Page 137
Static Pressure
Design
1. Introduction
Duct system losses are the irreversible transformation of mechanical energy into heat. The two types of losses are (1) friction
losses and (2) dynamic losses.
Friction losses are due to fluid viscosity and result from momentum exchange between molecules (in laminar flow) or between
individual particles of adjacent fluid layers moving at different velocities (in turbulent flow). Friction losses occur along the entire
duct length.
Dynamic losses result from flow disturbances caused by duct mounted equipment and fittings (e.g., entries, exits, elbows,
transitions, and junctions) that change the airflow path’s direction or area.
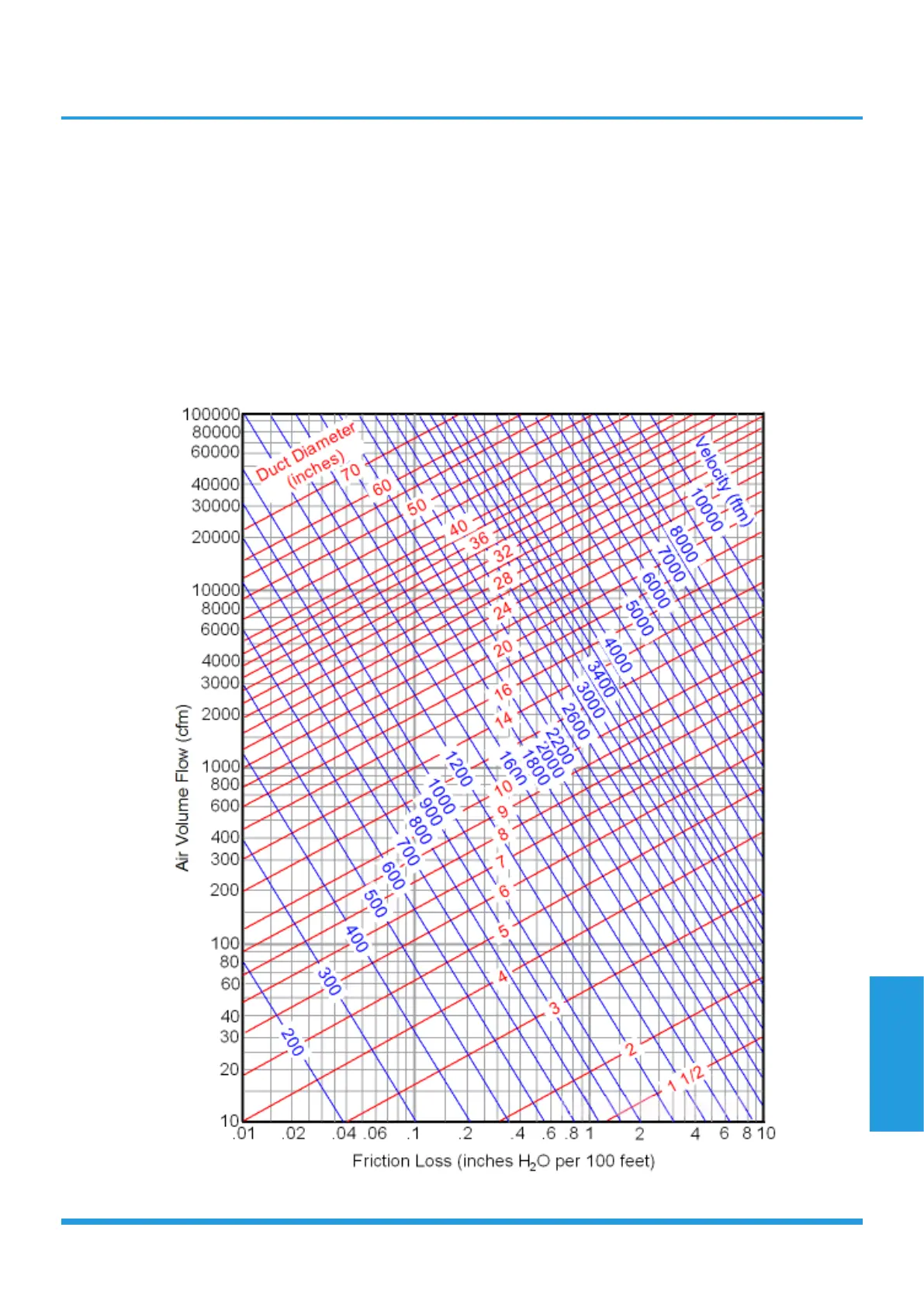
2. Charts For Friction Losses In Round Ducts
Fluid resistance caused by friction in round ducts can be determined by the friction chart. (based on galvanized sheet)

 Loading...
Loading...











