© National Instruments | 11-1
11
Triggering
A trigger is a signal that causes an action, such as starting or stopping the acquisition of data.
When you configure a trigger, you must decide how you want to produce the trigger and the
action you want the trigger to cause. All M Series devices support internal software triggering,
as well as external digital triggering. Some devices also support analog triggering. For
information about the different actions triggers can perform for each sub-system of the device,
refer to the following sections:
• The
Analog Input Triggering section of Chapter 4, Analog Input
• The Analog Output Triggering section of Chapter 5, Analog Output
• The Counter Triggering section of Chapter 7, Counters
Note Not all M Series devices support analog triggering. For more information
about triggering compatibility, refer to the specifications document for your device.
Triggering with a Digital Source
Your DAQ device can generate a trigger on a digital signal. You must specify a source and an
edge. The digital source can be any of the PFI, RTSI, or PXI_STAR signals.
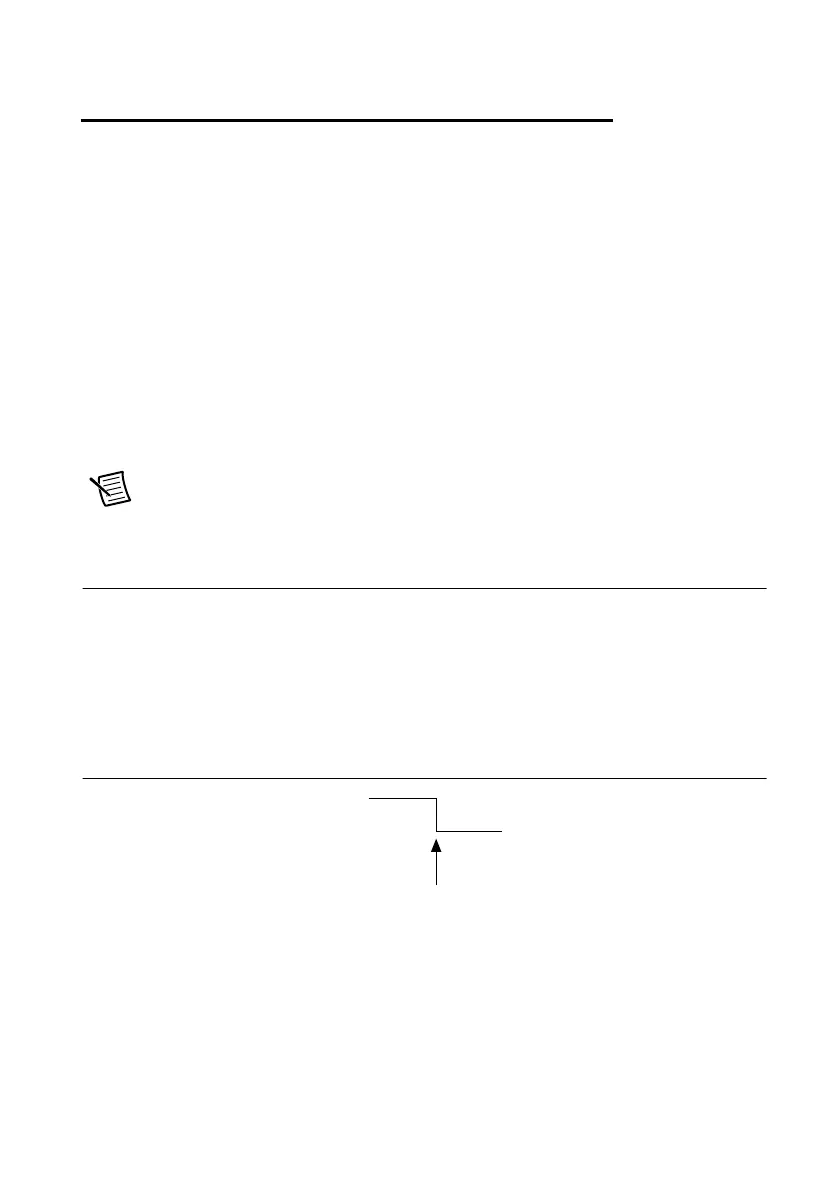
The edge can be either the rising edge or falling edge of the digital signal. A rising edge is a
transition from a low logic level to a high logic level. A falling edge is a high to low transition.
Figure 11-1 shows a falling-edge trigger.
Figure 11-1. Falling-Edge Trigger
You also can program your DAQ device to perform an action in response to a trigger from a
digital source. The action can affect the following:
• Analog input acquisition
• Analog output generation
• Counter behavior
• Digital waveform acquisition and generation
5 V
0 V
Falling Edge Initiates Acquisition
Digital Trigger

 Loading...
Loading...