Number of output points per common terminal
• On FX3U-16M, one common terminal is used for 1 output point.
• On models other than FX3U-16M, 1 common terminal is used
for 4 or 8 output points.
3.5.2 Life of relay output contact
The product life of relay contacts considerably varies depending on
the load type used. Take care that loads generating reverse
electromotive force or rush current may cause poor contact or
deposition of contacts which may lead to considerable reduction of
the contact product life.
1) Inductive load
Inductive loads generate large reverse electromotive force
between contacts at shutdown which may cause arcing. At a
fixed current consumption, as the power factor (phase between
current and voltage) gets smaller, the arc energy gets larger.
The standard life of the contact used for Inductive loads, such as
contactors and solenoid valves, is 500 thousand operations at
20VA.
The following table shows the approximate life of the relay based
on the results of our operation life test.
Test condition: 1 sec. ON / 1 sec.OFF.
The product life of relay contacts becomes considerably shorter
than the above conditions when the rush overcurrent is shut
down.
→ For countermeasures while using inductive loads,
refer to Subsection 3.5.4.
Some types of inductive loads generate rush current 5 to 15 times
the stationary current at activation. Make sure that the rush
current does not exceed the current corresponding to the
maximum specified resistance load.
2) Lamp load
Lamp loads generally generate rush current 10 to 15 times the
stationary current. Make sure that the rush current does not
exceed the current corresponding to the maximum specified
resistance load.
3) Capacitive load
Capacitive loads can generate rush current 20 to 40 times the
stationary current. Make sure that the rush current does not
exceed the current corresponding to the maximum specified
resistance load. Capacitive loads such as capacitors may be
present in electronic circuit loads including inverters.
→ For the maximum specified resistance load,
refer to Subsection 3.5.1.
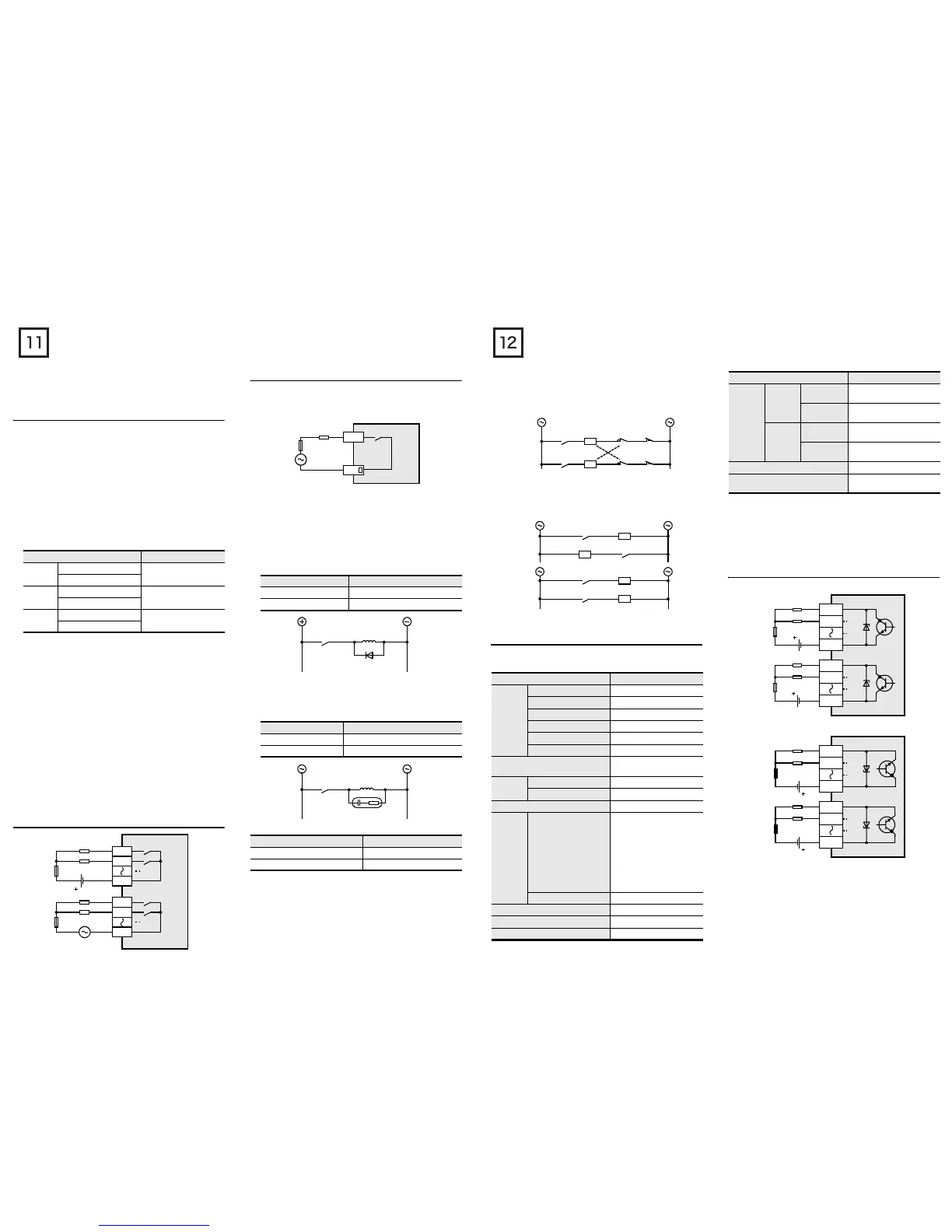
3.5.3 Example of relay output wiring
3.5.4 Cautions in external wiring
Protection circuit for load short-circuiting
When a load connected to the output terminal short-circuits, the
printed circuit board may be burnt out. Fit a protective fuse on the
output circuit.
Protection circuit of contact when inductive load is used
An internal protection circuit for the relays is not provided for the
relay output circuit in this product. It is recommended to use
inductive loads with built-in protection circuits. When using loads
without built-in protection circuits, insert an external contact
protection circuit, etc. to reduce noise and extend the product life.
1) DC circuit
Connect a diode in parallel with the load.
Use a diode (for commutation) having the following
specifications.
2) AC circuit
Connect the surge absorber (combined CR components such as
a surge killer and spark killer, etc.) parallel to the load.
Select the rated voltage of the surge absorber suitable to the
output used. Refer to the table below for other specifications.
Reference
Load capacity Contact life
20VA
0.2A/100V AC
3 million times
0.1A/200V AC
35VA
0.35A/100V AC
1 million times
0.17A/200V AC
80VA
0.8A/100V AC
2 hundred thousand times
0.4A/200V AC
PLC
24V DC
Fuse
Y000
100V AC
COM1
Y001
Load
Fuse
Y010
COM2
Y011
Load
Item Standard
Reverse voltage 5 to 10 times the load voltage
Forward current Load current or more
Item Standard
Electrostatic capacity Approx. 0.1µF
Resistance value Approx. 100 to 200Ω
Manufacturer Model name
Okaya Electric Industries Co., Ltd. CR-10201
Rubycon Corporation 250MCRA104100M B0325
PLC
100V AC
Load
Fuse
Y
COM
Inductive
load
PLC output
contact
Diode
(for commutation)
Surge absorber
PLC output
contact
Inductive
load
Interlock
Loads, such as contactors for normal and reverse rotations, that
must not be turned on simultaneously should have an interlock in the
PLC program and an external interlock as shown
below.
Common mode
Use output contacts (*) of the PLC in the common mode.
3.6 Transistor output specifications and example of
external wiring
→ Refer to FX3U Series User's Manual - Hardware
Edition.Transistor output specifications
*1 FX3U-128M does not have DC power supply.
*2 FX3U-16M terminal block cannot be installed/removed
Number of output points per common terminal
• On FX3U-16M, one common terminal is used for 1 output point.
• On models other than FX3U-16M, 1 common terminal is used
for 4 or 8 output points.
3.6.1 External Wiring of Transistor Output
1. External Wiring of Sink Output Type
2. External Wiring of Source Output Type
Item Specification
Number
of output
points
FX3U-16MT/ 8 points
FX3U-32MT/ 16 points
FX3U-48MT/ 24 points
FX3U-64MT/ 32 points
FX3U-80MT/ 40 points
FX3U-128MT/ES(S)
*1
64 points
Output connecting type
Removable terminal block
(M3 screw)
*2
Output
form
FX3U-MT/S(-A) Transistor(Sink)
FX3U-MT/SS Transistor(Source)
External power supply 5 to 30V DC
Max. load
Resistance load
The total load current of
resistance loads per
common terminal should be
the following value or less.
- 1 output point/common
terminal: 0.5 A
- 4 output point/common
terminal: 0.8A
- 8 output point/common
terminal: 1.6A
Inductive load 12 W/24V DC
Min. load −
Open circuit leakage current 0.1 mA or less/30V DC
ON voltage 1.5 V or less
Interlock
PLC output
contact
Limit of
normal
rotation
Limit of
reverse
rotation
PLC output
contact
*
*
*
*
Bad
Good
Response
time
OFF→ON
Y000 to Y002
5 µs or less/10 mA or more
(5 to 24V DC)
Y003 or more
0.2 ms or less/200 mA or
more (at 24V DC)
ON→OFF
Y000 to Y002
5 µs or less/10 mA or more
(5 to 24V DC)
Y003 or more
0.2 ms or less/200 mA or
more (at 24V DC)
Circuit insulation Photocoupler insulation
Display of output operation
LED on panel lights when
photocoupler is driven.
Item Specification
PLC
Load
24V DC
Fuse
Y000
Y001
COM1
Load
24V DC
Fuse
Y004
Y005
COM2
PLC
Load
24V DC
Fuse
Y000
Y001
+V0
Load
24V DC
Fuse
Y004
Y005
+V1
 Loading...
Loading...