Security Zones and Interfaces 7
Chapter 1: Configuring
There are three predefined security zones for interfaces operating at the Network
Layer (Layer 3) in the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model and three
predefined security zones for interfaces operating at the Data Link Layer (Layer 2):
Predefined Layer 3 security zones: Untrust, Trust, and DMZ
Predefined Layer 2 security zones: V1-Untrust, V1-Trust, and V1-DMZ
The example in this guide uses the three predefined Layer 3 security zones.
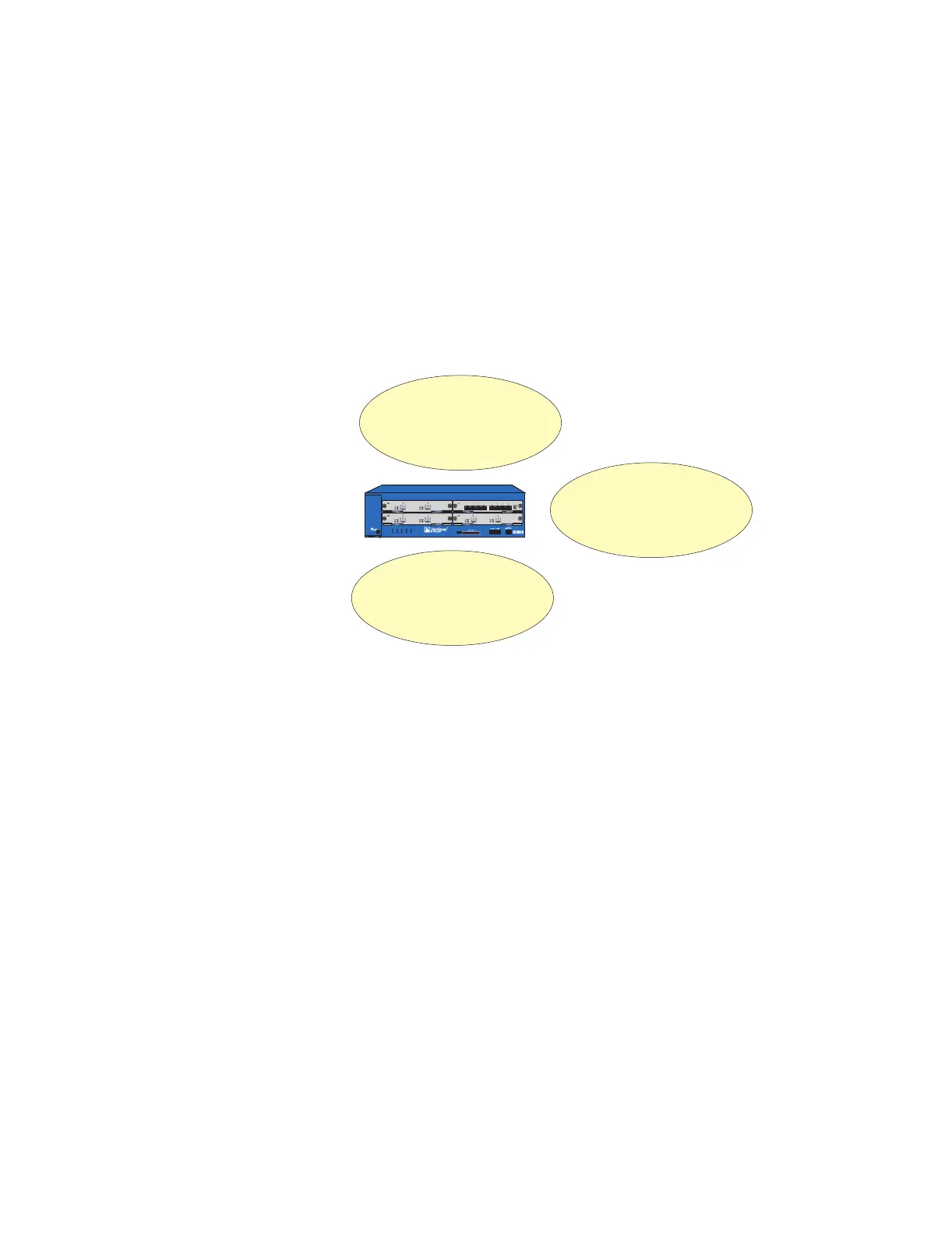
Figure 7: Untrust, DMZ, and Untrust Security Zones
You can define more security zones by using the following command:
set zone name zone [ l2 id_num ]
For information on creating zones, see the chapter on zones in the Fundamentals
volume in the NetScreen Concepts & Examples ScreenOS Reference Guide.
HA
FLASH
PWR
FAN
ALARM
MOD1
TEMP
MOD2
STATUS
MOD3
ISG 2000
Untrust Zone
DMZ Zone
Trust Zone
Note: This illustration shows the typical uses of each zone. However, this arrangement is
not compulsory. You can customize their uses to best suit your network environment.
This zone typically contains the public
network that the NetScreen-ISG 2000
protects against.
This zone typically contains
your public-facing resources,
such as web servers.
This zone typically contains your
protected internal resources.
 Loading...
Loading...