• The sub-sample tested is not representative of the bulk sample.
• Samples are taken close to the same moisture content (Figure 19, left). A good range
is necessary.
• There is a large scatter in the readings as shown in the calibration graph Figure 19
(right). This generally implies an unreliable or inconsistent approach to taking
samples for oven drying or poor sensor positioning with inadequate material flow over
the sensor.
• If the averaging facility is not used to ensure representative moisture reading for the
entire batch.
Figure 19 - Examples of Poor Material Calibration Points
7 Quadratic Calibration
Hydronix Microwave Moisture sensors are able to utilise a quadratic calibration function for use in
the rare occasions where a material is non-linear. For quadratic calibrations, where the
calibration points do not form a straight line the ‘A’ coefficient is utilised and a best fit curve is
generated (Figure 20). The equation used is show below:
Moisture % = A x (Unscaled value)² + B (Unscaled value) + C – D
The same procedure is used for linear calibrations (see Page 32) and should be followed to
collect samples and to determine the moisture % or the material.
Full details of the calibration process are contained in the Hydro-Com User Guide HD0682.
7.1 Good/Bad Quadratic Calibrations
A good calibration is made when the calibration samples are taken over the working range of
the material. As many points as possible should be taken to provide higher accuracy.
Figure 20 is an example of a good calibration. All of the points are close to the curve and
there is a good spread in the points covering the full moisture range of the material
 Loading...
Loading...