Protocol Unpack
Copyright © Nooploop LTd 2023. All Rights Reserved.
the method of left shift and then divide by 256. For example, for position data, we use int24 to
represent it, and the multiplier is 1000. The parsing code is as follows:
uint8_t byte[] = {0xe6,0x0e,0x00};//Decimal value: 3.814
//uint8_t byte[] = {0xec,0xfb,0xff};//Decimal value: -1.044
int32_t temp = (int32_t)(byte[0] << 8 | byte[1] << 16 | byte[2] << 24) / 256;
float result = temp/1000.0f;
Currently, the protocol verification is mainly based on the single-byte checksum at the end of the
protocol frame. Example code:
uint8_t verifyCheckSum(uint8_t *data, int32_t length){
uint8_t sum = 0;
for(int32_t i=0;i<length-1;++i){
sum += data[i];
}
return sum == data[length-1];
}
7.2 Example
The document assumes a single module continuous ranging scenario.
7.2.1 NLink_TOFSense_Frame0
Data source: Connect the module to the host computer, configure UART as active output mode,
using NLink_TOFSense_Frame0 protocol. For parsing distance data, please refer to the FAQ.
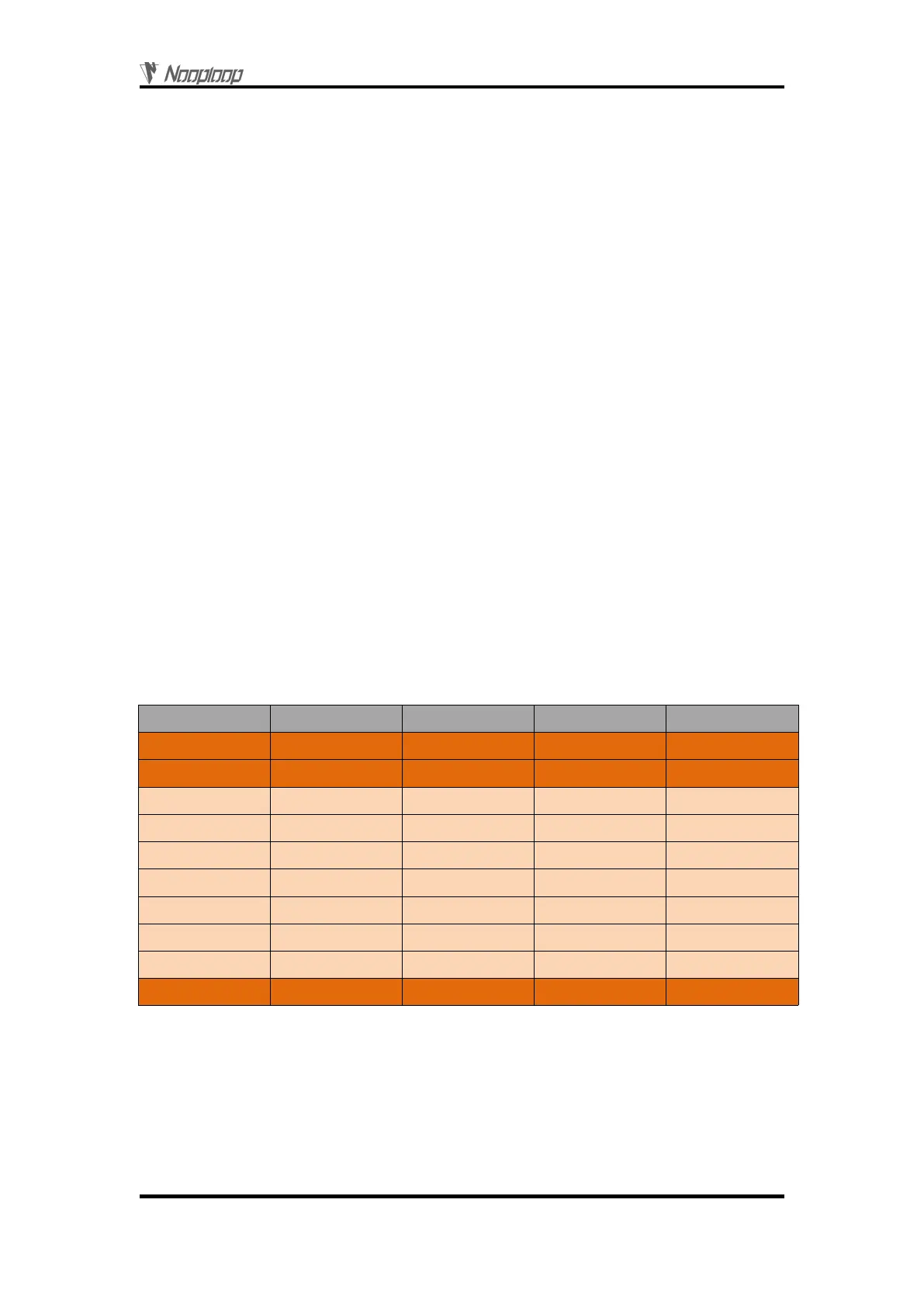
Raw data: 57 00 ff 00 9e 8f 00 00 ad 08 00 00 03 00 06 41
Table 1: NLink_TOFSense_Frame0 Parsing table
7.2.2 NLink_TOFSense_Read_Frame0
Data source: Connect the module to the host computer, configure it as UART query output mode
with ID set to 0. To query data, send the following bytes from the host computer. If you need to query
modules with different IDs, simply change the ID and checksum bytes accordingly.
Raw data: 57 10 FF FF 00 FF FF 63
 Loading...
Loading...