© National Instruments | 9-1
9
Digital Routing and Clock
Generation
The digital routing circuitry has the following main functions:
• Manages the flow of data between the bus interface and the acquisition/generation
sub-systems (analog input, analog output, digital I/O, and the counters). The digital routing
circuitry uses FIFOs (if present) in each sub-system to ensure efficient data movement.
• Routes timing and control signals. The acquisition/generation sub-systems use these
signals to manage acquisitions and generations. These signals can come from the following
sources:
– Your M Series device
– Other devices in your system through RTSI
– User input through the PFI terminals
– User input through the PXI_STAR terminal
• Routes and generates the main clock signals for the M Series device.
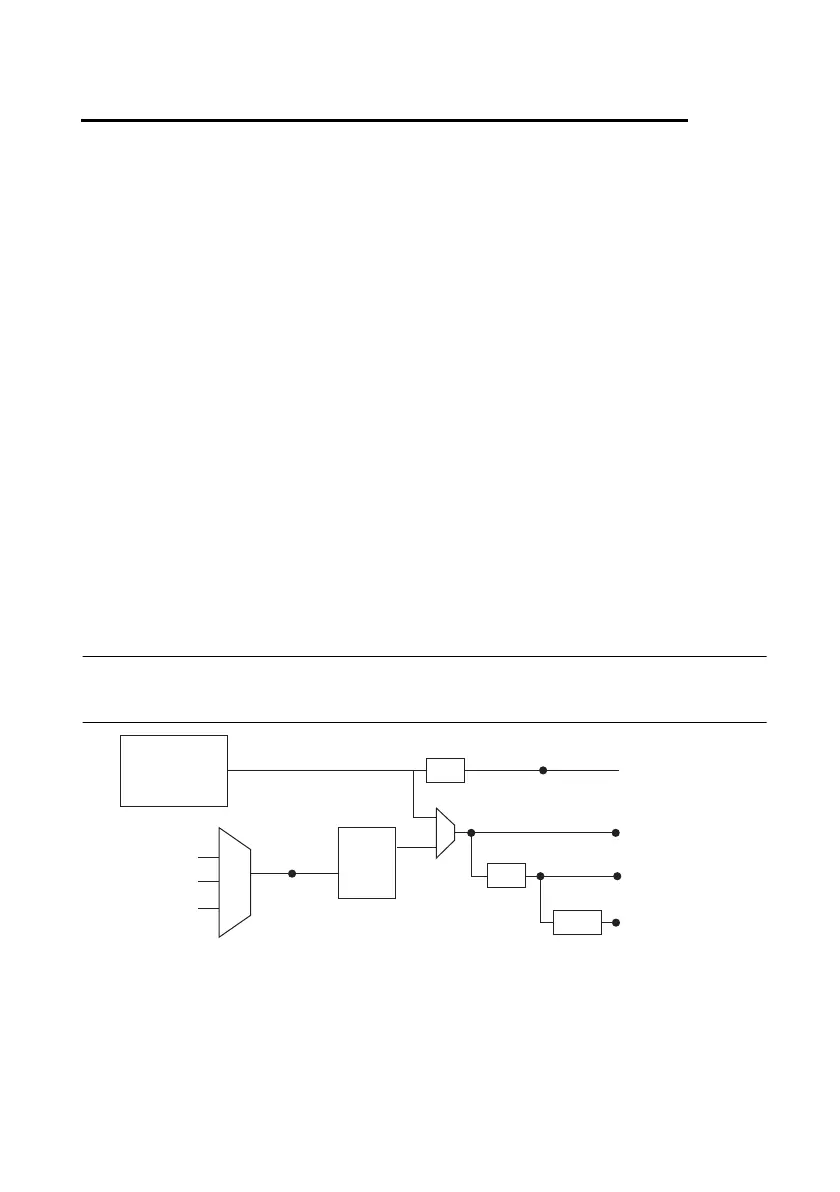
Clock Routing
Figure 9-1 shows the clock routing circuitry of an M Series device.
Figure 9-1. M Series Clock Routing Circuitry
RTSI <0..7>
Onboard
80 MHz
Oscillator
External
Reference
Clock
(To RTSI <0..7>
Output Selectors)
10 MHz RefClk
PLL
÷
4
÷
200
÷ 10
PXIe_CLK10
PXI_STA R
80 MHz
Timebase
100 kHz
Timebase
20 MHz
Timebase

 Loading...
Loading...