Chapter 7. Java 133
7.5 Application scaling
Large workloads using many threads on multi-CPU machines face extra challenges regarding
concurrency and scaling. In such cases, steps can be taken to decrease contention on
shared resources and reduce the processing impact.
7.5.1 Choosing the correct SMT mode
AIX and Linux represent each SMT thread as a logical CPU. Therefore, the number of logical
CPUs in an LPAR depends on the SMT mode. For example, an LPAR with four virtual
processors that are running in SMT4 mode has 16 logical CPUs; an LPAR with that same
number of virtual processors that are running in SMT2 mode has only eight logical CPUs.
Table 7-2 shows the number of SMT threads and logical CPUs available in ST, SMT2, and
SMT4 modes.
Table 7-2 ST, SMT2, and SMT4 modes - SMT threads and CPUs available
The default SMT mode on POWER7 depends on the AIX version and the compatibility mode
the processor cores are running with. Table 7-3 shows the default SMT modes.
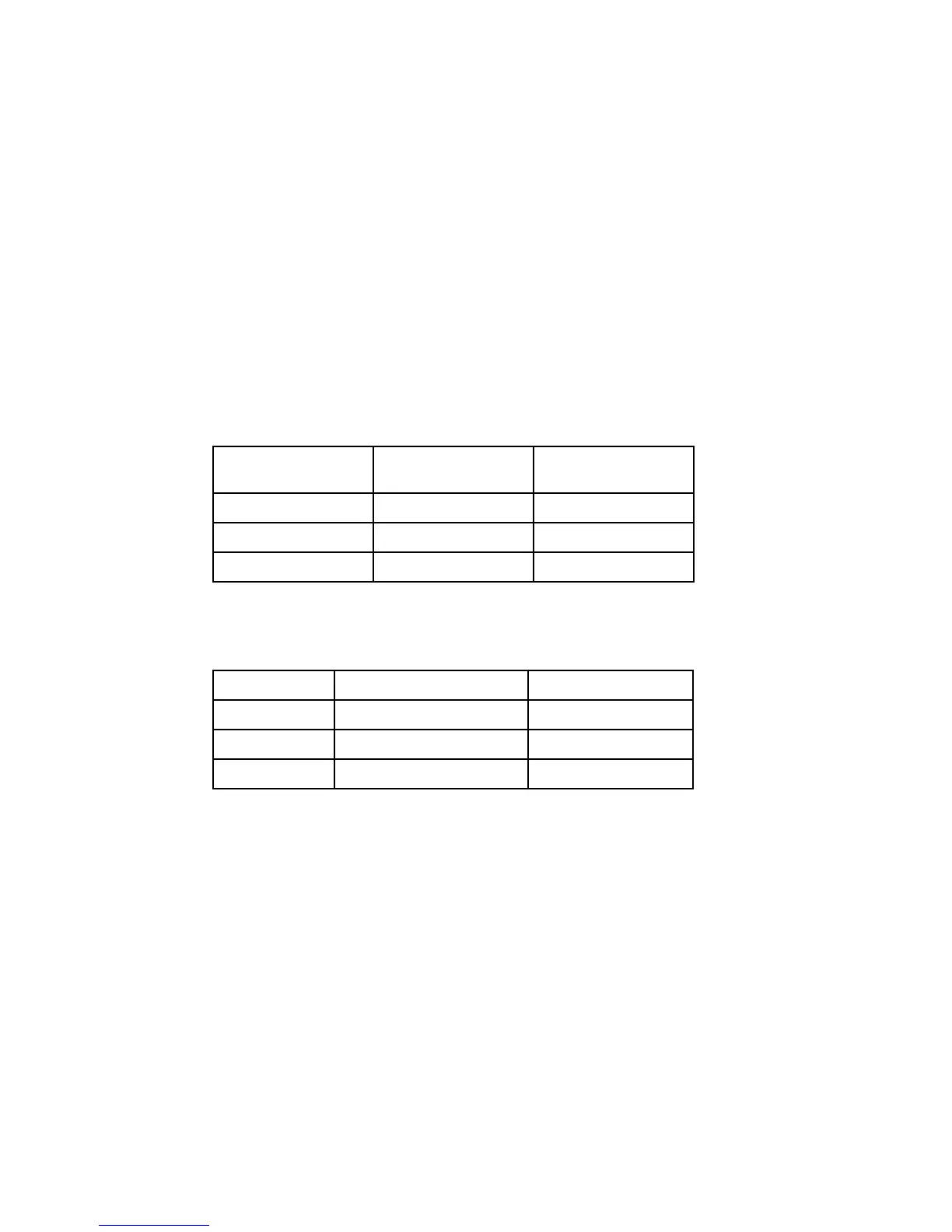
Table 7-3 SMT mode on POWER7 is dependent upon AIX and compatibility mode
Most applications benefit from SMT. However, some applications do not scale with an
increased number of logical CPUs on an SMT-enabled system. One way to address such an
application scalability issue is to make a smaller LPAR, or use processor binding, as
described in 7.5.2, “Using resource sets” on page 133. For applications that might benefit
from a lower SMT mode with fewer logical CPUs, experiment with using SMT2 or ST modes
(see “Hybrid thread and core ” on page 79 and “Selecting different SMT modes” on
page 105).
7.5.2 Using resource sets
Resource sets (RSETS) allow specifying which logical CPUs an application can run on. They
are useful when an application that does not scale beyond a certain number of logical CPUs
is run on a large LPAR. For example, an application that scales up to eight logical CPUs but is
run on an LPAR that has 64 logical CPUs.
SMT mode Number of SMT
threads
Number of logical
CPUs
ST 1 1
SMT2 2 2
SMT4 4 4
AIX version Compatibility mode Default SMT mode
AIX V6.1 POWER7 SMT4
AIX V6.1 POWER6/POWER6+ SMT2
AIX 5L V5.3 POWER6/POWER6+ SMT2

 Loading...
Loading...











