If you do not connect the 0b port to the correct domain (cross-connect domains), you expose
your system to resiliency issues that prevent you from performing nondisruptive procedures
safely.
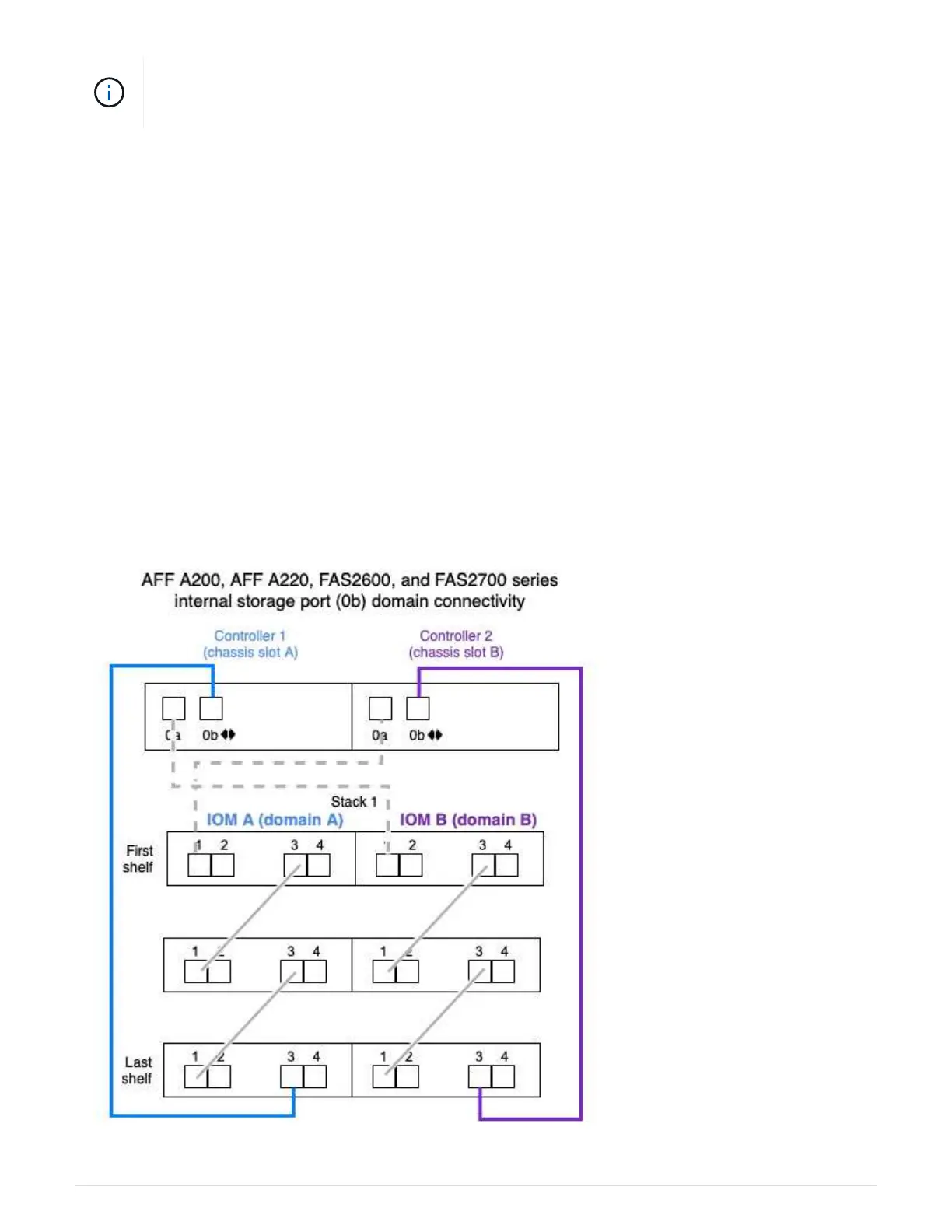
• Controller 0b port (internal storage port):
◦ Controller 1 0b port always connects to IOM A (domain A).
◦ Controller 2 0b port always connects to IOM B (domain B).
◦ Port 0b is always the primary path.
◦ Port 0b always connects to the logical last disk shelf in a stack.
◦ Port 0b always connect to disk shelf IOM port 3.
• Controller 0a port (internal HBA port):
◦ Controller 1 0a port always connects to IOM B (domain B).
◦ Controller 2 0a port always connects to IOM A (domain A).
◦ Port 0a is always the secondary path.
◦ Port 0a always connects to the logical first disk shelf in a stack.
◦ Port 0a always connect to disk shelf IOM port 1.
The following illustration highlights internal storage port (0b) domain connectivity for a AFF A200, AFF A220,
FAS2600 series and FAS2700 multipath HA configuration:
1585

 Loading...
Loading...