68 POWER7 and POWER7+ Optimization and Tuning Guide
4.1 AIX and system libraries
Here we present information about AIX and system libraries.
4.1.1 AIX operating system-specific optimizations
This section describes optimization methods specific to AIX.
Malloc
Every application needs a fast, scalable, and memory efficient allocator. However, each
application’s memory request patterns are different. It is difficult to provide one common
allocator or tunable that can satisfy the needs of all applications. AIX provides different
memory allocators and suboptions within the allocator, so that a system administrator or
developer can choose more suitable settings for their application. This chapter explains the
available choices and when to choose them.
Memory allocators
AIX provides three different allocators, and each of them uses a different memory
management algorithm and data structures. These allocators work independently, so the
application developer must choose one of them by exporting the MALLOCTYPE
environment variable. The allocators are:
Default allocator
The default allocator is selected when the MALLOCTYPE environment variable is unset. This
setting maintains a consistent performance, even in a worst case scenario, but might not
be as memory efficient as a Watson allocator. This allocator is ideal for 32-bit applications,
which do not make frequent calls to malloc().
Watson allocator
This allocator is selected when MALLOCTYPE=watson is set. This allocator is designed for
64-bit applications. It is memory efficient, scalable, and provides good performance. This
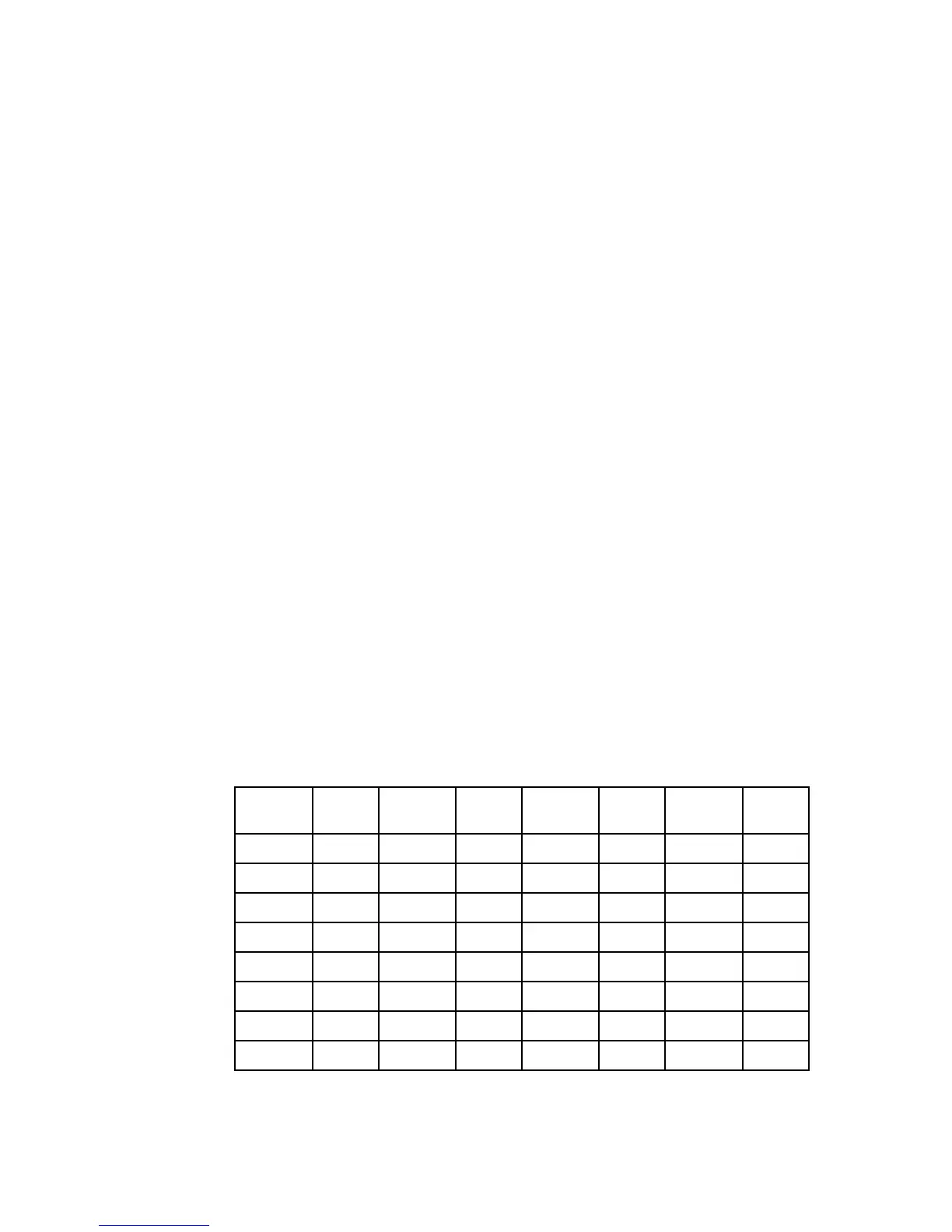
allocator has a built-in bucket component for allocation requests up to 512 bytes. Table 4-1
provides the mapping for the allocation requests to bucket size.
Table 4-1 Mapping for allocation requests to bucket size
This allocator is ideal for 64-bit memory-intensive applications.
Request
size
Bucket
size
Request
size
Bucket
size
Request
size
Bucket
size
Request
size
Bucket
size
1 - 4 33-40 40 129-144 144 257-288 288
5 - 8 41 - 48 48 145 - 160 160 289 - 320 320
9 - 12 12 49 - 56 56 161 - 176 176 321 - 352 352
13 - 16 16 57 - 64 64 177 - 192 192 353 - 384 384
17 - 20 20 65 - 80 80 193 - 208 208 385 - 416 416
21 - 24 24 81 - 96 96 209 - 224 224 417 - 448 448
25 - 28 28 97 - 112 112 224 - 240 240 449 - 480 480
29 - 32 32 113 - 128 128 241 - 256 256 481 - 512 512

 Loading...
Loading...











