Page 6 of 24 FLOMAX 8 BZ AL (en)
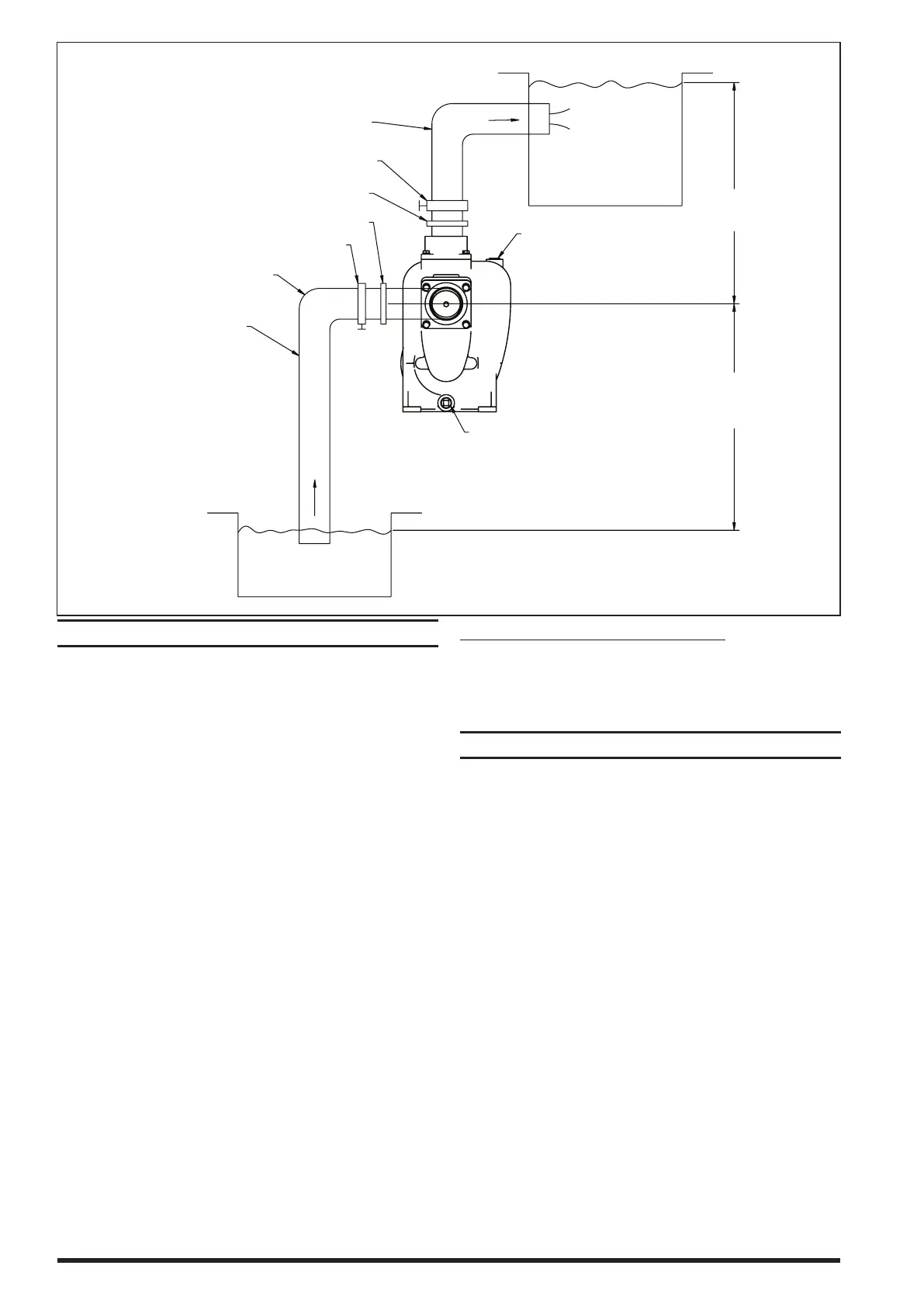
WORKING OF SELF PRIMING PUMP
Hd
DISCHARGE HEA
Hs
SUCTION HEAD
(NPSHr)
FILL PLUG
DRAIN PLUG
OVER HEAD
WATER TANK
SUCTION VALVE
UNION FLANGE
UNION FLANGE
DISCHARGE VALVE
DISCHARGE PIPE (2”)
SUCTION PIPE (2”)
SHARP BENDS NEAR INLET
Figure 3
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
The FLOMAX pump is a self-priming centrifugal pump and
only requires priming prior to its initial start. The pump will
retain sucient liquid for self priming thereafter.
Provision for a priming plug can be made by using a close
nipple and tee on the discharge opening.
A pipe plug installed in the top opening of the tee is easily
removed when necessary to prime pump. Prime pump by ll-
ing pump housing with liquid
If pump fails to prime or stops pumping, check for the follow-
ing possible causes:
1. No liquid in the pump housing.
2. Air leak in the suction line due to loose connections or
pin holes in the hose.
3. Collapsed suction line or clogged strainer.
4. Seal worn and leaking air.
5. Worn impeller - too much clearance between impeller
and wear plate.
6. Pump not running fast enough.
7. Suction lift is too high.
8. Trying to prime against too high a discharge head
Inspect the Pumpak as soon as it is received to make certain
that no parts are missing or have been broken in shipment.
Damage should be reported immediately to the shipping
company. CAUTION: Do not disturb the assembly shim in
the opening of the pump housing until after the Pumpak has
been completely assembled to the driver.
The Pumpak utilizes a single self-adjusting type mechanical
seal that is lubricated and cooled by the liquid in the pump.
NOTE: The Pump Must Never Be Operated Without Liquid
In The Housing.
WORKING OF SELF PRIMING PUMP:
A centrifugal pump operates through the transfer of rotation-
al energy from one or more driven rotors, called impellers.
The action of the impeller increases the fluid’s velocity and
pressure and directs it towards the pump outlet.
WEAR AND INSPECTION POINTS
Shaft: Inspect threads, keyways and shoulders. Replace if
damaged.
Ball bearings (Pedestal and hydraulic models): Replace if
worn, loose, or rough and noisy when rotated. If dirty, clean
with solvent, dry and coat with a good lubricant. New bear-
ings should not be unwrapped until ready for use.
Impellers: Replace if excessively worn or corroded. The im-
peller should have been statically and dynamically balanced
at the factory, and static and dynamic balance must be main-
tained for proper operation of your equipment.
Mechanical seals: Should be inspected for, lack of lubrica-
tion, misalignment, overheating, abrasive materials damage,
and corrosion.
Alignment: Proper alignment between pump shaft and
motor shaft is key to the performance of shaft seals and
bearings. Improper alignment can lead to premature pump
failure.
Pedestal Style: Inline shaft to shaft spacing is dependent
upon the coupling being used. Check the alignment carefully
between the pump and the drive.
 Loading...
Loading...