Page 18
FIGURE 18
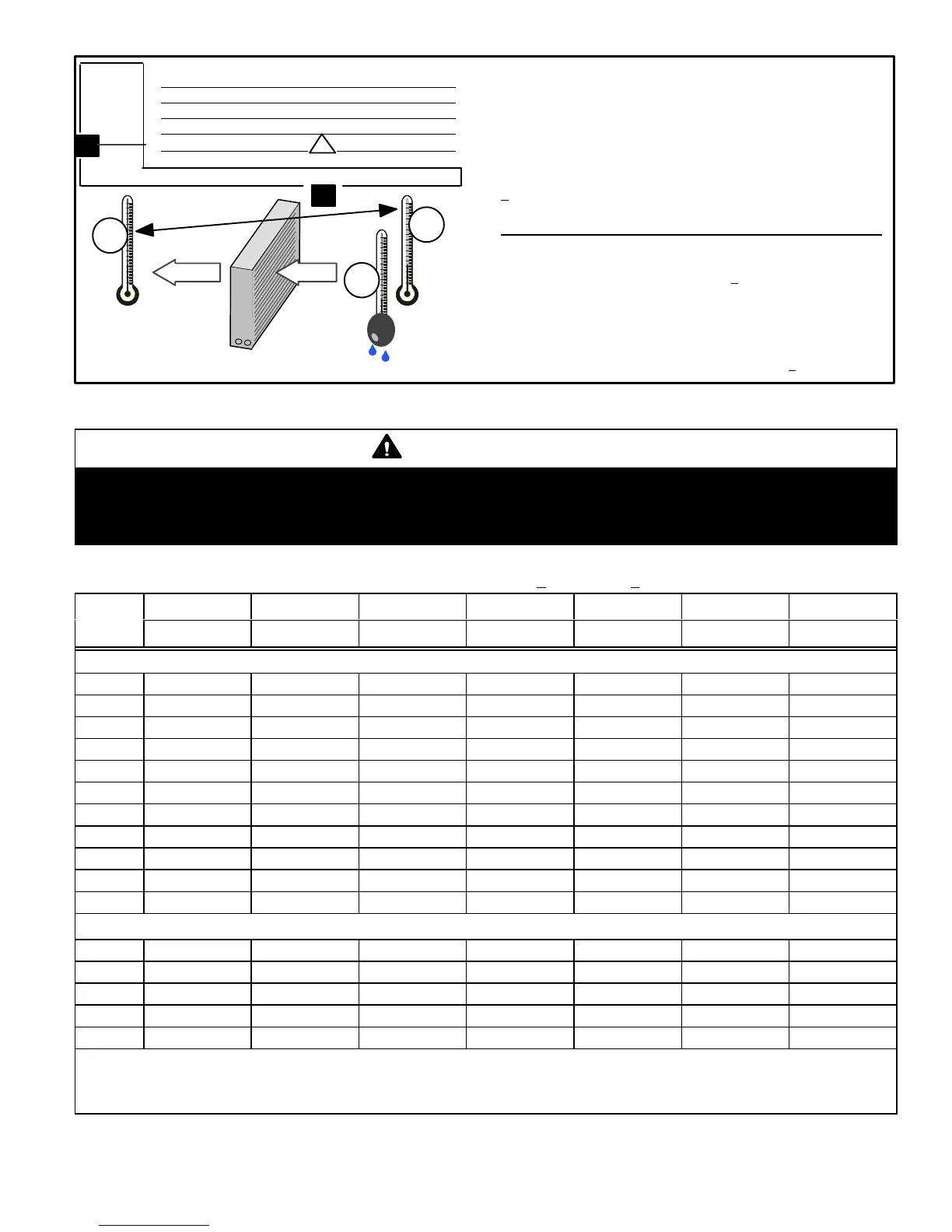
Step 1. Determine the desired DTMeasure entering air tempera-
ture using dry bulb (A) and wet bulb (B). DT is the intersecting value
of A and B in the table (see triangle).
Step 2. Find temperature drop across coilMeasure the coil’s dry
bulb entering and leaving air temperatures (A and C). Temperature
Drop Formula: (T
Drop
) = A minus C.
Step 3. Determine if fan needs adjustmentIf the difference be-
tween the measured T
Drop
and the desired DT (T
Drop
–DT) is within
+
3º, no adjustment is needed. See examples: Assume DT = 15 and
A temp. = 72º, these C temperatures would necessitate stated ac-
tions:
Cº T
Drop
– DT = ºF ACTION
53º 19 – 15 = 4 Increase the airflow
58º 14 – 15 = −1 (within +
3º range) no change
62º 10 – 15 = −5 Decrease the airflow
Step 4. Adjust the fan speedSee indoor unit instructions to in-
crease/decrease fan speed.
Changing air flow affects all temperatures; recheck temperatures to
confirm that the temperature drop and DT are within +
3º.
DT
80 24 24 24 23 23 22 22 22 20 19 18 17 16 15
78 23 23 23 22 22 21 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14
76 22 22 22 21 21 20 19 19 18 17 16 15 14 13
74 21 21 21 20 19 19 18 17 16 16 15 14 13 12
72 20 20 19 18 17 17 16 15 15 14 13 12 11 10
70 19 19 18 18 17 17 16 15 15 14 13 12 11 10
57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70
Temp.
of air
entering
indoor
coil ºF
INDOOR
COIL
DRY BULBDRY
BULB
WET
BULB
B
T
Drop
19º
A
Dry−bulb
Wet−bulb ºF
A
72º
B
64º
C
53º
air flowair flow
All temperatures are
expressed in ºF
C − Pre− Charge Maintenance Checks
IMPORTANT
Use table 5 as a general guide when performing maintenance checks. This is not a procedure for charging the
unit (Refer to Charging / Checking Charge section). Minor variations in these pressures may be expected due
to differences in installations. Significant differences could mean that the system is not properly charged or that
a problem exists with some component in the system.
Table 5
Normal Operating Pressures − Liquid +
10 & Vapor +5 PSIG*
14HPX−018 14HPX−024 14HPX−030 14HPX−036 14HPX−042 14HPX−048 14HPX−060
5F (5C)**
Liquid / Vapor Liquid / Vapor Liquid / Vapor Liquid/ Vapor Liquid / Vapor Liquid / Vapor Liquid / Vapor
Cooling
65 (18) 226 / 140 233 / 137 238 / 138 220 / 138 223 / 125 231 / 136 243 / 136
70 (21) 244 / 141 252 / 138 263 / 139 236 / 140 241 / 130 248 / 139 263 / 137
75 (24) 263 / 142 271 / 140 279 / 139 256 / 141 261 / 134 271 / 140 282 / 138
80 (27) 283 / 143 292 / 141 299 / 140 276 / 142 282 / 138 291 / 142 306 / 139
85 (29) 302 / 144 314 / 142 324 / 141 298 / 143 302 / 139 312 / 143 327 / 140
90 (32) 328 / 145 338 / 143 340 / 142 321 / 144 326 / 140 335 / 144 351 / 141
95 (35) 351 / 146 361 / 145 375 / 145 344 / 144 349 / 141 359 / 145 376 / 142
100 (38) 376 / 147 387 / 146 397 / 145 369 / 146 374 / 142 384 / 146 401 / 143
105 (41) 402 / 148 412 / 147 424 / 147 394 / 147 399 / 143 411 / 148 426 / 145
110 (38) 430 / 149 441 / 148 454 / 150 421 / 148 428 / 145 439 / 149 452 / 146
115 (45) 465 / 150 471 / 151 485 / 150 449 / 149 455 / 146 468 / 150 484 / 148
Heating
60 (15) 346 / 139 352 / 138 338 / 137 350 / 134 373 / 139 355 / 130 351 / 117
50 (10) 323 / 117 331 / 114 334 / 112 331 / 117 363 / 117 336 / 113 333 / 105
40 (4) 306 / 98 304 / 99 312 / 93 313 / 97 348 / 97 315 / 88 316 / 88
30 (−1) 278 / 84 299 / 80 302 / 74 298 / 83 336 / 74 296 / 72 308 / 70
20 (−7) 273 / 66 283 / 66 280 / 53 284 / 66 322 / 64 286 / 64 300 / 61
*IMPORTANTThese are most−popular−match−up pressures. Indoor match up and indoor load cause
pressures to vary.
**Temperature of the air entering the outside coil (outdoor ambient temperature).

 Loading...
Loading...











