3 - 5
Section F
Transmission
9803/6400
Section F
3 - 5
Issue 1
Motor/Gearbox
Operation (continued)
Counterbalance Valve (continued)
Brake Function
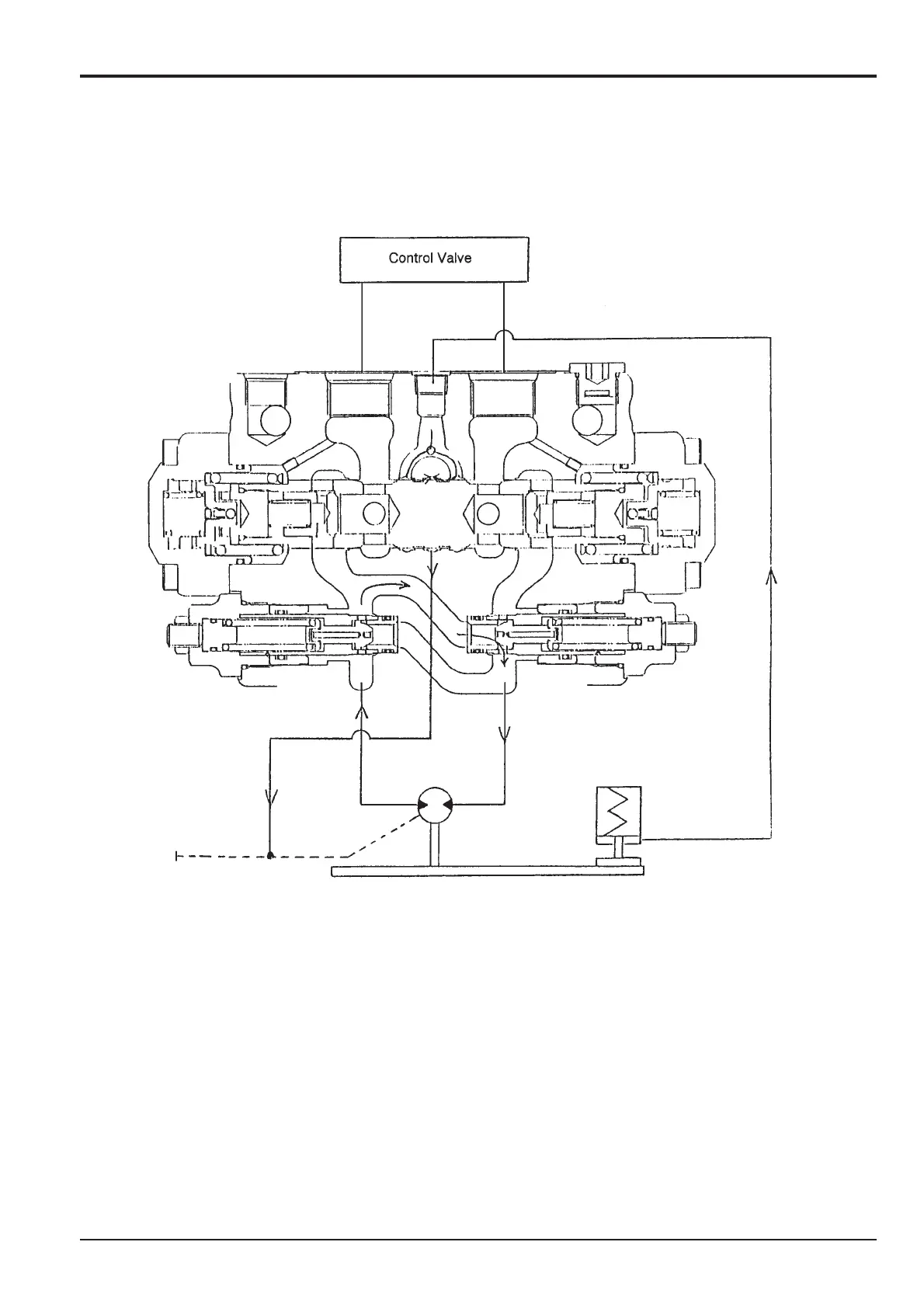
Fig. 4 Counterbalance Valve (Brake)
When the control valve is returned to neutral, the pressurised oil from the pump is blocked, and pressure at P1 and P2 become
equal, and the plunger tries to return to neutral position by the spring. When the plunger moves, the plunger opening becomes
smaller and because the piston motor continues to rotate due to inertia (motor pumping function), the pressure at M2 port side
rises and braking occurs. At this time, when the M2 port side pressure reaches the relief valve set pressure, the relief valve
works and allows oil to escape to M1 port side, absorbing shock pressure caused by inertia of M2 port side while also
preventing M1 port side cavitation.
P
2
P
1
M
2
M
1

 Loading...
Loading...