RF SIGNAL FROM
ANTENNA ON MAIN
BOARD
IF SIGNAL TO
MAIN BOARD
LOCAL
OSCILLATOR
TR102
MIXER
TR103
RF
AMPLIFIER
TR101
PSG/10439/1
RPR 550IS Series
Page 3 - 6 TM1188 Issue 1
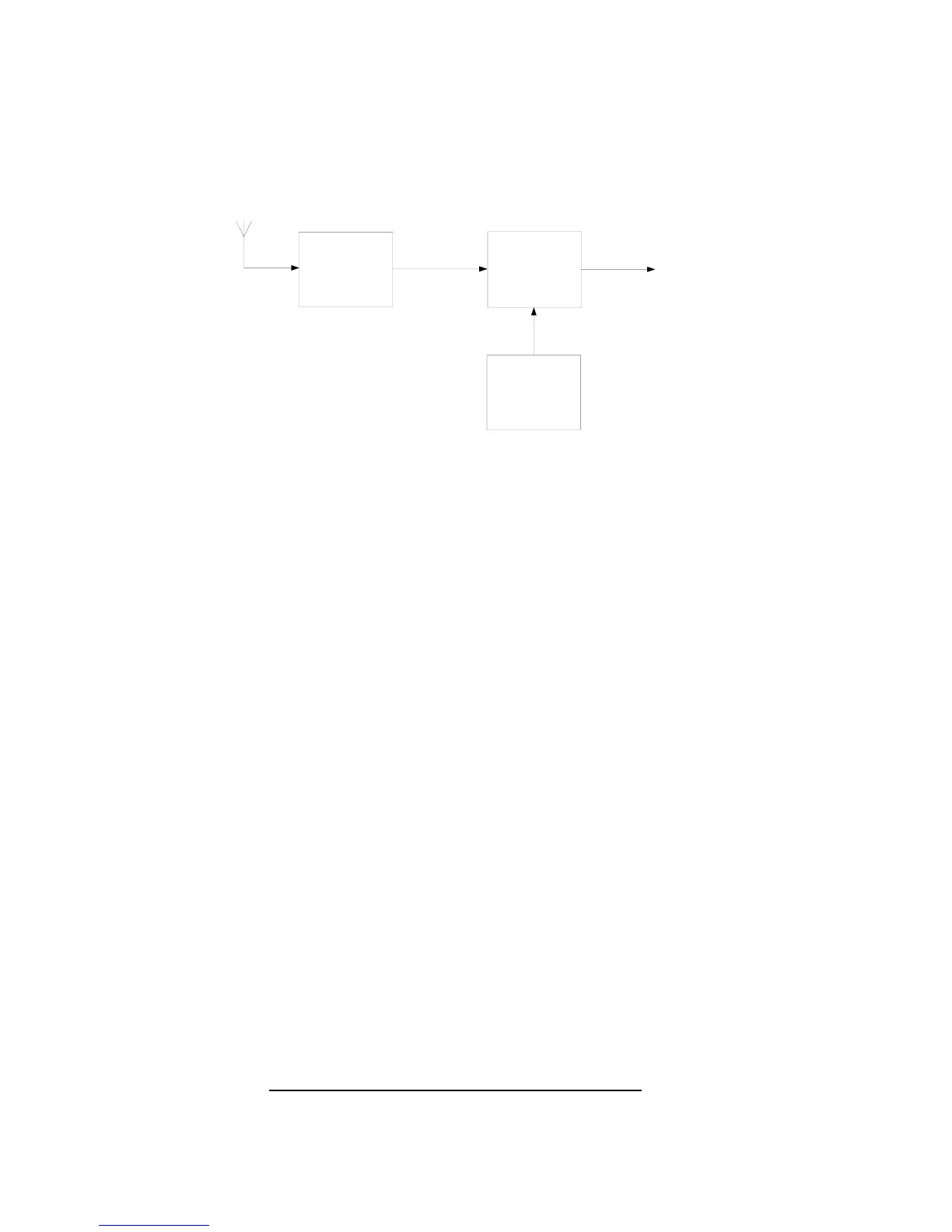
Figure 4: RPR 551IS Radio Board (Front End) Functional Block Diagram
RPR 551IS RADIO BOARD (FRONT END)
9. Figure 4 shows the functional block diagram of the RPR 551IS radio board (front end).
Antenna
10. The incoming RF signal is detected by AE1A, the ferrite rod antenna, which is located
on the main board. The antenna, tuned by C121, feeds the signal to the RF amplifier.
RF Amplifier
11. The signal passes to the emitter of amplifier TR101 via the matching network C101
and C102. TR101 is in the common base mode. Improved stability is given to the
amplifier by C108. The amplified output, from the collector of TR101, is tuned by the
resonant circuit formed by L101, C104 and C105 before passing into the mixer.
Local Oscillator
12. The self-doubling Colpitts crystal oscillator TR102 and associated components,
provides an injection frequency which is on the high side of the RF signal frequency.
The tuned circuit of L103 and C114 is resonant at the second harmonic of the
fundamental frequency of crystal XL101. Resistor R107 is the base bias resistor. The
signal passes via C117 to the mixer.
13. The frequency of the crystal is calculated by the following formula:
Crystal (XL101) frequency (MHz) =
Receiver channel frequency (MHz) + 0.455MHz
2
 Loading...
Loading...