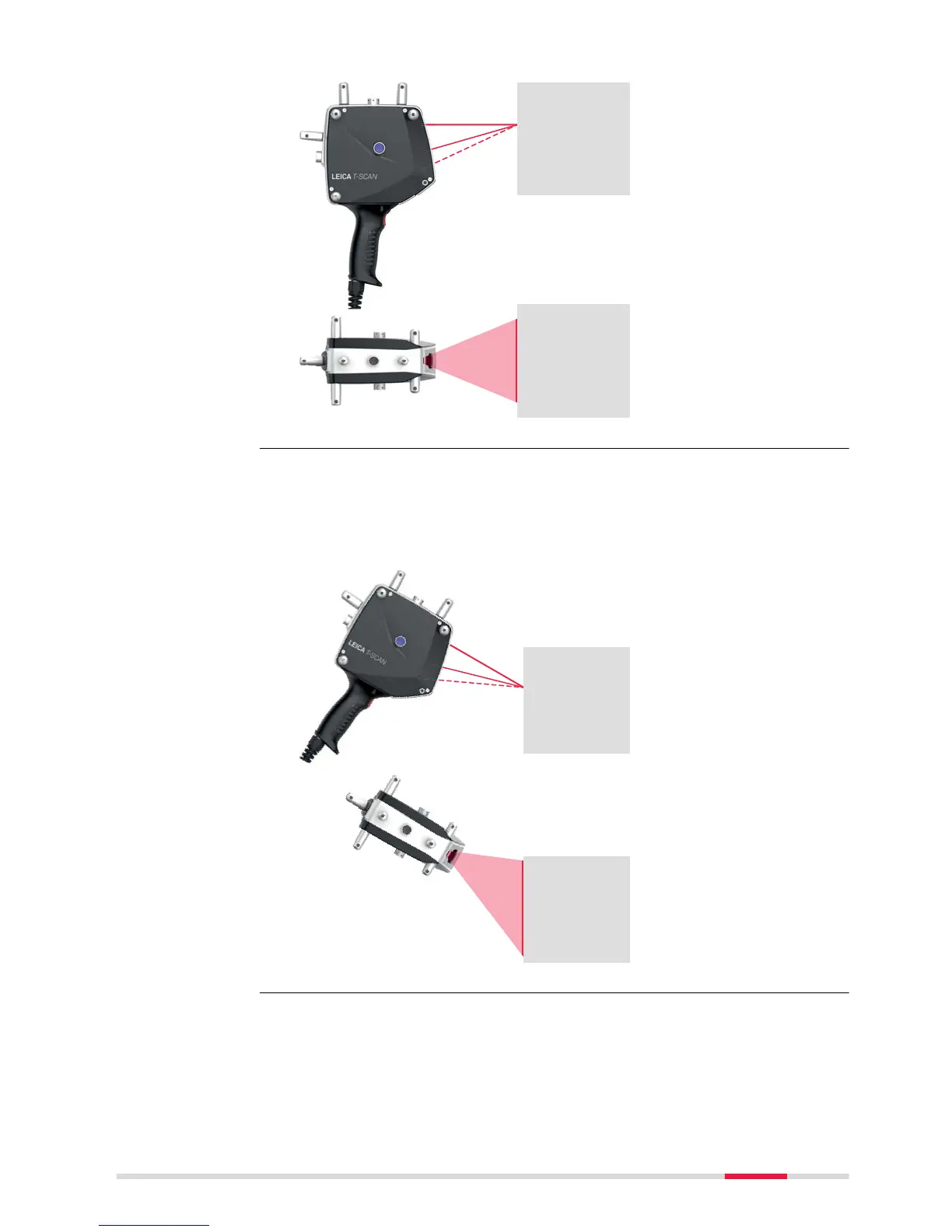
If the T
‑Scan sensor is used in an unfavourable orientation, some parts of the
scan line could exceed the working range of the sensor. In this case, the
measurement data may not be captured completely.
Example for unfavourable orientations of the T‑Scan sensor:
Certain shapes of the measuring object, for example edges, can cause an
interruption of the reflected laser beam. Before and after such an obstruction,
the measurement accuracy might be reduced because only a part of the
reflected light reaches the receiver optics.
To avoid the effect of obstruction, rotate the T‑Scan sensor in the appropriate
direction.
Unfavourable ori-
entations of the
T‑Scan sensor
Obstruction of the
laser beam
Operation 27

 Loading...
Loading...